Abstract
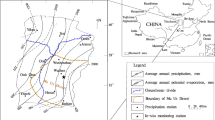
Accurate estimation of precipitation amount recharged to the groundwater is essential to the water balance calculation of a groundwater system in regional scale. In the torrid zones, the proportion of heavier water isotopes in precipitation presents a negative correlation with the precipitation amount. The physical processes explicating this so-called amount effect have not been well understood. This paper focuses on the δD relationships of local precipitation and groundwater to explain the isotopic variability in Ordos Plateau, China. In order to better understand the physical process interpreting the amount effect, a numerical threshold model in the vadose zone to relate the ineffective precipitation amount and isotopic abundance of precipitation and groundwater was supposed. By comparing the modelled δD with that in groundwater, ineffective precipitation, a value of 6.12 mm was obtained in Ordos Plateau. Thus, the potential groundwater recharge from the precipitation in the region can be deduced. The methodology proposed in this study will provide useful insights into the estimation of precipitation contribution to groundwater in other similar areas in the world.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bony S, Risi C, Vimeux F (2008) Influence of convective processes on the isotopic composition (δ18O and δD) of precipitation and water vapor in the tropics: 1. Radiative-convective equilibrium and Tropical Ocean-Global Atmosphere–Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Response Experiment (TOGA–COARE) simulations. J Geophys Res 113:D19305. doi:10.1029/2008JD009942
Carrera-Hernandez JJ, Gaskin SJ (2008) Spatio-temporal analysis of potential aquifer recharge: application to the Basin of Mexico. J Hydrol 353:228–246
Coplen TB et al (1994) 500,000-year stable carbon isotopic record from devils hole. Nevada Sci 263(5145):361–365
De Vries JJ, Simmers I (2002) Groundwater recharge: an overview of processes and challenges. Hydrogeol J 10:5–17
Gates JB, Edmunds WM, Ma J, Scanlon BR (2008) Estimating groundwater recharge in a cold desert environment in northern China using chloride. Hydrogeol J 5(16):893–910
Healy RW, Cook PG (2002) Using groundwater levels to estimate recharge. Hydrogeol J 10(1):91–109
Hogan JE, Phillips FM, Scanlon BR (2013) Evaluation of methods of estimating recharge in Semiarid and Arid Regions in the Southwestern U.S. American Geophysical Union, Washington, D.C., pp 235–254
Hou GC, Su X, Lin X et al (2007) Environmental isotopic composition of natural water in ordos cretaceous groundwater basin and its significance for hydrological cycle. J Jilin Univ (Earth Sci edn) 37(2):255–260
Murphy EM, Ginn TR, Phillips JL (1996) Geochemical estimates of recharge in the Pasco basin: evaluation of the chloride mass balance technique. Water Resour Res 32:2853–2868
Risi C, Bony S, Vimeux F (2008) Influence of convective processes on the isotopic composition (δ18O and δD) of precipitation and water vapor in the tropics: 2. Physical interpretation of the amount effect. J Geophys Res 113:D19306. doi:10.1029/2008JD009943
Scanlon BR, Healy RW, Cook PG (2002) Choosing appropriate techniques for quantifying groundwater recharge. Hydrogeol J 10:18–39
Scanlon BR et al (2006) Global synthesis of groundwater recharge in semiarid and arid regions. Hydrol Prog 20:3335–3370
Stewart MK (1975) Stable isotope fractionation due to evaporation and isotopic exchange of falling waterdrops: applications to atmospheric processes and evaporation of lakes. J Geophys Res Oceans 80(9):1133–1146
Walker GR, Zhang L, Ellis TW, Hatton TJ, Petheram C (2002) Estimating impacts of changed land use on recharge: a review of modelling and other approaches appropriate for management of dryland salinity. Hydrogeol J 10:68–90
Wilson IJ, Guan H (2004) Mountain-block hydrology and mountain-front recharge. In: Hogan JF, Phillips FM, Scanlon BR (eds) Groundwater recharge in a desert environment: the southwestern United States. AGU, Washington, pp 113–137
Yang YC, Hou GC, Wen DG, Pang ZH, Wang D (2005) Hydrogen–oxygen isotope composition of precipitation and seasonal effects of precipitation in Ordos Basin. Acta Geosci Sin 26(Suppl):289–292
Yang YC, Shen ZL, Weng DG, Hou GC, Zhao ZH, Wang D, Pang ZH (2009) Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes of waters in the Ordos Basin, China: implications for recharge of groundwater in the north of Cretaceous Groundwater Basin. Acta Geol Sin 81(1):103–113
Yin LH, Hou GC, Tao ZP, Li Y (2009a) Origin and recharge estimates of groundwater in the Ordos Plateau, P.R. China. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0310-3
Yin LH, Hou GC, Dou Y, Tao ZP, Li Y (2009b) Hydrogeochemical and isotopic study of groundwater in the Habor Lake Basin of the Ordos Plateau, NW China. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0383
Yin L et al (2011a) Groundwater-recharge estimation in the Ordos Plateau, China: comparison of methods. Hydrogeol J 19:1563–1575
Yin LH, Hou GC, Su XS, Wang D, Dong JQ, Hao YH, Wang XY (2011b) Isotopes (δD and δ18O) in precipitation, groundwater and surface water in the Ordos Plateau, China: implications with respect to groundwater recharge and circulation. Hydrogeol J. doi:10.1007/s10040-010-0671-4
Zagana E, Obeidat M, Kuells Ch, Udluft P (2007) Chloride, hydrochmeical and isotope methods of groundwater recharge estimation in eastern Mediterranean areas: a case study in Jordan. Hydrol Process 21:2112–2123
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the National Science Foundation of China Grant No. 41203014 and Technology New Star Plan of Shaanxi Province (2016KJXX-92). The financial support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41402202) was also appreciated. Thanks are given to Jochen W. Wenninger of UNESCO-IHE who analyzed the soil samples for the soil profile.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, H., Yang, Q., Yin, L. et al. The identification of precipitation amount effect with a water isotope-enabled threshold model in vadose zone: a case study in Ordos Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 75, 922 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5708-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5708-0