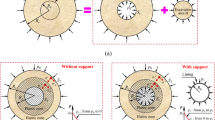
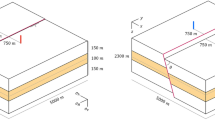
Abstract
The fluctuating nature of renewable energy sources can be managed by storing the surplus of electrical energy in an appropriate reservoir. The excess electricity available during off-peak periods of consumption may be used to compress air or electrolyze hydrogen. Afterward, the pressurized gas is stored in the rock salt cavities and discharged to compensate the shortage of energy when required. During this process, the rock salt surrounding the cavern undergoes thermo-mechanical cyclic loading. In order to achieve a reliable geotechnical design, the stress–strain response of rock salt under such loading condition has to be identified and predicted. In order to investigate the rock salt behavior under such loading, a comprehensive study using three concepts of geotechnical engineering, i.e., experimental investigation, constitutive modeling and numerical analysis, is conducted. A triaxial experimental setup is developed to supplement the knowledge of the cyclic thermo-mechanical behavior of rock salt. The imposed boundary conditions in the experimental setup are assumed to be similar to the stress state obtained from a full-scale numerical simulation. The computational model relies primarily on the governing constitutive model for predicting the behavior of rock salt cavity. Hence, a sophisticated elasto-viscoplastic creep constitutive model is developed to take into account the dilatancy and damage progress, as well as the temperature effects. The contributed input parameters in the constitutive model can be calibrated using the experimental measurements. In the following, the initial numerical simulation is modified based on the calibrated constitutive model. However, because of the significant levels of uncertainties involved in the design procedure of such structures, a reliable design can be achieved by employing probabilistic approaches. Therefore, the numerical calculation is extended by statistical tools such as sensitivity analysis, optimum experimental design, back analysis, probabilistic analysis and robust reliability-based design to get final design parameters of paramount need for practice.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkan H, Cin Y, Pusch G (2007) Rock salt dilatancy boundary from combined acoustic emission and triaxial compression tests. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 44:108–119
Allen RD, Doherty TJ, Thorns R (1982) Geotechnical factors and guidelines for storage of compressed air in solution mined salt cavities. Tech. Rep. PNL-4242, UC-94e, Pacific Northwest Laboratory, prepared for the U.S. Department of Energy under Contract DE-AC06-76RLO 1830
Au SK, Beck JL (2001) Estimation of small failure probabilities in high dimensions by subset simulation. Probab Eng Mech 16:263–277
Ayling MR, Meredith PG, Murrell SA (1995) Microcracking during triaxial deformation of porous rocks monitored by changes in rock physical properties, i. elastic-wave propagation measurements on dry rocks. Tectonophysics 245(3):205–221
Bardow A (2008) Optimal experimental design of ill-posed problems: the meter approach. Comput Chem Eng 32:115–124
Bauer SJ, Broome ST, Bronowski DR, Rinehart A, Ingraham M (2011) Experimental deformation of salt in cyclic loading insights from acoustic emission measurements. Tech. rep, Sandia National Laboratories (SNL-NM), Albuquerque, NM, USA
Bay CA (1963) Use of salt solution cavities for underground storage. In: Symp. On Salt, Northern Ohio Geol Soc., pp 564–578
Bérest P (2011) Thermomechanical aspects of high frequency cycling in salt storage caverns. In: International Gas Union Research Conference, Oct 2011, Seoul, South Korea
Bérest P, Brouard B (2003) Safety of salt caverns used for underground storage. Oil Gas Sci Technol 58:361–384
Bérest P, Brouard B, Feuga B, Karimi-Jafari M (2008) The 1873 collapse of the saint-maximilien panel at the varangeville salt mine. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 45(7):1025–1043
Berést P, Djizanne H, Brouard B, Hvin G (2013) Effects of a rapid depressurization in a salt cavern. In: Feng XT, Hudson JA, Tan F (eds) Rock characterisation, modelling and engineering design methods. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 653–658
Bolzon G, Buljak V (2011) An effective computational tool for parametric studies and identification problems in materials mechanics. Comput Mech 48:657–687
Bräuer V, Eickemier R, Eisenburger D, Grissemann C (2011) Description of the gorleben site part 4: geotechnical exploration of the gorleben salt dome. Die Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe
Brouard B, Berést P, Karimi-Jafari M (2007) Onset of tensile effective stresses in gas storage caverns. In: SMRI conference. Halifax, Canada, pp 1–16
Buljak V (2010) Proper orthogonal decomposition and radial basis functions algorithm for diagnostic procedure based on inverse analysis. FME Trans 38:129–136
Buljak V (2012) Inverse analysis with model reduction: proper orthogonal decomposition in structural mechanics. Springer, Berlin
Cacuci DG (2003) Sensitivity and uncertainty analysis, volume 1: theory. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Cekerevac C, Laloui L, Vulliet L (2005) A novel triaxial apparatus for thermo-mechanical testing of soils. Geotech Test J 28(2):161–170
Code-Bright user’s guide (2010) Code-Bright user’s guide. Department of the Geotechnical Engineering and Geosciences of the Technical University of Catalonia
Cristescu N (1987) Elastic viscoplastic constitutive equations for rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech 24(5):271–281
Cristescu N (1993) A general constitutive equation for transient and stationary creep of rock salt. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech 30(2):125–139
Cristescu N, Gioda G (1994) Visco-plastic behaviour of geomaterials. CISM International Centre for Mechanical Sciences. Springer, Vienna
Cristescu N, Hunsche U (1998) Time effects in rock mechanics. Wiley, New York
Crotogino F, Mohmeyer C, Scharf R (2001) More than 20 years of successful operation. In: SMRI conference. Orlando, USA, pp 1–7
Cukier RI, Fortuin CM, Schuler KE, Petschek AG, Schaibly JH (1973) Study of the sensitivity of coupled reaction systems to uncertainties in rate coefficients, i theory. J Chem Phys 59(8):3873–3878
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T (2002) A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. Trans Evol Comput 6(2):182–197
Desai C, Varadarajan A (1987) A constitutive model for quasi-static behavior of rock salt. J Geophys Res 92:445–456
Desai C, Zhang D (1987) Viscoplastic model for geologic material with generalized flow rule. Int J Numer Anal Methods 11:603–627
Djizanne H, Berést P, Brouard B (2012) Tensile effective stresses in hydrocarbon storage caverns. In: SMRI conference. Bremen, Germany, pp 1–18
Dusan K (ed) (1996) Damage mechanics, North-Holland series in applied mathematics and mechanics, vol 41. North-Holland, Amsterdam
Düsterloh U (2010) Geotechnische Sicherheitsnachweise für Hohlraumbauten im Salinargebirge unter besonderer Berücksichtigung laborativer Untersuchungen. Technische Universität Clausthal. Papierflieger
Düsterloh U, Lerche S, Lux KH (2013) Damage and healing properties of rock salt: long-term cyclic loading tests and numerical back analysis. In: Clean energy systems in the subsurface: production, storage and conversion. Springer, Berlin, pp 341–362
Efron B, Tibshirani R (1993) An Introduction to the bootstrap. Chapman & Hall, London
Forrester AIJ, Sobester A, Keane A (2008) Engineering design via surrogate modelling: a practical guide. Wiley, New York
Fuenkajorn K, Phueakphum D (2010) Effects of cyclic loading on mechanical properties of Maha Sarakham salt. Eng Geol 112(1):43–52
Gillhaus A (2007) Natural gas storage in salt caverns—present status, developments and future trends in Europe. In: SMRI conference. Basel, Switzerland, pp 1–18
Gray CT (1988) Introduction to quality engineering: designing quality into products and processes. Wiley, New York
Günther R, Salzer K (2007) A model for rock salt, describing transient, stationary, and accelerated creep and dilatancy. In: In 6th conference on the mechanical behavior of salt-SALTMECH6, Hannover, Germany, 22–25 May 2007
Guo Y, Yang C, Mao H (2012) Mechanical properties of Jintan rock salt undercomplex stress paths. Int J Rock Mech Min 56:54–61
Haldar A, Mahadevan S (2000) Probability, reliability, and statistical methods in engineering design. Wiley, New York
Hamm N, Hall J, Anderson M (2006) Variance-based sensitivity analysis of the probability of hydrologically induced slope instability. Comput Geosci 32(6):803–817
Hampel A, Schulze O (2007) The composite dilatancy model: a constitutive model for the mechanical behavior of rock salt. In: 6th conference on the mechanical behavior of salt-SALTMECH6, Hannover, Germany, 22–25 May 2007
Hansen F, Carter N (1983) Review creep of rock salt. Tectonophys J 92:275–333
Heusermann S, Rolfs O, Schmidt U (2003) Nonlinear finite element analysis of solution mined storage caverns in rock salt using the lubby2 constitutive model. Comput Struct J 81:629–638
Hölter R, Mahmoudi E, Schanz T (2015) Optimal sensor location for parameter identification in soft clay. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, vol 1684, p 030005
Homma T, Saltelli A (1996) Importance measure in global sensitivity analysis of nonlinear models. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 52:1–17
Hou Z, Gou Y, Xie L, Zhang R (2010) Natural gas storage cavern design under special consideration of the thin bedded salt layer in Jintan and the intermediate layers of mudstone. In: Hou M, Xie H, Yoon J (eds) Underground storage of CO2 and energy. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 211–216
Hunsche U, Hampel A (1999) Rock salt, the mechanical properties of the host rock material for radio active waste repository. Eng Geol 52:271–291
Jafari M, Berést P, Brouard B (2008) Subsidence, sinkholes and craters above salt caverns. In: SMRI conference. Porto, Portugal, pp 1–10
Jafari M, Gatelier N, Brouard B, Berést P (2011) Multi cycle gas storage in salt caverns. In: SMRI conference. York, UK, pp 1–18
Joshi M, Seidel-Morgenstern A, Kremling A (2006) Exploiting the bootstrap method for quantifying parameter confidence intervals in dynamical systems. Metab Eng 8:447–455
Juang CH, Wang L (2013) Reliability-based robust geotechnical design of spread foundations using multi-objective genetic algorithm. J Comput Geotech 48:96–106
Kennedy MC, O’Hagan A (2001) Bayesian calibration of computer models. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Stat Methodol) 63(3):425–464
Khaledi K, Miro S, König M, Schanz T (2014) Robust and reliable metamodels for mechanized tunnel simulations. Comput Geotech 61:1–12
Khaledi K, Mahmoudi E, König D, Schanz T (2015) Sensitivity analyses on the influence of constitutive parameters on the numerical simulation of the behavior of a cavern in rock salt. In: Geomechanics from micro to macro, pp 933–938
Khaledi K, Mahmoudi E, Datcheva M, König D, Schanz T (2016a) Sensitivity analysis and parameter identification of a time dependent constitutive model for rock salt. J Comput Appl Math 293:128–138
Khaledi K, Mahmoudi E, Datcheva M, Schanz T (2016b) Stability and serviceability of underground energy storage caverns in rock salt subjected to mechanical cyclic loading. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 86:115–131
Knabe T, Schweiger HF, Schanz T (2012) Calibration of constitutive parameters by inverse analysis for a geotechnical boundary problem. Can Geotech J 49(2):170–183
Lahmer T (2011) Optimal experimental design for nonlinear ill-posed problems applied to gravity dams. Inverse Probl 27(12):125005
Lancaster P, Salkauskas K (1981) Surfaces generated by moving least squares methods. Math Comput 37(155):141–158
Liang W, Zhang C, Gao H, Yang X, Xu S, Zhao Y (2012) Experiments on mechanical properties of salt rocks under cyclic loading. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 4(1):54–61
Liu J, Xie H, Hou Z, Yang C, Chen L (2014) Damage evolution of rock salt under cyclic loading in uniaxial tests. Acta Geotech 9(1):153–160
Lux KH (2013) Recent developments in geotechnical design of natural gas storage cavities regarding physical modelling as well as numerical simulation. In: Hou MZ, Xie H, Were P (eds) Clean energy systems in the subsurface: production, storage and conversion. Springer, Berlin, pp 451–485
Lux KH, Duesterloh U, Hou Z (2002) Erhoehung der wirtschaftlichkeit von speicherkavernen durch anwendung eines neuen entwurfsund nachweiskonzeptes. Erdoel Erdgas Kohle 118(6):294–300
Lj M, Xy L, Wang My X, Hf HR, Px F, Sr J, Ga W, Qk Y (2013) Experimental investigation of the mechanical properties of rock salt under triaxial cyclic loading. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 62:34–41
Minkley M, Muehlbauer J (2007) Constitutive models to describe the mechanical behavior of salt rocks and the imbedded weakness planes. In: 6th conference on the mechanical behavior of salt-SALTMECH6, Hannover, Germany, pp 119–127
Miro S, Hartmann D, Schanz T (2014) Global sensitivity analysis for subsoil parameter estimation in mechanized tunneling. Comput Geotech 56:80–88
Miro S, König M, Hartmann D, Schanz T (2015) A probabilistic analysis of subsoil parameters uncertainty impacts on tunnel-induced ground movements with a back-analysis study. Comput Geotech 68:38–53
Mollon G, Dias D, Soubra AH (2013) Probabilistic analyses of tunneling-induced ground movements. Acta Geotech 8(2):181–199
Morris MD (1991) Technometrics, factorial sampling plans for preliminary computational experiments. Taylor & Francis, Ltd, Oxfordshire
Nazary S, Mirzabozorg H, Noorzad H (2013) Modeling time-dependent behavior of gas caverns in rock salt considering creep, dilatancy and failure. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 33:171–185
Nguyen MD, Braham S, Durup JG (1993) Surface subsidence over deep solution mined storage cavern field. In: International conference on case histories in geotechnical engineering
Nieland J, Ratingen J (2006) Geomechanical evaluation of two gulf coast natural gas storage caverns. In: Solution Mining Research Institute, SMRI
Nova R, Castellanza R, Tamagnini C (2003) A constitutive model for bonded geomaterials subject to mechanical and/or chemical degradation. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 27:705–732
Phoon KK, Ching J (2014) Risk and reliability in geotechnical engineering. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Phoon KK, Kulhawy FH (1999) Characterization of geotechnical variability. Can Geotech J 36(4):612–624
Pollak R (1994) History of first U.S. compressed-air energy storage (caes) plant (110mw, 26h), volume 2: construction. Final report, Electric Power Research institute
Popp T, Kern H (1998) Ultrasonic wave velocities, gas permeability and porosity in natural and granular rock salt. Phys Chem Earth 23(3):373–378
Popp T, Kern H, Schulze O (2001) Evolution of dilatancy and permeability in rock salt during hydrostatic compaction and triaxial deformation. J Geophys Res Sol Earth (1978–2012) 106(B3):4061–4078
Powell MJD (1987) Radial basis functions for multivariable interpolation: a review, in algorithms for approximation. In: Mason JC, Cox MG (eds) Algorithms for approximation, vol 3. Clarendon Press, New York, pp 143–167
Pudewills A (2007) Modeling of hydro-mechanical behavior of rock salt in the near field of repository excavation. In: 6th conference on the mechanical behavior of salt-SALTMECH6, Hannover, Germany, 22–25 May 2007
Ratigan J, Yogt T (1993) Lpg storage at Mont Belvieu, Texas: a case history. SPE Adv Technol Ser 1:204–211
Ratigan WR, Hannum WD (1980) Mechanical behavior of new mexico rock salt in triaxial compression up to 200 °C. J Geophys Res 85:891–900
Roberts LA, Buchholz SA, Mellegard KD, Düsterloh U (2015) Cyclic loading effects on the creep and dilation of salt rock. Rock Mech Rock Eng 48(6):2581–2590
Saltelli A, Tarantola S, Campolongo F, Ratto M (2004) Sensitivity analysis in practice: a guide to assessing scientific models. Wiley, New York
Saltelli A, Andres T, Ratto M (2008) Global sensitivity analysis. The primer. Wiley, New York
Sane S, Desai C, Jenson J, Contractor D, Carlson A, Clark P (2008) Disturbed state constitutive modeling of two pleistocene tills. Quat Sci Rev 27:267–283
Schanz T, Zimmerer MM, Datcheva M, Meier J (2006) Identification of constitutive parameters for numerical models via inverse approach. Felsbau 24(2):11–21
Schenkendorf R, Kremling A, Mangold M (2009) Optimal experimental design and model selection by a sigma point approach. IET Syst Biol 3:10–23
Schulze O, Popp T, Kern H (2001) Development of damage and permeability in deforming rock salt. Eng Geol 61:163–180
Sobol’ IM (1990) On sensitivity estimation for nonlinear mathematical models. Mat Modelirovanie 2(1):112–118
Thomas R, Gehle R (2000) A brief history of salt cavern use. In: Proceedings of 8th world salt symposium, pp 207–2014
Ucinski D (2005) Optimal measurement methods for distributed parameter system identification. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Urai J, Spiers C (2007) The effects of grain boundary water on deformation mechanisms and rheology of rock salt during long-term deformation. In: 6th conference on the mechanical behavior of salt-SALTMECH6, Hannover, Germany, 22–25 May 2007
VanSambeek LL, Ratigan JL, Hansen FD (1993) Dilatancy of rock salt in laboratory tests. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 30(7):735–738
Voyiadjis GZ, Ju JWW, Chaboche JL (1998) Damage mechanics in engineering materials. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Wang L, Hwang JH, Juang CH, Atamturktur S (2013a) Reliability-based design of rock slopes a new perspective on design robustness. Eng Geol 154:56–63
Wang T, Yan X, Yang H, Yang X, Jiang T, Zhao S (2013b) A new shape design method of salt cavern used as underground gas storage. Appl Energy J 104:50–61
Wang T, Yang C, Ma H, Li Y, Shi X, Li J, Daemen J (2016) Safety evaluation of salt cavern gas storage close to an old cavern. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 83:95–106
Xing W, Zhao J, Hou Z, Were P, Li M, Wang G (2015) Horizontal natural gas caverns in thin-bedded rock salt formations. Env Earth Sci 73(11):6973–6985
Zhang G, Wu Y, Wang L, Zhang K, Daemen JJ, Liu W (2015) Time-dependent subsidence prediction model and influence factor analysis for underground gas storages in bedded salt formations. Eng Geol 187:156–189
Acknowledgments
This work was performed in the frame of the project ANGUS+ funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) under Grant No. 03EK3022C. The authors are grateful for this support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of a Topical Collection in Environmental Earth Sciences on “Subsurface Energy Storage”, guest-edited by Sebastian Bauer, Andreas Dahmke, and Olaf Kolditz.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoudi, E., Khaledi, K., von Blumenthal, A. et al. Concept for an integral approach to explore the behavior of rock salt caverns under thermo-mechanical cyclic loading in energy storage systems. Environ Earth Sci 75, 1069 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5850-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5850-8