Abstract
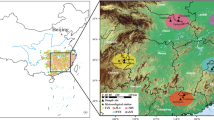
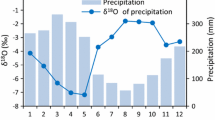
This study was conducted to examine the spatial variability in hydrogen and oxygen isotopic composition of Korean Red Pine (Pinus densiflora S. et Z.) and to explore the possibility of using wood isotopic composition as an indicator of geographical origin. Wood specimens were collected from 13 locations in South Korea, and isotopic composition was analyzed for the bulk wood and α-cellulose extracts. The isotopic composition of pines varied with growing location. δ2H and δ18O values of both bulk woods and α-cellulose decreased toward the high-latitude and inland areas, largely following variability in the isotopic composition of surface waters. Geographical variability was better represented by the bulk wood isotopic composition than by α-cellulose. Korean Red Pine is a common construction material that is threatened by illegal cutting and forgeries of origin. Therefore, the results obtained in this study provide a possible isotopic method for the tracing of wood origin.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbour MM (2007) Stable oxygen isotope composition of plant tissue: a review. Funct Plant Biol 34:83–94
Barbour MM, Roden JS, Farquhar GD, Ehleringer JR (2004) Expressing leaf water and cellulose oxygen isotope ratios as enrichment above source water reveals evidence of a Péclet effect. Oecologia 138:426–435
Boner M, Förstel H (2004) Stable isotope variation as a tool to trace the authenticity of beef. Anal Bioanal Chem 378:301–310
Bong YS, Shin WJ, Lee AR, Kim YS, Kim K, Lee KS (2010) Tracing the geographical origin of beefs being circulated in Korean markets based on stable isotopes. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 24:155–159
Bong YS, Gautam MK, La MR, Lee KS (2012) Geographic origins of Korean and Chinese Kimchi determined by multiple elements. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 76:2096–2100
Bong YS, Song BY, Gautam MK, Jang CS, An HJ, Lee KS (2013) Discrimination of the geographic origin of cabbages. Food Control 30:626–630
Borella S, Leuenberger M (1998) Reducing uncertainties in δ13C analysis of tree rings: pooling, milling, and cellulose extraction. J Geophys Res 103(D16):19519–19526
Bowen GJ, Wassenaar LI, Hobson KA (2005) Global application of stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes to wildlife forensics. Oecologia 143:337–348
Brendel O, Iannetta PM, Stewart D (2000) A rapid and simple method to isolate pure alpha-cellulose. Phytochem Anal 11:7–10
Camin F, Wietzerbin K, Cortes AB, Haberhauer G, Lees M, Versini G (2004) Application of multielement stable isotope ratio analysis to the characterization of French, Italian, and Spanish cheeses. J Agric Food Chem 52:6592–6601
Camin F, Bontempo L, Heinrich K, Horacek M, Kelly SD, Schlicht C, Thomas F, Monahan FJ, Hoogewerff J, Rossmann A (2007) Multi-element (H, C, N, S) stable isotope characteristics of lamb meat from different European regions. Anal Bioanal Chem 389:309–320
Christoph N, Baratossy G, Kubanović V, Kozina B, Rossman A, Schlicht C, Voerkelius S (2004) Possibilities and limitations of wine authentication using stable isotope ratio analysis and traceability. Part 2: wines from Hungary, Croatia and other European countries. Mitteilungen Klosterneuburg 54:144–158
Chung TH, Lee WT (1965) Forest zone of Korea and proper site for tree. Bull Sungkyunwan Univ 10:329–435
Clark ID, Fritz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton
Critchfield WB, Little EL (1966) Geographic distribution of the pines of the world, vol 991. US Dept of Agric, Misc Publication, Washington, DC
da Sternberg LDS, Deniro MJ, Savidge RA (1986) Oxygen isotope exchange between metabolites and water during biochemical reactions leading to cellulose synthesis. Plant Physiol 82:423–472
Dansgaard W (1964) Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 16:436–468
Day MP, Zhang BL, Martin GJ (1994) The use of trace element data to complement stable isotope methods in the characterization of grape musts. Am J Enol Vitic 45:79–85
Ehleringer JR, Bowen GJ, Chesson LA, West AG, Podlesak DW, Cerling TE (2008) Hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios in human hair are related to geography. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:2788–2793
Epstein S, Yapp CJ (1977) Isotope tree thermometers. Nature 266:477–478
Epstein S, Yapp CJ, Hall JH (1976) The determination of D/H ratio of non-exchangeable hydrogen in cellulose extracted from aquatic and land plants. Earth Planet Sci Lett 30:241–251
Feng X, Epstein S (1994) Climatic implications of an 8,000-year hydrogen isotope time series from bristlecone pine trees. Science 265:1079–1081
Fraser I, Meier-Augenstein W, Kalin RM (2006) The role of stable isotopes in human identification: a longitudinal study into the variability of isotopic signals in human hair and nails. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 20:1109–1116
Gaudinski JB, Dawson TE, Quideau S, Schuur EA, Roden JS, Trumbore SE, Sandquist DR, Oh SW, Wasylishen RE (2005) Comparative analysis of cellulose preparation techniques for use with 13C, 14C, and 18O isotopic measurements. Anal Chem 77:7212–7224
Gray J, Thompson P (1976) Climatic information from 18O/16O ratios of cellulose in tree rings. Nature 262:481–482
Griffiths H (1998) Stable isotopes: integration of biological, ecological and geochemical processes. Bios, Oxford
Hobson KA, Bowen GJ, Wassenaar LI, Ferrand Y, Lormee H (2004) Using stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope measurements of feathers to infer geographical origins of migrating European birds. Oecologia 141:477–488
Horacek M, Jakusch M, Krehan H (2009) Control of origin of larch wood: discrimination between European (Austrian) and Siberian origin by stable isotope analysis. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 23:3688–3692
Jeong CH, Koh YK, Shin SH, Nagao K, Kim KH, Kim GY (2009) Hydrochemistry and noble gas origin of hot spring water of Icheon and Pocheon area in Korea. J Eng Geol 19:529–541
Keppler F, Harper DB, Kalin RM, Meier-Augenstein W, Farmer N, Davis S, Schmidt HL, Brown DM, Hamilton JTG (2007) Stable hydrogen isotope ratios of lignin methoxyl groups as a paleoclimate proxy and constraint of the geographical origin of wood. New Phytol 176:600–609
Kim KH, Nakai N (1988) Isotopic compositions of precipitations and groundwaters in South Korea. J Geol Soc Korea 24:37–46
Koh YK, Yun ST, Kim CS, Bae DS, Park SS (2001) Geochemical Evolution and Deep Environment of the geothermal waters in the Bugok area: reconsideration on the origin of sulfate-type geothermal water. Econ Environ Geol 34:329–343
Korea Geography Information Research Society (2006) Physical geography dictionary. Hanul Publishing Group, Korea, p 122
Krivan V, Barth P, Morales AF (1993) Multielement analysis of green coffee and its possible use for the determination of origin. Mikrochim Acta 110:217–236
Kruskal WH, Wallis WA (1953) Errata: use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. J Am Stat Assoc 48:907–911
Lee KS, Lee CB (1999) Oxygen and hydrogen isotopic composition of precipitation and river water in South Korea. J Geol Soc Korea 35:73–84
Lee AR, Gautam M, Kim J, Shin WJ, Choi MS, Bong YS, Hwang GS, Lee KS (2011) A multianalytical approach for determining the geographical origin of Ginseng using strontium isotopes, multielements, and 1H NMR analysis. J Agric Food Chem 59:8560–8567
Mann HB, Whitney DR (1947) On a test of whether one of two random variables is stochastically larger than the other. Ann Math Stat 18:50–60
McCarroll D, Loader NJ (2004) Stable isotopes in tree rings. Quat Sci Rev 23:771–801
Mirov NT (1967) The genus pinus. The Ronald Press, New York, pp 281–282
Nachar N (2008) The Mann–Whitney U: a test for assessing whether two independent samples come from the same distribution. Tutor Quant Methods Psychol 4:13–20
Pillonela L, Badertschera R, Froidevauxb P, Haberhauerc G, Hölzld S, Hornd P, Jakobe A, Pfammatterf E, Piantinig U, Rossmannh A, Tabacchii R, Bosset JO (2003) Stable isotope ratios, major, trace and radioactive elements in emmental cheeses of different origins. LWT-Food Sci Technol 36:615–623
Richardson DM (2000) Ecology and biogeography of pinus. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Roden JS, Lin G, Ehleringer JR (2000) A mechanistic model for interpretation of hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios in tree-ring cellulose. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64:21–35
Rossmann A, Haberhauer G, Hölzl S, Horn P, Pichlmayer F, Voerkelius S (2000) The potential of multielement stable isotope analysis for regional origin assignment of butter. Eur Food Res Technol 211:32–40
Saurer M, Robertson I, Siegwolf R, Leuenberger M (1998) Oxygen isotope analysis of cellulose: an interlaboratory comparison. Anal Chem 70:2074–2080
Wilson AT, Grinsted MJ (1977) 12C/13C in cellulose and lignin as palaeothermometers. Nature 265:133–135
Yakir D, da Sternberg SLL (2000) The use of stable isotopes to study ecosystem gas exchange. Oecologia 123:297–311
Yakir D, DeNiro MJ (1990) Oxygen and hydrogen isotope fractionation during cellulose metabolism in Lemna gibba L. Plant Physiol 93:325–332
Yapp CJ, Epstein S (1982) A reexamination of cellulose carbon-bound hydrogen δD measurements and some factors affecting plant–water D/H relationships. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 46:955–965
Yun ST, Chae GT, Koh YK, Kim SR, Choi BY, Lee BH, Kim SY (1998) Hydrogeochemical and environmental isotope study of groundwaters in the Pungki area. J Korean Soc Groundw Environ 5:177–191
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (MSIP) (2013, University-Institute cooperation program), by the NAP (National Agenda Project) of the Korea Research Council of Fundamental Science and Technology, and by KBSI grant (C34700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S., Park, B.S., Lee, D. et al. Spatial variability in hydrogen and oxygen isotopic composition of Korean Red Pine and its implication for tracing wood origin. Environ Earth Sci 73, 8045–8052 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3960-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3960-8