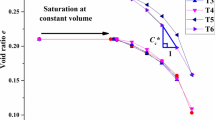
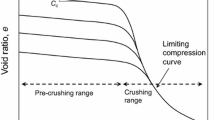
Abstract
The present study focuses on the compression characteristics of a crushed sandstone–mudstone particle mixture. The mixture is artificially prepared by mixing sandstone particles and mudstone particles (MP) on the basis of five scheduled particle size distribution (PSD) curves and six MP contents by weight. In order to investigate the compression characteristics, 120 confined uniaxial compression tests are performed. The compression curve for each specimen, which represents the relationship between the logarithm (base 10) of the applied stress and void ratio, is obtained from test data. Two defining features of the compression curve, namely the compression index (I c) and pre-compression stress (σ p), are determined. The effects of two-type factors on the two parameters I c and σ p are analyzed. Factors of the first type are the properties of tested material, which include the PSD curve [the characteristics of which are denoted by the median particle diameter (D 50), gravel content (G c), non-uniformity coefficient (C u), curvature coefficient (C c), characteristic size (α), PSD shape (β)], and MP content by weight (MPc). Factors of the other type are the properties of the specimen, which include the initial water content (w), initial dry bulk density (ρ d), and initial void ratio (e 0). The results indicate that both the parameters I c and σ p are correlative with the properties of the tested material and specimen.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbas SO, Kulhawy FH (2009a) Axial compression of footings in cohesionless soils. I: Load-settlement behavior. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 135(11):1562–1574
Akbas SO, Kulhawy FH (2009b) Axial compression of footings in cohesionless soils. II: Bearing capacity. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 135(11):1575–1582
Alexandrou A, Earl R (1998) The relationship among the pre-compaction stress, volumetric water content and initial dry bulk density of soil. J Agric Eng Res 71:75–80
An J, Zhang Y, Yu N (2015) Quantifying the effect of soil physical properties on the compressive characteristics of two arable soils using uniaxial compression tests. Soil Tillage Res 145:216–223
Arthur E, Schjønning P, Moldrup P, Tuller M, de Jonge LW (2013) Density and permeability of a loess soil: long-term organic matter effect and the response to compressive stress. Geoderma 193–194:236–245
Arvidsson J (1998) Influence of soil texture and organic matter content on bulk density, air content, compression index and crop yield in field and laboratory compression experiments. Soil Tillage Res 49:159–170
Arvidsson J, Keller T (2004) Soil precompression stress: I. A survey of Swedish arable soils. Soil Tillage Res 77:85–95
Assouline S (2002) Modeling soil compaction under uniaxial compression. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:1784–1787
ASTM (1985) Standard practice for classification of soils for engineering purposes (Unified Soil Classification System), ASTM D2487. Annual Book of ASTM Standards. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
ASTM (1998) Standard test method for particle-size analysis of soils, ASTM D422-63. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
ASTM (2011) Standard test methods for one-dimensional consolidation properties of soils using incremental loading, ASTM D2435M-11. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
Cavalieri KMV, Arvidsson J, da Silva AP, Keller T (2008) Determination of precompression stress from uniaxial compression tests. Soil Tillage Res 98:17–26
Cetin H (2004) Soil-particle and pore orientations during consolidation of cohesive soils. Eng Geol 73:1–11
Chongqing Geological and Mineral Resource Exploration and Development Corporation (CGMREDC) (2002) Chongqing geological map (scale 1:500 000). Chongqing Yangtze River Map Printing Factory, Chongqing
Chowdhury B, Haque A, Muhunthan B (2014) New pressure-void ratio relationship for structured soils in the virgin compression range. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 140:06014009
da Silva AP, Kay BD, Perfect E (1997) Management versus inherent soil properties effects on bulk density and relative compaction. Soil Tillage Res 44:81–93
Day RW (1989) Relative compaction of fill having oversize particles. J Geotech Eng ASCE 115(10):1487–1491
Défossez P, Richard G, Boizard H, O’Sullivan MF (2003) Modeling change in soil compaction due to agricultural traffic as function of soil water content. Geoderma 116:89–105
Deng D-P (2013) Experimental study on compaction behavior and particle crushing of crushed sandstone-mudstone particle mixtures. Master’s thesis, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing (in Chinese)
Etana A, Comia RA, Håkansson I (1997) Effects of uniaxial stress on the physical properties of four Swedish soils. Soil Tillage Res 44:13–21
Fakhimi A, Hosseinpour H (2011) Experimental and numerical study of the effect of an oversize particle on the shear strength of mined-rock pile material. Geotech Test J 34:131–138
Fredlund MD, Wilson GW, Fredlund DG (2002) Use of the grain-size distribution for estimation of the soil-water characteristic curve. Can Geotech J 39:1103–1117
Fritton DD (2001) An improved empirical equation for uniaxial soil compression for a wide range of applied stresses. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65:678–684
Fritton DD (2006) Fitting uniaxial soil compression using initial dry bulk density, water content, and matric potential. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:1262–1271
Gregory AS, Whalley WR, Watts CW, Bird NRA, Hallett PD, Whitmore AP (2006) Calculation of the compression index and precompression stress from soil compression test data. Soil Tillage Res 89:45–57
Håkansson I, Lipiec J (2000) A review of the usefulness of relative bulk density values in studies of soil structure and compaction. Soil Tillage Res 53:71–85
Ham T-G, Nakata Y, Orense RP, Hyodo M (2010a) Influence of water on the compression behavior of decomposed granite soil. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 136(5):697–705
Ham T-G, Nakata Y, Orense RP, Hyodo M (2010b) Influence of gravel on the compression characteristics of decomposed granite soil. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 136(11):1574–1577
Hamidi A, Alizadeh M, Soleimani SM (2009) Effect of particle crushing on shear strength and dilation characteristics of sand-gravel mixtures. Int J Civil Eng 7:61–71
Hao J-Y (2014) Experimental study on compression deformation behavior and coefficient of lateral earth pressure of sandstone-mudstone particle mixtures. Master’s thesis, Chongqing Jiaotong University (in Chinese)
Ibrahim NM, Rahim NL, Amat RC, Salehuddin S, Ariffin NA (2012) Determination of plasticity index and compression index of soil at Perlis. APCBEE Preced 4:94–98
Imhoff S, da Silva AP, Fallow D (2004) Susceptibility to compaction, load support capability, and soil compressibility of Hapludox. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68:17–24
Jamei M, Guiras H, Chtourou Y, Kallel A, Romero E, Georgopoulos I (2011) Water retention properties of perlite as a material with crushable soft particles. Eng Geol 122(3–4):261–271
Jiang MJ, Li T, Hu HJ, Thornton C (2014) DEM analyses of one-dimensional compression and collapse behaviour of unsaturated structure loess. Comput Geotech 60:47–60
Keller T, Arvidsson J (2007) Compressive properties of some Swedish and Danish structured agricultural soils measured in uniaxial compression tests. Eur J Soil Sci 58:1373–1381
Keller T, Håkansson I (2010) Estimation of reference bulk density from soil particle size distribution and soil organic matter content. Geoderma 154:398–406
Keller T, Arvidsson J, Dawidowski JB, Koolen AJ (2004) Soil precompression stress: II. A comparison of different compaction tests and stress-displacement behaviour of the soil during wheeling. Soil Tillage Res 77:97–108
Keller T, Défossez P, Weisskopf P, Arvidsson J, Richard G (2007) SoilFlex : a model for prediction of soil stresses and soil compaction due to agricultural field traffic including a synthesis of analytical approaches. Soil Tillage Res 93:391–411
Keller T, Lamandé M, Schjønning P, Dexter AR (2011) Analysis of soil compression curves from uniaxial confined compression tests. Geoderma 163:13–23
Larson WE, Gupta SC, Useche RA (1980) Compression of agricultural soils from eight soil orders. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44:450–457
Lebert M, Horn R (1991) A method to predict the mechanical strength of agricultural soils. Soil Tillage Res 19:275–286
Lim Y, Miller G (2004) Wetting-induced compression of compacted Oklahoma soils. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 130(10):1014–1023
Lipiec J, Hatano R (2003) Quantification of compaction effects on soil physical properties and crop growth. Geoderma 116:107–136
Macías-García A, Cuerda-Correa EM, Díaz-Díez MA (2004) Application of the Rosin-Rammler and Gates–Gaudin–Schuhmann models to the particle size distribution analysis of agglomerated cork. Mater Charact 52:159–164
McBride RA (1989) Estimation of density-moisture-stress functions from uniaxial compression of unsaturated, structured soils. Soil Tillage Res 13:383–397
Mesri G, Vardhanabhuti B (2009) Compression of granular materials. Can Geotech J 46:369–392
Mohammadzadeh SD, Bazaz JB, Alavi AH (2014) An evolutionary computational approach for formulation of compression index of fine-grained soils. Eng Appl Artif Intell 33:58–68
Monkul MM, Önal O (2006) A visual basic program for analyzing oedometer test results and evaluating intergranular void ratio. Comput Geosci 32:696–703
Nhantumbo ABJC, Cambule AH (2006) Bulk density by Proctor test as a function of texture for agricultural soils in Maputo province of Mozambique. Soil Tillage Res 87:231–239
O’Sullivan MF, Simota C (1995) Modelling the environmental impacts of soil compaction: a review. Soil Tillage Res 35:69–84
O’Sullivan MF, Henshall JK, Dickson JW (1999a) A simplified method for estimating soil compaction. Soil Tillage Res 49:325–335
O’Sullivan MF, Robertson EAG, Henshall JK (1999b) Shear effects on gas transport in soil. Soil Tillage Res 50:73–83
Park S (2010) Effect of wetting on unconfined compressive strength of cemented sands. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 136(12):1713–1720
Paz A, Guérif J (2000) Influence of initial packing density, water content and load applied during compression on tensile strength of dry soil structural units. Adv Geoecol 32:22–31
Perfect E, Kay BD, Ferguson JA, da Silva AP, Denholm KA (1993) Comparison of functions for characterizing the dry aggregate size distribution of tilled soil. Soil Tillage Res 28:123–139
Qiu Z-F, Wang J-J (2015) Experimental study on the anisotropic hydraulic conductivity of a sandstone–mudstone particle mixture. J Hydrol Eng ASCE. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001220
Reinsch TG, Grossman RB (1995) A method to predict bulk density of tilled Ap horizons. Soil Tillage Res 34:95–104
Rios S, Viana da Fonseca A, Baudet BA (2012) Effect of the porosity/cement ratio on the compression of cemented soil. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 138:1422–1426
Rücknagel J, Hofmann B, Paul R, Christen O, Hülsbergen KJ (2007) Estimating precompression stress of structured soils on the basis of aggregate density and dry bulk density. Soil Tillage Res 92:213–220
Rücknagel J, Brandhuber R, Hofmann B, Lebert M, Marschall K, Paul R, Stock O, Christen O (2010) Variance of mechanical precompression stress in graphic estimations using the Casagrande method and derived mathematical models. Soil Tillage Res 106:165–170
Rücknagel J, Christen O, Hofmann B, Ulrich S (2012) A simple model to estimate change in precompression stress as a function of water content based on the basis of precompression stress at field capacity. Geoderma 177–178:1–7
Rücknagel J, Götze P, Hofmann B, Christen O, Marschall K (2013) The influence of soil gravel content on compaction behaviour and pre-compression stress. Geoderma 209–210:226–232
Saffih-Hdadi K, Défossez P, Richard G, Cui YJ, Tang AM, Chaplain V (2009) A method for predicting soil susceptibility to the compaction of surface layers as a function of water content and bulk density. Soil Tillage Res 105:96–103
Salire EV, Hammel JE, Hardcastle JH (1994) Compression of intact subsoils under short-duration loading. Soil Tillage Res 31:235–248
Sánchez-Girón A, Andreu E, Hernanz JL (1998) Response of five types of soil to simulated compaction in the form of confined uniaxial compression tests. Soil Tillage Res 48:37–50
Santagata M, Bobet A, Johnston CT, Hwang J (2008) One-dimensional compression behavior of a soil with high organic matter content. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 134(1):1–13
Shipton B, Coop MR (2012) On the compression behaviour of reconstituted soils. Soils Found 52(4):668–681
Soane BD (1990) The role of organic matter in soil compactibility: a review of some practical aspects. Soil Tillage Res 16:179–201
Tang A-M, Cui Y-J, Eslami J, Défossez P (2009) Analysing the form of the confined uniaxial compression curve of various soils. Geoderma 148:282–290
Thibodeau S, Alamdari H, Ziegler DP, Fafard M (2014) New insight on the restructuring and breakage of particles during uniaxial confined compression tests on aggregates of petroleum coke. Powder Technol 253:757–768
Trade Standard of P.R. China SL237-006 (1999) Standard method for particle size distribution of soils. In specification of soil test. The Ministry of Water Resources of P.R. China, Beijing (in Chinese)
Trade Standard of P.R. China SL237-015 (1999) Standard method for one-dimensional consolidation properties of soils. In specification of soil test. The Ministry of Water Resources of P.R. China, Beijing (in Chinese)
Ueda T, Matsushima T, Yamada Y (2011) Effect of particle size ratio and volume fraction on shear strength of binary granular mixture. Granular Matter 13:731–742
van den Akker JJH (2004) SOCOMO: a soil compaction model to calculate soil stresses and the subsoil carrying capacity. Soil Tillage Res 79:113–127
Wang J-J (2010) Behaviour of an over-length pile in layered soils. Geotech Eng ICE 163(5):257–266
Wang J-J (2014) Hydraulic fracturing in earth-rock fill dams. John Wiley & Sons Singapore Pte Ltd and China Water & Power Press, Singapore
Wang J-J, Lin X (2007) Discussion on Determination of critical slip surface in slope analysis. Géotechnique 57(5):481–482
Wang J-J, Liu Y-X (2010) Hydraulic fracturing in a cubic soil specimen. Soil Mech Found Eng 47(4):136–142
Wang J-J, Zhu J-G, Chiu CF, Chai H-J (2007a) Experimental study on fracture behavior of a silty clay. Geotech Test J 30(4):303–311
Wang J-J, Zhu J-G, Chiu CF, Zhang H (2007b) Experimental study on fracture toughness and tensile strength of a clay. Eng Geol 94(1–2):65–75
Wang J-J, Liu F-C, Ji C-L (2008a) Influence of drainage condition on Coulomb-type active earth pressure. Soil Mech Found Eng 45(5):161–167
Wang J-J, Zhang H-P, Chai H-J, Zhu J-G (2008b) Seismic passive resistance with vertical seepage and surcharge. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 28(9):728–737
Wang J-J, Zhang H-P, Liu M-W, Chen Y-Y (2012a) Seismic passive earth pressure with seepage for cohesionless soil. Mar Georesour Geotechnol 30(1):86–101
Wang J-J, Zhang H-P, Zhang L, Liang Y (2012b) Experimental study on heterogeneous slope responses to drawdown. Eng Geol 147–148:52–56
Wang J-J, Zhang H-P, Deng D-P, Liu M-W (2013a) Effects of mudstone particle content on compaction behavior and particle crushing of a crushed sandstone–mudstone particle mixture. Eng Geol 167:1–5
Wang J-J, Zhang H-P, Tang S-C, Liang Y (2013b) Effects of particle size distribution on shear strength of accumulation soil. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 139(11):1994–1997
Wang J-J, Zhang H-P, Zhang L, Liang Y (2013c) Experimental study on self-healing of crack in clay seepage barrier. Eng Geol 159:31–35
Wang J-J, Zhao D, Liang Y, Wen H-B (2013d) Angle of repose of landslide debris deposits induced by 2008 Sichuan Earthquake. Eng Geol 156:103–110
Wang J-J, Liang Y, Zhang H-P, Wu Y, Lin X (2014a) A loess landslide induced by excavation and rainfall. Landslides 11(1):141–152
Wang J-J, Liu M-W, Zhang H-P, Wang D-Y, Deng W-J (2014b) Effects of wetting on mechanical behavior and particle crushing of a mudstone particle mixture. In: Proceedings of the 6th international conference on unsaturated soils, UNSAT 2014, vol 1, p 233–238
Wang J-J, Qiu Z-F, Deng W-J (2014c) Shear strength of a crushed sandstone-mudstone particle mixture. Int J Arch Eng Technol 1:33–37
Wang J-J, Qiu Z-F, Deng W-J, Zhang H-P (2014d) Effects of mudstone particle content on shear strength of a crushed sandstone–mudstone particle mixture. Mar Georesour Geotechnol. doi:10.1080/1064119X.2014.961621
Wang J-J, Yang Y, Zhang H-P (2014e) Effects of particle size distribution on compaction behavior and particle crushing of a mudstone particle mixture. Geotech Geol Eng 32(4):1159–1164
Wang J-J, Zhang H-P, Deng D-P (2014f) Effects of compaction effort on compaction behavior and particle crushing of a crushed sandstone-mudstone particle mixture. Soil Mech Found Eng 51(2):67–71
Wang J-J, Zhang H-P, Liu M-W, Deng D-P (2014g) Compaction behaviour and particle crushing of a crushed sandstone particle mixture. Eur J Environ Civil Eng 18(5):567–583
Wang J-J, Cheng Y-Z, Zhang H-P, Deng D-P (2015a) Effects of particle size on compaction behavior and particle crushing of crushed sandstone–mudstone particle mixture. Environ Earth Sci 73(12):8053–8059
Wang J-J, Zhang H-P, Tang S-C, Liang Y (2015b) Closure to “Effects of particle size distribution on shear strength of accumulation soil” by Jun-Jie Wang, Hui-Ping Zhang, Sheng-Chuan Tang, and Yue Liang. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 141(1):07014031
Wang J-J, Zhang H-P, Wen H-B, Liang Y (2015c) Shear strength of an accumulation soil from direct shear test. Mar Georesour Geotechnol 33(2):183–190
Xiao Y, Liao J (2015) Discussion of “effects of particle size distribution on shear strength of accumulation soil” by Jun-Jie Wang, Hui-Ping Zhang, Sheng-Chuan Tang, and Yue Liang. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 141(1):07014030
Xiao Y, Liu H, Chen Y, Chu J (2014a) Influence of intermediate principal stress on the strength and dilatancy behavior of rockfill material. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 140(11):04014064
Xiao Y, Liu H, Chen Y, Zhang W (2014b) Particle size effects in granular soils under true triaxial conditions. Geotechnique 64(8):667–672
Yan Z-L, Wang J-J, Chai H-J (2010) Influence of water level fluctuation on phreatic line in silty soil model slope. Eng Geol 113(1–4):90–98
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 51479012, the National Science and Technology Support Program of China under Grant No. 2015BAK09B01, and from the Chongqing Science & Technology Commission of China under Grant Nos. cstc2013jcyja30009 and cstc2014jcyjA30003, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, JJ., Qiu, ZF., Hao, JY. et al. Compression characteristics of an artificially mixed soil from confined uniaxial compression tests. Environ Earth Sci 75, 152 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5042-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5042-y