Abstract
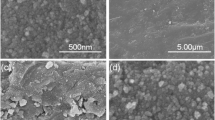
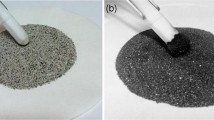
In this paper, for the first time we describe the removal of poisonous element ‘arsenic (V)’ from drinking water by nanoscale magnetite coated sand. The removal efficiency of newly formed adsorbent was studied by varying various parameters, for example, contact time, pH, adsorbent dosage and initial As(V) concentration. Also, the experiments were performed in the presence of co-existing cations (Zn2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, Ni2+, Mg2+, Cr3+ and Fe3+) to study their influence on As(V) removal efficiency. The adsorption kinetics data fitted well in both the pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetics with high correlation coefficients (R 2 > 0.99). Adsorption isotherm data are fitted in Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models. It is observed that thus formed adsorbent shows significant As(V) removal efficiency, and reduces the As(V) concentration below 5 µg/L from 6700 µg/L, which is much less than the maximum contaminant level set by WHO (10 µg/L). Here, the co-existing cations do not show any significant effect on As(V) removal efficiency. The observed Freundlich adsorption capacity of 2.06 mg/g for As(V) removal is comparable with certain other adsorbents.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
An B, Liang Q, Zhao D (2011) Removal of arsenic (V) from spent ion exchange brine using a new class of starch-bridged nanoparticles. Water Res 45:1961–1972
Armienta MA, Rodriguez R, Cruz O (1997) Arsenic content in hair of people exposed to natural ar-senic polluted groundwater in Zimapan, Mexi-co. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 59:583–589
Benjamin MM (1983) Adsorption and surface precipitation of metals on amorphous iron oxyhydroxide. Environ Sci Technol 17:686–692
Berg M, Tran HC, Nguyeu TC, Pham MV, Scherteuleib R, Giger W (2001) Arsenic contamina-tion of groundwater and drinking water in Viet-nam: a human health threat. Environ Sci Tech-nol 35:2621–2626
Bhaskar PB, Gupta AK, Ayoob S, Kandu S (2006) Investigation of arsenic (V) removal by modified calcined bauxite. Colloids Surf A 281:237–245
British Geological Survey (1999). Groundwater stud-ies for arsenic contamination in Bangladesh. Phase I: rapid investigation phase. Final report. Newcastle upon Tyne: Mott MacDonald Ltd., pp S1–S12
British Geological Survey (2001). Arsenic contami-nation of groundwater in Bangladesh (phase 2). In: Kinniburgh DG, Smedley PL (eds), Key-worth: British geological survey, pp 231–253. (BGS technical report no. WC/00/19)
Caceras LV, Grttner ED, Cantreras RN (1992) Water recycling in arid regions. Ambio 21:138–144
Chakraborti D, Basu GK, Biswas BK, Chowdhury UK, Rahman MM, Paul K, Chowdhury TR, Chanda CR, Lodh D (2001) Characterization of arsenic bearing sediments in Gangetic delta of West Bengal-India. In: Chappell WR, Abernathy CO, Calderon RL (eds.) Arsenic exposure and health effects, Elsevier, Amsterdam, Lausanne, New York, Oxford, Tokyo, pp 27–52
Chandra V, Park J, Chun Y, Lee JW, Hwang IC, Kim KS (2010) Water-dispersible magnetite-reduced graphene oxide composites for arsenic removal. ACS Nano 4:3979–3986
Chowdhury SR, Yanful EK (2010) Arsenic and chromium removal by mixed magnetite-maghemite nanoparticles and the effect of phosphate on removal. J Environ Manage 91:2238–2247
Das GK, Bonifacio CS, Rojas JD, Liu K, Benthem KV, Kennedy LM (2014) Ultra-long magnetic nanochains for highly efficient arsenic removal from water. J Mater Chem A 2:12974–12981
Datta GA, Pratip BA (1997) Technologies and options for arsenic removal. IWWA, Annual convention, Calcutta, 1–9
De Sastre MSR, Varillas A, Kirschbaum P (1992) Arsenic content in water in the northwest area of Argentina. In: Arsenic in the environment and its incidence on health. (International seminar proceedings). Santiago, Universidad de Chile, pp 91–9
Diaz-Barriga F, Santos MA, Mejia JJ, Batres L, Yanez L, Carrizales L, Vera E, del Razo LM, Cebrian ME (1993) Arsenic and cadmium exposure in children living near a smelter complex in San Luis Potosi, Mexico. Environ Res 62:242–250
Dixit S, Hering JG (2003) Comparison of arsenic (V) and arsenic (III) sorption onto iron oxide minerals: implications for arsenic mobility. Environ Sci Technol 37:4128–4189
Driehaus W, Jekel M, Hildebrandt U (1998) Granular ferric hydroxides—a new adsorbent for the removal of arsenic from natural water. J Water SRT Aqua 47:30–35
Elwakeel KJ (2014) Removal of arsenate from aqueous media by magnetic chitosan resin immobilized with molybdate oxoanions. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:1051–1062
EPA (2000) Arsenic occurence in public drinking water supplies. Rep. No. EPA-815-R-00-023, USEPA, Washington
Escudero C, Fiol N, Villaescusa I, Bollinger JC (2009) Arsenic removal by waste metal (hydr) oxide entrapped into calcium alginate beads. J Hazard Mater 164:533–541
Fan T, Liu Y, Feng B, Zeng G, Yang C, Zhou M, Zhou H, Tan Z, Wang X (2008) Biosorption of cadmium(II), zinc(II) and lead(II) by Penicillium simplicissimum: isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. J Hazard Mater 160:655–661
FAO (1985) Water quality guidelines for maximum crop production. Food and agriculture organization/UN, http://www.fao.org/docrep/T0551E (13.9.06)
Farrell J, Wang J, O’Day P, Conklin M (2001) Electrochemical and spectroscopic study of arsenate removal from water using zero-valent iron media. Environ Sci Technol 35:2026–2032
Freundlich HMFZ (1906) Stoechiometrie und Verwandtschaftslehre. Zeitschriftfuer Physikalische. Chemie 57:385–470
Goldberg S, Johnston CT (2001) Mechanisms of arsenic adsorption on amorphous oxides evaluated using macroscopic measurements, vibrational spectroscopy, and surface complexation modeling. J Colloid Interface Sci 234:204–216
Gomez-Arroyo S, Armienta MA, Cortes-Es-lava J, Villalobos-Pietrini R (1997) Sister chromatid exchanges in Vicia faba induced by arsenic contaminated drinking water from Zimapan, Hidalgo, Mexico. Mutat Res 394:1–7
Grantham DA, Jones JF (1977) Arsenic contamination of water wells in Nova Scotia. J Am Water Works Assoc 69:653–657
Guo H, Struben D, Berner Z (2007) Removal of arsenic from aqueous solution by natural siderite and hematite. Appl Geochem 22:1039–1051
Gupta A, Mohammed Y, Sankararmakrishnan N (2013) Chitosan- and Iron–chitosan-coated sand filters: a cost-effective approach for enhanced arsenic removal. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:2066–2072
Hinwood A, Bannister R, Shugg A, Sim M (1998) En-vironmental arsenic in rural Victoria: an update. Water Melbourne Then Artarmon 25:34–36
Hussam A, Munir AKM (2007) A simple and effective arsenic filter based on composite iron matrix: development and deployment studies for groundwater of Bangladesh. J Environ Sci Health Part A 42:1869–1878
Jekel MR (1994) Removal of arsenic in Drinking Water Treatment. In: Nriagu JO (ed) Arsenic in the environment, Part 1: cycling and characterization. Wiley, New York, pp 1–448
Kaczala F, Marques M, Hogland W (2009) Lead and vanadium removal from a real industrial wastewater by gravitational settling/sedimentation and sorption onto Pinus sylvestris sawdust. Bioresour Technol 100:235–243
Katsoyiannis IA, Zouboulis AI (2004) Application of biological processes for the removal of arsenic from groundwater. Water Res 38:17–26
Katsoyiannis IA, Zouboulis AI, Jekel M (2004) Kinetics of bacterial As(III) oxidation and subsequent As(V) removal by sorption onto biogenic manganese oxides during groundwater treatment. Ind Eng Chem Res 43:486–493
Kemp KC, Seema H, Saleh M, Le H, Mahesh K, Chandra V, Kim KS (2013) Environmental applications using graphene composites: water remediation and gas adsorption. Nanoscale 5:3149–3171
Korngold E, Belayev N, Aronov L (2001) Removal of arsenic from drinking water by anion exchangers. Desalination 141:81–84
Lackovic JA, Nikolaidis NP, Dobbs GM (2000) Inorganic arsenic removal by zerovalent iron. Environ Eng Sci 17:29–39
Lakshmipathiraj P, Narasimhan BRV, Prabhakar S, Raju SGB (2006) Adsorption of arsenate on synthetic goethite from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 136:281–287
Luo X, Wang C, Luo S, Dong R, Tua X, Zeng G (2012) Adsorption of As(III) and As(V) from water using magnetite Fe3O4-reduced graphite oxide–MnO2 nanocomposites. Chem Eng J 187:45–52
Magalhães MCF (2002) Arsenic: an environmental problem limited by solubility. Pure Appl Chem 74:1843–1850
Maji SK, Pal M, Pal T, Adak A (2007) Adsorption thermodynamic of As on laterite soil. J Surf Sci Technol 22:161–176
Manning BA, Fendorf SE, Bostick B, Suarez DL (2002a) Arsenic(III) and arsenic(V) adsorption reactions on synthetic birnessite. Environ Sci Technol 36:976–981
Manning BA, Hunt ML, Amrhein C, Yarmoff JA (2002b) Arsenic(III) and arsenic(V) reactions with zerovalent iron corrosion products. Environ Sci Technol 36:5455–5461
Matschullat J, Borba RP, Deschamps E, Figueiredo BR, Gabrio T, Schwenk M (2000) Human and environmental contamination in Iron Quadrangle, Brazil. Appl Geochem 15:181–190
Mohan D, Pittman CU (2007) Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—a critical review. J Hazard Mater 142:1–53
Mondal P, Majumder CB, Mohanty B (2006) Laboratory based approaches for arsenic remediation from contaminated water: recent developments. J Hazard Mater 137:464–479
Mukherjee A, Sengupta MK, Hossain MA, Ahamed S, Das B, Nayak B, Lodh D, Rahman MM, Chakraborti D (2006) Arsenic contamination in groundwater: a global perspective with emphasis on the Asian scenario. J Health Popul Nutr 24:142–163
Neriowlm (2004) Pre-seminar proceedings from national seminar on arsenic and fluoride contamination in groundwater organized by North eastern regional institute of water and land management. Tezpur, Assam, pp 1–10
Nikolaidis NP, Dobbs GM, Lackovic JA (2003) Arsenic removal by zero valent iron: field, laboratory and modelling studies. Water Res 37:1417–1425
Nishida S, Takesoe S, Yamasaki Y, Nakahira A (2004) Attempt of arsenic removal in wasted water by inorganic materials. In: 14th International Conference on the properties of water and steam, Japan
Nordstrom DK, Archer DG (2003) Arsenic thermodynamic data and environmental geochemistry. In: Cai Y, Braids OC (eds) Biogeochemistry of environmentally important trace elements. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 1–25
NRC (2001) Arsenic in drinking water: 2001 Update. National Research Council, National Academy Press, Washington
Pandey PK, Choubey S, Verma Y, Pandey M, Chandrashekhar K (2009) Biosorptive removal of arsenic from drinking water. Bioresour Technol 100:634–637
Parga JR, Cocke DL, Valenzuela JL, Gomes JA, Kesmez M, Irwin G, Moreno H, Weir M (2005) Arsenic removal via electrocoagulation from heavy metal contaminated groundwater in La Comarca Lagunera M’exico. J Hazard Mater 124:247–254
Park H, Myung NV, Jung H, Choi H (2009) As(V) remediation using electrochemically synthesized maghemite nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 11:1981–1989
Pfeifer HR, Zobrist J (2002) Arsenic in drinking waters—also a problem in Switzerland. EAWAG News 53:15–17
Pillewan P, Mukherjee S, Roychowdhury T, Das S, Bansiwal A, Rayalu S (2011) Removal of As(III) and As(V) from water by copper oxide incorporated mesoporous alumina. J Hazard Mater 186:367–375
Rome L, Gadd GM (1987) Copper adsorption by Rhizopus arrhizus, Cladosorium resinae and Penicillium italicum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 26:84–90
Samanta G, Chowdhury TR, Mandal BK, Chowdhury UK, Basu GK, Chanda CR, Lodh D, Chakraborti D (1999) Flow injection hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometery for determination of arsenic in water and biological samples from arsenic-affected districts of West Bengal, India and Bangladesh. Michrochem J 62:174–191
Shrestha RK, Regmi D, Kafle BP (2006) Seasonal variation of arsenic concentration in ground water of Nawalparasi district of Nepal. Int J Appl Sci Biotechnol 2:59–63
Sinha S, Amy G, Yoon Y, Her N (2011) Arsenic removal from water using various adsorbents: magnetic ion exchange resins, hydrous iron oxide particles, granular ferric hydroxide, activated alumina, sulfur modified iron, and iron oxide-coated microsand. Environ Eng Res 16:165–173
Southwick JW, Western AE, Beck MM, Whit-ney T, Isaacs R, Petajan J, Hansen CD (1983) An epi-demiological study of arsenic in drinking water in Millard county, Utah. In: Leaderer WH, Rob-ert JF (eds) Arsenic: industrial, biomedical, environmental perspectives. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, pp 210–225
Su C, Puls RW (2001) Arsenate and arsenite removal by zerovalent iron: kinetics, redox transformation, and implications for in situ groundwater remediation. Environ Sci Technol 35:1487–1492
Su C, Puls RW (2003) In situ remediation of arsenic in simulated groundwater using zerovalent iron: laboratory column tests on combined effects of phosphate and silicate. Environ Sci Technol 37:2582–2587
Turk T, Alp I, Deveci H (2009) Adsorption of As(V) from water using Mg-Fe-based hydrotalcite (FeHT). J Hazard Mater 171:665–670
Turk T, Alp I, Deveci H (2010) Adsorption of As(V) from water using nanomagnetite. J Environ Eng 136:399–404
USAToday.Com (2007) Arsenic in drinking water seen as threat
USEPA (2000) Technologies and costs for removal of arsenic from drinking water. Office of water environmental protection agency, Washington (EPA/815/R00/028)
Wang X, Guo Y, Yang L, Han M, Zhao J, Cheng X (2012) Nanomaterials as sorbents to remove heavy metal ions in wastewater treatment. J Environ Anal Toxicol 2(154):1–7
WHO (1963) International standards for drinking-water, 2nd ed
WHO (1993) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, vol 1. Recommendations, 2nd ed. WHO, Geneva
Wickramasinghe SR, Han B, Zimbron J, Shen Z, Karim MN (2004) Arsenic removal by coagulation and filtration: comparison of groundwaters from the United States and Bangladesh. Desalination 169:231–244
Yavuz CT, Mayo JT, Yu WW, Prakash A, Falkner JC, Yean SJ, Cong LL, Shipley HJ, Kan A, Tomson M, Natelson D, Colvin VL (2006) Low-field magnetic separation of monodisperse Fe3O4 nanocrystals. Science 314:964–967
Yean S, Cong L, Yavuz CT, Mayo JT, Yu WW (2005) Effect of magnetite particle size on adsorption and desorption of arsenite and arsenate. J Mater Res 20:3255–3264
Ying W, Kongjun Z, Fen W, Kazumichi Y (2009) Novel Fe/glass composite adsorbent for As(V) removal. J Environ Sci 21:434–439
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Delhi (Project number: FTP/PS-40/2011) and Nanotechnology Lab, Jaypee University of Information Technology, Waknaghat, Solan-173234, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kango, S., Kumar, R. Magnetite nanoparticles coated sand for arsenic removal from drinking water. Environ Earth Sci 75, 381 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5282-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5282-5