Abstract
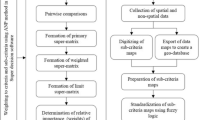
To guarantee sustainability in urban coastal areas, it is essential to have more conservation plans in these areas under various pressures. The first large urban conurbation in Malaysia, which stretches from the central mountain spine to the west coast, has expanded and emerged as a potential mega-urban region. To evaluate its sustainability, several critical criteria and indicators must be identified. The process of choosing criteria is very sensitive. If too many criteria are selected, the focus of the plan becomes narrow, and this simplification often leads to poor decision making. The use of a limited number of criteria allows accommodation of spatial and temporal changes and also makes it easier to collect data. This paper presents an innovative, reliable method for identification of the most important criteria and alternatives using integrated extent analysis and fuzzy TOPSIS (technique for order preference by similarity to an ideal solution). The weights of the criteria are determined using the fuzzy pairwise comparison of the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) method. Criteria were also selected by interviewing thirty experts in the fields of economic, social and environmental sustainability. This set of criteria was drawn from several policies and strategies for development in Malaysia. Interviews with coastal managers, town and country planners and academic experts at the national and local levels provided information used to refine and modify these criteria. Seventeen criteria in three clusters of ecological, social and economic issues were considered in the evaluation of six alternatives sites for conservation in coastal areas, Port Dickson, Kelanang, Jugra, Pulau Indah, Kuala Selangor and Morib. Jugra was determined to be the most appropriate area for conservation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul SH, Shaharudin I, Abdul HH, Ahmad FM (2010) Malaysian urbanization transition: from Nascent, pseudo to livable mega-urban region. Malays J Environ Manag 11(1):3–13
Abdul SH, Shaharudin I, Abdul HH, Ahmad FM (2011) Critical urbanization transition in Malaysia: the challenge of rising Bernam to Linggi basin extended mega urban region. Akademika 81(2):11–21
Belfiore S (2000) Recent developments in coastal management in the European Union. Ocean Coast Manag 43:123–135
Brody SD, Arilkatti WH, Roubabah DH, Ismailova M (2004) Conflict on the coast: using Geographic Information Systems to map potential environmental disputes in Matagorda Bay Texas. Environ Manag 34(1):11–25
Buckley JJ (1985) Fuzzy hierarchical analysis. Fuzzy Sets Syst 17:233–247
Chang DY (1992) Extent analysis and synthetic decision optimization techniques and applications. World Scientific, Singapore
Chang DY (1996) Applications of the extent analysis method on fuzzy AHP. Eur J Oper Res 95:649–655
Chen SJ, Hwang CL (1992) Fuzzy multiple attribute decision making: methods and applications. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Dagdeviren M, Yuksel I, Kurt M (2008) A fuzzy analytic network process model to identify faulty behavior risk in work system. Saf Sci 46:771–783
Doody JP, Pamplin CF (1999) Information required for integrated coastal zone management. European Commission
Douven WJ, Buurman JJ, Kiswara W (2003) Spatial information for coastal zone management: the example of the Banten Bay sea grass ecosystem, Indonesis. Ocean Coast Manag 46:615–630
Erensal YC, Oncan T, Demircan ML (2006) Determining key capabilities in technology management using fuzzy analytic hierarchy process: a case study of Turkey. Inf Sci 176:2755–2770
FAO (1998) Integrated Coastal management and agriculture, forestry and fisheries. FAO, Rome
Flanders L (2000) Sustainable development of coastal zones and instruments for its evaluation. Germany
Horstman EM, Kathelijne MW, Alfons JS, Suzanne JM, Hulscher H (2009) On the consequences of a long-term perspective for coastal management. Ocean Coast Manag 52:593–611
Hwang CL, Yoon K (1981) Multiple attribute decision making. In: Lecture Notes in economics and mathematical systems 186. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Kahraman C, Kaya I, Cebi S (2009) A comparative analysis for multi attribute selection among renewable energy alternatives using fuzzy axiomatic design and fuzzy analytic hierarchy process. Energy 34:1603–1616
Kangas J, Kangas A (2002) multiple criteria decision support methods in forest management. An overview and comparative analyses. In: Pukkala T(ed.) Multi-objective forest planning. Kluwer Academic Publishers. Managing Forest Ecosystems 6:37–70
Leung LC, Cao D (2000) On consistency and ranking of alternatives in fuzzy AHP. Eur J Oper Res 124:102–113
Mc Gee TG (2007) Planning for mega-urban regions: policies for the twenty-first century. International symposium on regional planning in the Yangtze River Delta in Shanghai, 1 December
Mc Gee TG (2013) Rural–urban relations in the mega–urban regions of East Asia. http://penanginstitute.org/v3/resources/articles/event/177-qrural-urban-relations-in-the-mega-urban-regions-of-east-asia-implications-for-the-role-of-penang-conurbation-in-the-development-of-the-koridor-utaraq-by-professor-terry-mc-gee-?format=pdf. Accessed 26 Nov 2013
Meadows D (1988) Indicators and information systems for sustainable development. The Sustainability Institute. Hartland Four Corners, p 78
Mikhailov L (2004) A fuzzy approach to deriving priorities from interval pair wise comparison judgements. Eur J Oper Res 159:687–704
National coastal zone management (2000) Department of Town and Country Planning. Malaysia
Opricovic S, Tzeng GH (2004) Compromise solution by MCDM methods: a comparative analysis of VIKOR and TOPSIS. Eur J Oper Res 156:445–455
Pohekar SD, Ramachandran M (2004) Application of multi-criteria decision-making to sustainable energy planning–a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 8:365–381
Pourebrahim SH, Hadipour M, Mokhtar MB, Ibrahim HM (2010) Analytic network process for criteria selection in sustainable coastal land use planning. Ocean Coast Manag 53(9):544–551
Pourebrahim SH, Hadipour M, Mokhtar MB (2011) Integration of spatial analysis for land use planning in coastal areas; case of Kuala District, Selangor, Malaysia. Landsc Urb Plan 101:84–97
Pourebrahim SH, Hadipour M, Mokhtar MB, Taghavi S (2014) Application of VIKOR and fuzzy AHP for conservation priority assessment in coastal areas: case of Khuzestan district, Iran. Ocean Coast Manag 98:20–26
Ryu J, Leschine TM, Nam J, Chang WK, Dyson K (2011) A resilience-based approach for comparing expert preferences across two large-scale coastal management programs. J Environ Manag 92:92–101
Saaty TL (2004) The analytic network process: dependence and feedback in decision making (Part 1) theory and validation examples. MCDM. Whistler BC, Canada
Sarda R, Conxita A, Joan M (2005) A methodological approach to be used in integrated coastal zone management processes: the case of the Catalan Coast. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 62:427–439
Scottish Executive Central Research Unit (2001) Indicators to monitor the progress of Integrated Coastal Zone Management: a review of worldwide practice. Cordah Ltd, Edinburgh
Sevkli M, Oztekin A, Uysal O, Torlak G, Turkyilmaz A, Delen D (2012) Development of a fuzzy ANP based SWOT analysis for the airline industry in Turkey. Expert Syst Appl 39:14–24
Shaharudin I, Abdul SH, Abdul HH Sulaiman SU (2013) Kemunculan Kuala Lumpur Sebagai Wilayah Perbandaran Mega Diperluas. ProsidingGeografidanAlamSekitar ke-4. Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris (UPSI), TanjungMalim, Perak. 5–6 March
The Ninth Malaysia Plan (2006) Economic Planning Unit (EPU) Government Printer, Kuala Lumpur
Third National Agricultural Policy (1999) Ministry of Agriculture Malaysia. Kuala Lumpur, p 265
Tolga K, Kahraman C (2010) Multi criteria renewable energy planning using an integrated fuzzy VIKOR & AHP methodology: the case of Istanbul. Energy 35:2517–2527
Tsoutos T, Drandaki M, Frantzeeskaki N et al (2009) Sustainable energy planning by using multi criteria analysis application in the island of Crete. Energy Policy 37:1587–1600
Turner RK (2000) Integrating natural and socio-economic science in coastal management. J Mar Sci 25:447–460
UNEP, MAP, PAP (1999) Conceptual framework and planning guidelines for integrated coastal area and river basin management. Priority Actions Programme, Split
UN-HABITAT (2005). http://www.citymayors.com/society/asian_cities.html
Vollenweider RA (1992) Coastal Marine Eutrophication. In: Vollenweider RA, Marchetti R, Viviani R (ed) Marine coastal eutrophication, Elsevier, London
Waltz R (2000) Development of environmental indicator systems: experiences from Germany. Environ Manag 25(6):613–623
Wang JJ, Jing YY, Zhang CF et al (2010) Review on multi-criteria decision analysis aid in sustainable energy decision-making. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 13:2263–2278
Yoon K (1987) A reconciliation among discrete compromise solutions. J Oper Res Society 38(3):272–286
Zadeh L (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Zeleny M (1982) Multiple criteria decision making. Mc-Graw-Hill, New York
Zimmermann HJ (1991) Fuzzy set theory and its applications, 2nd edn. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston/Dordrech/London
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the LRGS grant 203/PKT/6720004, UKM: XX-11-2012, and XX-15-2012. The authors gratefully acknowledge use of the facilities of University of Tehran, Iran and UKM, Malaysia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pourebrahim, S., Mokhtar, M.B. Conservation priority assessment of the coastal area in the Kuala Lumpur mega-urban region using extent analysis and TOPSIS. Environ Earth Sci 75, 348 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5276-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5276-3