Abstract
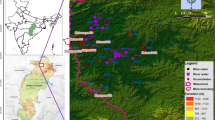
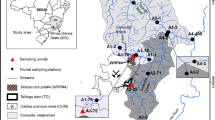
Worldwide, old disposal sites of uranium mine and mill wastes are the objects of environmental restoration programs or have already been remediated. This is the case of Los Gigantes in Córdoba, Argentina, where uranium was extracted and processed in the 1980s; a local source of pollution to watercourses was generated as a consequence of disposal of solid and liquid wastes. The present study aims at describing the physicochemical characteristics of the surface watercourses that run across the complex, finding a grouping structure of the sampling sites according to their degree of pollution, and defining the variables that are significant to that grouping. The problem is addressed with both traditional and robust statistics techniques; additional chemometrical tools are also applied. It was found that streams close to the tailings and the pond exhibit lower pH and higher concentration of anions and metals compared to upstream watercourses. As the distance downstream to these pollution sources increases, all physicochemical parameters recover gradually, reaching levels close to background and complying with provincial and national regulations, proving that pollution is locally constrained.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelouas A (2006) Uranium mill tailings: geochemistry, mineralogy, and environmental impact. Elements 2(6):335–341
Argentina (2003) Argentina Mining and Milling Uranium Wastes Sites Restoration (PRAMU) environmental assessment. Joint Convention on the Safety of Spent Fuel Management and on the safety of radioactive waste management. National report
Argentinean Legislation (1993) Regulation decree 831/93 of Hazardous Wastes National Law 24.051. In: Official sate bulletin 27.630. Buenos Aires
Berthold MR, Hand DJ (2003) Intelligent data analysis: an introduction, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin
British Columbia Ministry of Environment (BCME) (2001) Outliers, a Guide for data analysts and interpreters on how to evaluate unexpected high values. Contaminated sites statistical applications guidance document 12-8 (Internet). http://www.env.gov.bc.ca/epd/remediation/guidance/technical/pdf/12/gd08_all.pdf. Accessed 2 Nov 2014
Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (CCME) (2001) CCME Water Quality Index 1.0, user’s manual. In: Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (eds) Canadian environmental quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life, Winnipeg
Cicerone D, Gómez del Río J, Sánchez Proaño P, Grande Cobián D (2009) Technical feasibility study for the design and installation of a permeable reactive barrier. Comisión Nacional de Energía Atómica internal report: PP-SNAGQ_DAS-01
División Química del Agua y del Suelo (DQAS) (2012) Comisión Nacional de Energía Atómica internal report IN-GQ_DQAS-00
Einax JW, Zwanziger HW and Geiß S (1997) Chemometrics in environmental analysis. VCH Verlagsgesellschaft mbH Weinheim
Folguera L, Zupan J, Cicerone DS, Magallanes JF (2015) Self-organizing maps for imputation of missing data in incomplete data matrices. Chemometr Intell Lab 143:146–151
García-Reiriz A, Magallanes JF, Zupan J, Líberman S (2011) Artificial neural networks to evaluate the boron concentration decreasing profile in blood-BPA samples of BNCT patients. Appl Radiat Isotopes 69:1793–1795
Hubert M, Rousseuw PJ, Branen KV (2003) ROBPCA: a new approach to robust principal component analysis. Technometrics 47(1):64–79
Instituto Nacional del Agua (INA) (2001) Investigación Hidrogeológica en el Área Los Gigantes. Subsecretaría de Recursos Hídricos de la Nación, Ministerio de Panificación Federal, Inversión Pública y Servicios de la República Argentina. Technical report IT-201
International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) (2008) Estimation of global inventories of radioactive waste and other radioactive materials. Technical document IAEA-TECDOC-1591
Junninen H, Niska H, Tuppurainen K, Ruuskanen J, Kolehmainen M (2004) Methods for imputation of missing values in air quality data sets. Atmos Environ 38:2895–2907
Kaufman L, Rousseeuw PJ (1990) Finding groups in data: an introduction to cluster analysis. Wiley, New York
Magallanes JF, García Reiriz AG, Líberman S, Zupan J (2011) Kohonen classification applying ‘missing variables’ criterion to evaluate the pboronophenylalanine human-body-concentration decreasing profile of boron neutron capture therapy patients. J Chemometrics 25(6):340–347
Maronna RA, Douglas DM, Yohai VJ (2006) Robust statistics, theory and methods. Wiley, England
Massart DL, Vandeginste BGM, Buydens LMC, De Jong S, Lewi PJ, Smeyers-Verbeke J (1997) Handbook of chemometrics and qualimetrics. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Mwale F, Adeloye A, Rustum R (2012) Infilling of missing rainfall and streamflow data in the Shire river basin, Malawi. A self organizing map approach. Phys Chem Earth 50–52:34–43
Nuclear Energy Agency (NEA) (2014) Managing environmental and health impacts of uranium mining. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. NEA 7062, Paris
The World Bank (2014) Restructuring paper on a proposed project restructuring of Argentina mining environmental restoration project (P110462). Report 79771-AR
Uranium Mining Environmental Restoration Project (PRAMU) (2005) Evaluación Ambiental, document Marco. Comisión Nacional de Energía Atómica. Internal report INF-04-010
Verboven S, Hubert M (2005) LIBRA: a MATLAB library for robust analysis. Chemometr Intell Lab 75:127–136
Zupan J, Gasteiger J (1999) Neural networks in chemistry and drug design. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Zupan J, Novič M, Ruisánchez I (1997) Kohonen and counterpropagation artificial neural networks in analytical chemistry. Chemometr Intell Lab 38:1–2
Acknowledgments
This study was made possible with the financial support provided by the Comisión Nacional de Energía Atómica through the project PP-SNA_GQ_GQA-DSA-01. The authors would like to thank the coworkers of the División Química del Agua y del Suelo and División Química Analítica of the Centro Atómico Constituyentes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Folguera, L., Magallanes, J. & Cicerone, D. Analysis of the environmental liabilities generated by past activities in uranium mining exploitation in the Province of Córdoba, Argentina. Environ Earth Sci 75, 407 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5178-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5178-9