Abstract
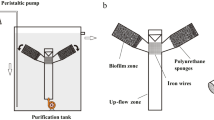
Biofilms, abundantly attached on the surfaces of multiple media (such as pebbles and aquatic plants) in rivers or lakes reusing reclaimed water (RW), are of great significance to contaminants’ self-purification of water bodies. In this paper, the nitrogen and phosphate adsorption characteristics of such biofilms were studied by the batch method, using biofilms cultivated under an outdoor simulative process. Two types of RW treated by anaerobic-anoxic-oxic process (A2/O) and cyclic activated sludge technology (CASS), and surface water (NW) were chosen as the experimental water bodies. And the glasses of surface roughness of 0.1, 1.0, and 10 μm, respectively, were used as the substrates, where the biofilms adhere to them. The results indicated that the isothermal adsorption of biofilms for ammonia nitrogen and phosphates was proved to conform to the Langmuir and the Freundlich equation, whereas the adsorption capacity was significantly lower than that of soils and sediments limited by the pore structure and surface area. There were also significant differences between the adsorption behaviors. The distribution coefficients were ranked as K dCASS > K dNW > K 2dA /O, and the maximum adsorption capacities (S m), under these conditions were ranked as S 2mA /O > S mNW > S mCASS, while other parameters did not change regularly. Extracellular polymers (\(R^{ 2}_{\text{N}}\) = 0.95**, \(R^{ 2}_{\text{p}}\) = 0.84**), iron oxides (\(R^{ 2}_{\text{N}}\) = 0.86**, \(R^{ 2}_{\text{p}}\) = 0.68*), and aluminum oxides (\(R^{ 2}_{\text{N}}\) = 0.95**, \(R^{ 2}_{\text{p}}\) = 0.81**) in the biofilms had a significant impact on the S m for ammonia and phosphates. The roughness of media surfaces also had a considerable influence on the S m, which was in the order of S m10μm > S m0.1μm > S m1.0μm, whereas other parameters did not change regularly. The research aimed to provide theory reference for in situ decontamination of RW in rivers or lakes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behra R, Landwehrjohann R, Vogal L et al (2002) Copper and zinc content of periphyton from two rivers as a function of dissolved metal concentration. Aquat Sci 64:300–306. doi:10.1007/s00027-002-8074-9
Cao Z, Li CK (1988) Phosphorus sorption and desorption isotherms for some loessial soils of north china plain. Chin Acta Pedologica Sinica 25(3):218–226
Chen S (2006) Characteristics and efficiency investigation of suspended carrier biofilm for treating highly concentrated organic wastewater. Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin
Costerton JW, Stewat PS, Greenberg EP (1999) Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Sci 284:1318–1322. doi:10.1126/science.284.5418.1318
Farag AM, Woodward DF, Goldstein JM, Brumbaugh W, Meyer JS (1998) Concentrations of metals associated with mining waste in sediments, biofilm, benthic macroinvertebrates and fish from the Coeur d’Alene River Basin, Idaho. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 34:119–127
Headley JV, Gandrass J, Kuballa J et al (1998) Rates of sorption and partitioning of contaminants in river biofilm. Environ Sci Technol 32:3968–3973. doi:10.1021/es980499l
Jeong YS, Jong SC (2006) Simultaneous removal of COD, thiocyanate, cyanide and nitrogen from coal process wastewater using fluidized biofilm process. Process Biochem 41:141–1147. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.12.010
Jiang GH (2004) Discussion about NH4 + −N adsorptive ability in soils. Chin J Chang’an Univer 21(2):32–38
Jiang M, Liu JJ, Hu WT et al (2012) Preliminary study of characteristics of phosphorus adsorption on sediment of dishui lake. Chin Environ Sci Technol 35(5):18–23. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2012.05.005
Koeadagistan B, Koeadagistan E, Topcu N, Demircioğlua N (2004) Wastewater treatment with combined upflow anaerobic fixed-bed and suspended aerobic reactor equipped with a membrane unit. Process Biochem 40:177–182. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2003.11.055
Kurniawan A, Yamamoto TY, Tsuchiya YK, Morisaki H (2012) Analysis of the ion adsorption-desorption characteristics of biofilm matrices. Microbes Environ 27(4):399–406. doi:10.1264/jsme2.ME11339
Lawrence JR, Kopf G, Headley JV (2001) Sorption and metabolism of selected herbicides in river biofilm communities. Can J Microbiol 47:634–641
Lenardos N, Lucas I (2000) The nutritional value of algae grown under different culture conditions for Mytilus edulis L. Larvae. Aquaculture 182:301–315. doi:10.1016/S0044-8486(99)00269-0
Li Y, Dong DM, Hua XY et al (2002) Comparison of Pb and Cd adsorption to surface coatings developed in the aquatic environment of wetland. Chin Scientia Geographica Sincia 22(4):445–448
Li YK, Yang PL, Liu PB et al (2012) Environmental impact of reclaimed water to Yongding river for ecological use and key technology study. China Water Res 5:30–34
Liang MC, Wang TZ, Li YK et al (2013) Structural and fractal characteristics of biofilm attached on the surfaces of aquatic plant and gravels in the river and lake reusing reclaimed wastewater. Environ Earth Sci 70:2319–2333. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2285-3
Liang MC, Ning ZG, Li YK et al (2014) Dynamic biofilm component in reclaimed water during rapid growth period. Environ Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3717-4
Mowla D, Ahmadi M (2007) Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of Biodegradation of Hydrocarbon Polluted Water in a three Phase Fluidized-bed Bioreactor with PVC Biofilm Support. Biochem Eng J 36:147–156. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2007.02.031
OECD (2000) OECD guidelines for testing of chemicals, test guideline 106: adsorption/desorption using a batch equilibrium method. OECD, Revised Draft Document, Paris, pp 1–45
Opuwaribo E, Odu CTI (1978) Ammonium Fixed in Nigerian soil: 4. The effects of, time, potassium and wet and dry cycles on ammonium fixation. Soil Sci 125:137–145. doi:10.1097/00010694-197803000-00003
Rao TS, Rani PG, Venugopalan VP, Nair KVK (1999) Biofilm formation in a fresh water environment under photic and aphotic conditions. Biofouling 11(4):265–282. doi:10.1080/08927019709378336
Raunkjær K, Hvitved-Jacobson T, Nielson PH (1994) Measurement of pools of protein, carbohydrate and lipid in domestic wastewater. Water Res 28:251–262. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(94)90261-5
Rusten B, Johnson CH, Devall S, Davoren D, Cashiont BS (1999) Biological pretreatment of a chemical plant wastewater in high-rate moving bed biofilm reactors. Water Sci Technol 39:257–264. doi:10.1016/S0273-1223(99)00286-3
Suvilampi J, Lehtomaki A, Rintala J (2003) Comparison of laboratory-scale thermophilic biofilm and activated sludge processes integrated with a mesophilic activated sludge process. Bioresource Technol 88(3):207–214. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(03)00006-3
Tatlor GT, Zheng D, Lee M, Troy PJ, Gyananath G, Sharma SK (1997) Influence of surface properties on accumulation of conditioning films and marine bacterial on substrata exposed to oligotrophic water. Biofouling 11(1):31–57. doi:10.1080/08927019709378319
Wang WJ, Wang WH, Zhang XL, Wang DH (2002) Adsorption of p-chlorophenol by biofilm components. Water Res 36:551–560. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00267-6
Wimpenny J (1996) Ecological determinants of biofilm formation. Biofouling 10:43–63. doi:10.1080/08927019609386270
Zhai LH, Liu HL, Xu HD, Xi BD (2007) Property of ammonium adsorption on sediments in ditches and adjacent soils. Chin J Environ Sci 28(8):1770–1773
Zhang JL (2008) Studies on the characteristics and purification capacity of substrate biofilms in constructed wetland. Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences
Zhang R, Han ZY, Chen CJ et al (2011) Microstructure and microbial ecology of biofilm in the bioreactor for nitrogen removing from wastewater: a review: Chinese. J Ecol 30(11):2628–2636
Zhao W, Li YK, Zhao Q et al (2013) Adsorption and desorption characteristics of ammonium in eight loams irrigated with reclaimed wastewater from intensive hogpen. Environ Earth Sci 69:41–49. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-1932-4
Zhou CF, Ning ZG, Zhao W et al (2013) Impact of DOM in reclaimed water on nitrogen-phosphate adsorption in sediments. Appl Mechan Mater. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.395-396.678
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for financial support from the National Natural Science Fund of China (No. 51321001), Key Project of the Beijing Eleventh-Five Year Research Program (No. D090409004009004), Special Fund for Water Conservancy scientific Research in the Public Interest (No. 201001067).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zigong Ning, Mingchao Liang, Zhenhua Wang and Yunkai Li equally contributed to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ning, Z., Liang, M., Wang, Z. et al. Nitrogen and phosphate adsorption on biofilms in reclaimed water. Environ Earth Sci 74, 451–461 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4053-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4053-z