Abstract
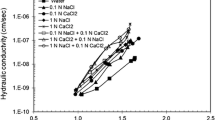
Due to its high swelling capacity, contaminant adsorption capacity, and low value of hydraulic conductivity, compacted bentonite is used as a liner material at the waste disposal site. However, the presence of various heavy metal pollutants in the leachate could affect the swelling and sorption capacity of bentonite and in turn reduce its usefulness as a liner material. Hence, to design a clay liner it is quite essential to study the behaviour of bentonites in the presence of the different chemicals present in the leachate. In this study, the effects of heavy metals of varying concentrations were experimentally investigated on the behaviour of two bentonites with different mineralogical compositions. The bentonites were evaluated for their free swelling, Atterberg limits, swelling potential, swelling pressure, and hydraulic conductivity in the presence of different concentrations of Zn2+, Pb2+, and Cu2+ metal ions. The results showed that with the increase in the heavy metal concentration the liquid limit, free swelling, swelling pressure, and swelling potential of the bentonite decreased and the hydraulic conductivity increased. These reductions are attributed to the adsorption of heavy metals to the bentonite and decrease in the thickness of the double layer. The effects due to metal ion concentration were found to be more pronounced for the bentonite of higher quality which is marked by a higher swelling capacity, liquid limit, cation exchange capacity, exchangeable sodium percentage, and specific surface area.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abollino O, Aceto M, Malandrino M, Sarzanini C, Mentasti E (2003) Adsorption of heavy metals on Na-Montmorillonite, effect of pH and organic substances. Water Res 37:1619–1627
ASTM (1996) Standard test method for one-dimensional consolidation properties of soils. D 2435. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia
ASTM (2000) Standard test methods for liquid limit, plastic limit, and plasticity index of soils. D 4318. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia
ASTM (2001) Standard test method for swell index of clay mineral component of geosynthetic clay liners. D 5890. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia
ASTM (2002) Standard test method for particle-size analysis of soils. D 422-63. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia
Bailey SE, Olin TJ, Bricka RM, Adrian DD (1999) A review of potentially low-cost sorbents for heavy metals. Water Res 33(11):2469–2479
Cerato AB, Lutenegger AJ (2002) Determination of surface area of fine-grained soils by the ethylene glycol monoethyl ether (EGME) method. Geotech Test J 25:1–7
Chapman HD (1965) Cation Exchange Capacity. Methods of soil analysis, part 2 chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd edn. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 891–895
Chen FH (1975) Foundation on expansive soils, developments in geotechnical engineering, vol 12. Elsevier Scientific, New York, p 280
Ernst WHO (1990) Mine vegetation in Europe. Heavy metal tolerance in plants: evolutionary aspects. In: Shaw AJ (ed) CRC, BocaRaton, pp 21–51
Ernst WHO (1995) Decontamination or consolidation of metal-contaminated soils by biological means. Heavy metals: problems and solutions. In: Salomons W, Forstner U, Mader P (eds) Springer, Berlin, pp 141–149
Lambe T (1954) The permeability of compacted fine-grained soils. Special Technical Publication, 163, ASTM, Philadelphia, pp 56–67
Lambe TW (1958) The engineering behavior of compacted clay. J Soil Mech Found Div Proc ASCE 1655:1–35
Lee JM, Shackelford D (2005) Impact of bentonite quality on hydraulic conductivity of geosynthetic clay liners. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 131(1):64–77
Li LY (2003) Multi-component of heavy metal contaminants adsorptivity and compatibility onto variable charge clay mineral. Clay Sci 12:73–80
Li LY, Li F (2001) Heavy metal sorption and hydraulic conductivity studies using three types of Bentonite Admixes. J Environ Eng 127(5):420–429
Lo I, Luk A, Yang X (2004) Migration of heavy metals in saturated sand and bentonite/soil admixture. J Environ Eng 130, Special Issue: Waste Containment Barrier Materials, pp 906–909
Mishra AK, Dhawan S, Rao SM (2008) Analysis of swelling and shrinkage behavior of compacted clays. Geotech Geol Eng 26(3):289–298
Mishra AK, Ohtsubo M, Li L, Higashi T, Park J (2009) Effect of salt of various concentrations on liquid limit, and hydraulic conductivity of different soil-bentonite mixtures. Environ Geol 57(5):1145–1153
Mishra AK, Ohtsubo M, Li Loretta, Higashi T (2011) Controlling factors of the swelling of various Bentonites and their correlations with the hydraulic conductivity of soil-bentonite mixtures. Appl Clay Sci 52:78–84
Mitchell JK, Soga K (2005) Fundamentals of soil behavior, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Nakano A, Li LY, Ohtsubo M, Mishra AK (2008) Lead retention mechanisms and hydraulic conductivity studies of various bentonites for geoenvironment applications. Environ Technol 29:505–514
Ouhadi VR, Sedighi M (2003) Variation of experimental results of oedometer testing due to the changes of pore fluid. In: Deformation characteristics of geomaterials. Taylor & Francis, New York, pp 299–304
Ouhadi VR, Yong RN, Sedighi M (2006) Influence of heavy metal contaminants at variable pH regimes on rheological behaviour of bentonite. Appl Clay Sci 32:217–231
Pratt PF (1965) Sodium, methods of soil analysis, part 2 chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd edn. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 1031–1034
Prudent P, Domeizel M, Massiani C (1996) Chemical sequential extraction as a decision-making tool: application to municipal solid waste and its individual constituents. Sci Total Environ 178:55–61
Rao SM, Thyagaraj T, Thomas HR (2006) Swelling of compacted clay under osmotic gradients. Geotechnique 56(10):707–713
Sridharan A, Gurtug Y (2004) Swelling behavior of compacted fine grained soils. Eng Geol 72:9–18
Sridharan A, Rao GV (1975) Mechanism controlling liquid limit of clays. Proc Istanbul Conf Soil Mech Found Eng 1:75–84
Sridharan A, Rao AS, Sivapullaiah PV (1986) Swelling pressure of clays. Geotech Test J 9(1):24–33
Taylor DW (1948) Fundamentals of soil mechanics. Wiley, New York
Terzaghi K (1943) Theoretical soil mechanics. Wiley, New York
Vega JL, Ayala J, Loredo J, Iglesias JG (2005) Bentonites as adsorbents of heavy metals ions from mine waste leachates: experimental data. In: 9th international mine water congress, pp 603–609
Warkentin BP (1961) Interpretation of the upper plastic limit of clays. Nature 190:287–288
Yong RN, Warkentin BP (1975) Soil properties and behaviour. Elsevier Scientific Publishing Co., New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dutta, J., Mishra, A.K. Influence of the presence of heavy metals on the behaviour of bentonites. Environ Earth Sci 75, 993 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5811-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5811-2