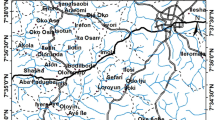
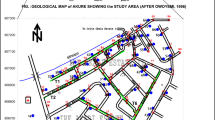
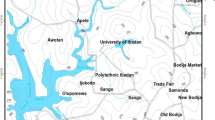
Abstract
A new approach of modeling very low frequency–electromagnetic (VLF–EM) and vertical electrical sounding (VES) data with a view of evaluating groundwater resources potential via application of GIS-based multi-criteria technique is investigated in this study. On eight VLF–EM traverses established in the site, 40 VES locations were combed. The acquired geophysical data (VLF–EM and VES) were processed applying Fraser/Karous–Hjelt filter and Win-Resist program geophysical software to determine the area subsurface geophysical parameters. Five hydrogeologic maps were produced based on the results of the interpreted geophysical parameters. The produced hydrogeologic maps were assigned suitable weights and different rankings to the individual classes boundary within the maps using the standard Saaty’s scale principle in the context of analytical hierarchy process (AHP) data mining technique. A raster-based empirical GIS model was developed for integrating the hydrogeologic maps to compute the groundwater potential index (GWPI) values in the range of 1.02–2.82 for the study area. Based on the estimated GWPI results, a final map zoning the area into low (0.0930–1.3922), medium (1.3922–1.9109) and high (1.9109–2.8173) groundwater potential classes was produced in GIS environment. The prediction accuracy of the produced potential map was established via cross-validation and in situ well correlation analysis. The results of the study established a new approach of modeling geophysical data for exploring groundwater productivity potential in the study area.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adabanija MA, Omidiora EO, Olayinka AI (2010) Fuzzy logic modeling of the resistivity parameter and topography features for aquifer assessment in hydrogeological investigation of a crystalline basement complex. Hydrogeol J 2008 16:461–481. doi:10.1007/s10040-007-0221-x
Adelusi AO, Ayuk MA, Kayode JS (2014) VLF–EM and VES: an application to groundwater exploration in a Precambrian basement terrain SW Nigeria. Ann Geophys 57(1):1–11. doi:10.4401/ag-6291
Adiat KAN, Nawawi MNM, Abdullah K (2012) Assessing the accuracy of GIS-based elementary multi criteria decision analysis as a spatial prediction tool—a case of predicting potential zones of sustainable groundwater resources. J Hydrol 440:75–89. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.03.028
Adiat KAN, Nawawi MN, Abdullah M (2013) Application of multi-criteria decision analysis to geoelectric and geologic parameters for spatial prediction of groundwater resources potential and aquifer evaluation. Pure Appl Geophys 170:453–471
Aizebeokhai PA, Oyeyemi KD (2014) Application of geoelectrical resistivity imaging and VLF–EM for subsurface characterization in a sedimentary terrain, Southwestern Nigeria. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-014-1482-z
Al Saud M (2010) Mapping potential areas for groundwater storage in Wadi Aurnah Basin, western Arabian Peninsula, using remote sensing and geographic information system techniques. Hydrogeol J 18:1481–1495. doi:10.1007/s10040-010-0598-9
Ariff H, Salit MS, Ismail N, Nukman Y (2008) Use of Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) for selecting the best design concept. J Teknol 49(A):1–18
Awasthi A, Chautan SS (2011) Using AHP and Dempste—Shafer theory for evaluating sustainable transport solution. Environ Model Softw 26:781–796
Bala AN, Ike EC (2001) The aquifer of the crystalline basement rocks in Gusau area, North-western Nigeria. J Min Geol 37(2):177–184
Benson AK, Payne KL, Stubben MA (1997) Mapping groundwater contamination using DC resistivity and VLF geophysical methods—a case study. Geophysics 62:80–86
Bernard J, Valla P (1991) Groundwater exploration in fissured media with electrical and VLF methods. Geoexploration 27:81–91
Chandra S, Ch R, Rao VA, Singh VS, Jain SC (2004) Estimation of natural recharge and its dependency on sub-surface geoelectric parameters. J Hydrol. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.04.001
Chowdhury A, Jha MK, Chowdary VM, Mal BC (2009) Integrated remote sensing and GIS-based approach for assessing ground-water potential in West Medinipur district, West Bengal, India. Int J Remote Sens 30(1):231–250
Chowdhury A, Jha MK, Chowdary VM (2010) Delineation of groundwater recharge zones and identification of artificial recharge sites in West Medinipur district, West Bengal, using RS, GIS and MCDM techniques. Environ Earth Sci 59:1209–1222
Dan-Hassan MA, Olorunfemi MO (1999) Hydro-geophysical investigation of a basement terrain in the north central part of Kaduna State Nigeria. J Min Geol 35(2):189–206
Dar IA, Sankar K, Dar MA (2011) Deciphering groundwater potential zones in hard rock terrain using geospatial technology. Environ Monit Assess 173(1–4):597–610
De Lima OAL, Niwas S (2000) Estimation of hydraulic parameters of shaly sandstone aquifers from geological measurements. J Hydrol 235:12–26
Dhakate R, Singh VS (2005) Estimation of hydraulic parameters from surface geophysical methods, Kaliapani Ultramafic Complex, Orissa, India. J Environ Hydrol 13(12):1–11
Edet AE, Okereke CS (1996) Assessment of hydrogeological conditions in basement aquifers of the Precambrian Oban Massif, Southwestern Nigeria. J Appl Geophys 36:195–204
Elewa HH, Fathy RG, Qaddah AA (2010) The contribution of geographic information systems and remote sensing in determining priority areas for hydrogeological development, Darb el-Arbain area, Western Desert, Egypt. Hydrogeol J 18:1157–1171. doi:10.1007/s10040-010-0590-4
Fraser DC (1969) Contouring of VLF–EM data. Geophysics 34:958–967
Jaiswal RK, Mukherjee S, Krishnamurthy J, Saxena R (2003) Role of remote sensing and GIS techniques for generation groundwater prospectzones towards rural development—an approach. Int J Remote Sens 24(5):993–1008
Janssen R (1992) Multiobjective decision support for environmental management. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Jayeoba A, Oladunjoye MA (2013) Hydro-geophysical evaluation of groundwater potential in hard rock terrain of southwestern Nigeria. RMZ M&G 60:271–285
Jha MK, Peiffer S (2006) Applications of remote sensing and GIS technologies in groundwater hydrology: past, present and future, vol 201. BayCEER, Bayreuth, pp 15–29
Jha MK, Chowdhury A, Chowdary VM, Peiffer S (2007) Groundwater management and development by integrated remote sensing and geographic information systems: prospects and constraints. Water Resour Manag 21(2):427–467
Jha MK, Chowdary VM, Al Chowdhury (2010) Groundwater assessment in Salboni Block, West Bengal (India) using remote sensing, geographical information system and multi-criteria decision analysis techniques. Hydrogeol J 18:1713–1728. doi:10.1007/s10040-010-0631-z
Johnston K, Hoef JMV, Krivoruchko K, Lucas N (2003) Using ArcGIS geostatistical analyst, environmental systems research institute, Redlands, USA, 2001, p 300
Karous M, Hjelt SE (1983) Linear filtering of VLF dip-angle measurements. Geophys Prospect 31:782–894
Katie S, Yohay C, Jean C, Chris W (2009) Uses and misuses of multicriteria decision analysis (MCDA) in environmental decision making. Risk Anal 29:1
Kelly W (1977) Geoelectric sounding for estimating aquifer hydraulic conductivity. Groundwater 15(6):420–425
Khalil MH (2006) Geoelectric resistivity sounding for delineating salt water intrusion in the Abu Zanima area, west Sinai, Egypt. J Geophys Eng 3:243–251
Kosinki WK, Kelly WE (1981) Geoelectric soundings for predicting aquifer properties. Groundwater 19:163–171
Kumar R, Yadav GS (2014) Geohydrological investigation using Schlumberger sounding in part of hard rock and alluvial area of Ahraura region, Mirzapur district, Uttar Pradesh, India. Arab J Geosci 8:3645–3654
Lahdelma R, Salminen P, Hokkanen J (2000) Using multicriteria methods in environmental planning and management. Environ Manag 26(6):595–605
Lee S, Kim YS, Oh HJ (2011) Application of a weights-of-evidence method and GIS to regional groundwater productivity potential mapping. J Environ Manag 96(1):91–105
Linkov I, Satterstrom K, Kiker G, Batchelor C, Bridges T (2006) From comparative risk assessment to multi-criteria decision analysis and adaptive management: recent developments and applications. Environ Int 32:1072–1093
Louis I, Karantonis G, Voulgaris N, Louis F (2004) Geophysical methods in the determination of aquifer parameters: the case of Mornos river delta, Greece. Res J Chem Environ 18(4):41–49
Machiwal D, Rangi N, Sharma A (2014) Integrated knowledge- and data-driven approaches for groundwater potential zoning using GIS and multi-criteria decision making techniques on hard-rock terrain of Ahar catchment, Rajasthan, India. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3544-7
Madrucci V, Taioli F, Araujo CC (2008) Groundwater favorability map using GIS multicriteria data analysis on crystalline terrain, Sao Paulo State, Brazil. J Hydrol 357:153–173
Maillet R (1974) The fundamental equations of electrical prospecting. Geophysics 12:529–556
Manap MA, Sulaiman WNA, Ramli MF, Pradhan B, Surip N (2011) A knowledge-driven GIS modelling technique for groundwater potential mapping at the Upper Langat Basin, Malaysia. Arab J Geosci 6(5):1621–1637. doi:10.1007/s12517-011-0469-2
Manap MA, Nampak H, Pradhan B, Lee S, Sulaiman WNA, Ramli MF (2014) Application of probabilistic-based frequency ratio model in groundwater potential mapping using remote sensing data and GIS. Arab J Geosci 7:711–724. doi:10.1007/s12517-012-0795-z
McNeill JD (1988) Electromagnetics. In: Proceedings on the application of geophysics to engineering and environmental problems, pp 251–348
Mogaji KA, Olayanju GM, Oladapo MI (2011a) Geophysical evaluation of rock type impact on aquifer characterization in the basement complex areas of Ondo State, Southwestern Nigeria: geo-electric assessment and geographic information systems (GIS) approach. Int J Water Resour Environ Eng 3(4):77–86
Mogaji KA, Omosuyi GO, Olayanju GM (2011b) Groundwater system evaluation and protective capacity of overburden material at Ileoluji Southwestern Nigeria. J Geol Min Res 3(11):294–304
Mogaji KA, Lim HS, Abdullah K (2013) Modeling groundwater vulnerability prediction using geographic information system (GIS)-based ordered weighted average (OWA) method and DRASTIC model theory hybrid approach. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-013-1391-1
Mogaji KA, Lim HS, Abdullah K (2014) Regional prediction of groundwater potential mapping in a multifaceted geology terrain using GIS-based Dempster-Shafer model. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-014-1391-1
Mogaji KA, Lim HS, Abdullah K (2015) Modeling of groundwater recharge using a multiple linear regression (MLR) recharge model developed from geophysical parameters: a case of groundwater resources management. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3476-2
Mohamed SEJ, Shaharin I, Wan NA, Puziah AL (2013) Groundwater resources assessment using integrated geophysical techniques in the southwestern region of Peninsular Malaysia. Arab J Geosci 6(11):4129–4144
Mufid Al-Hadithi DC, Israil M, Kumar B (2006) Groundwater-recharge estimation using a surface electrical resistivity method in the Himalayan foothill region, India. Hydrogeol J 14:44–50
Muthukrishnan A, Manjunatha V (2008) Role of remote sensing and GIS in artificial recharge of the groundwater aquifer in the Shanmuganadi sub water shed in the Cauvery River Basin, Tiruchirappalli District, Tamil Nadu. GIS Ideas, 4–6 December 2008
Nabighian MN, Macae JC (1991) Time domain electromagnetic prospecting methods. In: Nabighian MN (ed) Electromagnetic methods in applied geophysics, 2: applications, Part B. Society of Exploration Geophysicists, Tulsa, pp 427–520
Ndatuwong LG, Yadav GS (2014) Application of geo-electrical data to evaluate groundwater potential zone and assessment of overburden protective capacity in part of Sonebhadra district, Uttar Pradesh. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3649-z
Nigeria Geological Survey Agency (2006) Published by the Authority of the Federal Republic of Nigeria
Niwas S, de Lima OAL (2003) Aquifer parameter estimation from surface resistivity data. Groundwater 41(1):94–99
Niwas S, Singhal DC (1985) Aquifer transmissivity of porous media from resistivity data. J Hydrol 82:143–153
Obi-Reddy GP, Chandra-Mouli K, Srivastava SK, Mali AK (2000) Evaluation of groundwater potential zones using remote sensing data—a case study of Gaimukh watershed, Bhandara district Maharastra. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 28(1):19–32
Ofomola MO, Adiat KAN, Olayanju GM, Ako BD (2009) Integrated geophysical methods for post foundation studies, Obanla Staff Quarters of the University of Technology, Akure, Nigeria. Pac J Sci Technol 10(2):93–111
Ogilvy RD, Lee AC (1991) Interpretation of VLF–EM inphase data using current density pseudosections. Geophys Prospect 39:567–580
Park I, Kim Y, Lee S (2014) Groundwater productivity potential mapping using evidential belief function. Groundwater 52:201–207. doi:10.1111/gwat.12197
Pirttijarvi M (2004) KHF filtering program: a geophysical software for Karous–Hjelt and Fraser filtering on geophysical VLF data. Geophysical Division, Department of Geosciences, University of Oulu, Finland
Pradhan B (2009) Ground water potential zonation for basaltic watersheds using satellite remote sensing data and GIS techniques. Cent Eur J Geosci 1(1):120–129. doi:10.2478/v10085-009-0008-5
Pradhan B, Youssef AM (2010) Manifestation of remote sensing data and GIS for landslide hazard analysis using spatial—based statistical models. Arab J Geosci 3(3):319–326
Pradhan B, Singh RP, Buchroithner MF (2006) Estimation and stress and its use in evaluation of landslide prone regions using remote sensing data. Adv Space Res 37:698–709
Prasad RK, Mondal NC, Banerjec P, Nandakumar MV, Singh VS (2008) Deciphering potential of groundwater zones in hardrock through application of GIS. Environ Geol 55:467–475
Pratap K, Ravindran KV, Prabakaran B (2000) Groundwater prospect zoning using remote sensing and geographical information system: a case study in Dala–Renukoot area, Sonbhadra district, Uttar Pradesh. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 28:249–263
Rahaman MA (1988) Recent advances in the study of the Basement complex of Nigeria. In: Oluyide PO et al (eds) Precambrian Geology of Nigeria. Geological survey of Nigeria, pp 11–43
Regan HM, Davis FW, Andelman SJ, Widyanata A, Freese M (2007) Comprehensive criteria for biodiversity evaluation in conservation planning. Biodivers Conserv 16:2715–2728
Reynolds JM (1987) An introduction to applied and environmental geophysics. Wiley, England, p 796
Saaty TL (1980) The analytic hierarchy process: planning, priority setting, resource allocation. McGraw-Hill, New York
Saaty TL, Vargas GL (1991) Prediction, projection and forecasting. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Satpathy BN, Kanungo BN (1976) Groundwater exploration in hard rock, a case study. Geophys Prospect 24(4):725–736
Sener E, Davra A, Ozcelik M (2005) An integration of GIS and remote sensing in groundwater investigation: a case study in Bunduc, Turkey. Hydrogeol J 13(5):826–839
Sharma SP, Baranwal VC (2005) Delineation of groundwater bearing fracture zones in a hardrock area integrating very low frequency electromagnetic and resistivity data. J Appl Geophys 57:155–166
Sinha AK (1990) Interpretation of ground VLF–EM data in terms of vertical conductor models. Geoexploration 26:213–231
Solomon S, Quiel F (2006) Groundwater study using remote sensing and geographic information system (GIS) in the central highlands of Eritrea. Hydrogeol J 14(5):729–741
Soupios PM, Kouli M, Vallianatos F, Vafidis A, Stavroulakis G (2007) Estimation of aquifer hydraulic parameters from surficial geophysical methods: a case study of Keritis Basin in Chania (Crete–Greece). J Hydrol 338:122–131. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.02.02
Srinivasa RY, Jugran DK (2003) Delineation of groundwater potential zones and zones of groundwater quality for domestic purposes using remote sensing and GIS. Hydrol Sci 48(5):821–833
Sundararajan NG, Nandakumar MN, Srinivas Y (2007) VES and VLF—an application to groundwater exploration, Khammam, India. Lead Edge 26(6):708–716
Thirumalaivasan D, Karmegam M, Venugopal K (2003) AHP-DRASTIC: software for specific aquifer vulnerability assessment using DRASTIC model and GIS. Environ Model Softw 18:645–656
Tijani MN, Osinowo OO, Ogedengbe O (2009) Mapping subsurface fracture systems using integrated electrical resistivity profiling and VLF–EM methods: a case study of suspected gold mineralization. RMZ Mater Geoenviron 56(4):415–436
Ungemach P, Moslaghini F, Duprat A (1969) Emphasis in determination of transmissivity coefficient and application in nappe alluvial aquifer Rhine. Bult Instt Assoc Sci Hydrol 14(3):169–190
Vijith HM (2007) Application of GIS and frequency ratio model in mapping the potential surface failure sites in the Poonjar subwatershed of Meenachil river in Western Ghats of Kerala. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 35(3):261–271
Worthington PR (1977) Geophysical investigations of groundwater resources in the Kalahari Basin. Geophysics 42(4):838–849
Yatsalo B, Kiker GA, Kim J, Bridges TS, Seager TP, Gardner K (2007) Application of multicriteria decision analysis tools to two contaminated sediment case studies. Integr Environ Assess Manag 3(2):223–233
Zekster IS, Everett LG (eds) (2004) Groundwater resources of the world and their use, IHP-VI, Series on Groundwater. UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation), Paris
Zhou L, Chen Y (2014) Exploring the potential of community-based grassland management in Yanchi County of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China: an application of the SWOT-AHP method. Environ Earth Sci 72:1811–1820. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3090-3
Zohdy AAR, Eaton GP, Mabey DR (1974) Application of surface geophysics to groundwater investigations, techniques water resources investigations of the US Geological Survey. Washington, pp 195–205
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank Olajuyigbe, Ahmed and the Technical staff of Applied Geophysics Department, FUTA, Nigeria for assisting in Data acquisition for this research work. The author also expressed his profound appreciation to the editor and reviewers for their valuable suggestions to improve the paper to its best.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mogaji, K.A. Combining geophysical techniques and multi-criteria GIS-based application modeling approach for groundwater potential assessment in southwestern Nigeria. Environ Earth Sci 75, 1181 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5897-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5897-6