Abstract
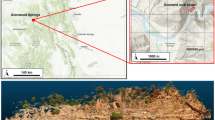
Underground coal mining produces ground subsidence that adversely impacts the environment. Huainan coalfield, one of the largest coalfields in East China, experiences fast ground subsidence that restricts agricultural, urban and rural developments in this region. We used stacking and the small baseline subset interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) techniques to perform a spatio-temporal analysis of ground subsidence in Huainan coalfield caused by underground coal mining activities. Fourteen L-band ALOS PALSAR images acquired during 2007–2010 were used to retrieve high-resolution and high-precision time series of ground deformation and the mean deformation rate. The results show that subsidence with a rate of up to 15 cm/year is widely spread over the studied area in response to mining operation. In regions where mining lasted for many years, ground subsidence continues at a steady rate during the entire observation period. In regions of recent (i.e., since 2007–2009) mining activities, ground subsidence is rapidly accelerating. Accumulated subsidence already caused submerging of the agriculture lands, limiting further mining activities and farming. The InSAR results are consistent with the ground leveling measurements and observations. It is confirmed that the L-band InSAR can be successfully utilized for mapping long-term subsidence in Huainan coalfield in China caused by underground coal mining activities.












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Longwall Mining, http://www.umwa.org/?q=content/longwall-mining.
GAMMA SAR processing software, http://www.gamma-rs.ch/software.
References
Abdikan S, Arikan M, Sanli FB, Cakir Z (2014) Monitoring of coal mining subsidence in peri-urban area of Zonguldak city (NW Turkey) with persistent scatterer interferometry using ALOS-PALSAR. Environ Earth Sci 71(9):4081–4089
Berardino P, Fornaro G, Lanari R, Sansosti E (2002) A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 40(11):2375–2383
Bian Z, Inyang HI, Daniels J, Otto F, Struthers S (2010) Environmental issue from coal mining and their solutions. Min Sci Technol 20(2):215–223
Chen C (2012) Environment problems and comprehensive management in Huainan coal mining area. Resour Inhabitant Environ 11:61–62 [in Chinese]
Costantini M, Rosen P (1999) A generalized phase unwrapping approach for sparse data. In Proc. Int. Geosci. Remote Sensing Symp., Hamburg, Germany, pp 267–269
Cuenca MC, Hooper AJ, Hanssen RF (2013) Surface deformation induced by water influx in the abandoned coal mines in Limburg, The Netherlands observed by satellite radar interferometry. J Appl Geophys 88:1–11
Dong S, Samsonov S, Yin H, Ye S, Cao Y (2014) Time-series analysis of subsidence associated with rapid urbanization in Shanghai, China measured with SBAS InSAR method. Environ Earth Sci 72(3):677–691
Düzgün HS, Demirel N (2011) Remote sensing of the mine environment. CRC Press, USA, p 208
Ferretti A, Prati C, Rocca F (2001) Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 39(1):8–20
Gupta M, Mohanty KK, Kumar D, Banerjee R (2014) Monitoring surface elevation changes in Jharia coalfield, India using synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Environ Earth Sci 71(6):2875–2883
He XW, Jiang R, Xu R, Xu GQ, Wang WN (2010) Quality analysis and evaluation of shallow groundwater in Huainan coal mine. J China Hydrol 30(4):18–22 [in Chinese]
Hu Z, Wu X (2013) Optimization of concurrent mining and reclamation plans for single coal seam: a case study in northern Anhui, China. Environ Earth Sci 68(5):1247–1254
Hu Z, Hu F, Li J, Li H (1997) Impact of coal mining subsidence on farmland in eastern China. Int J Surf Min Reclam Environ 11(2):91–94
Hu RL, Yue ZQ, Wang LC, Wang SJ (2004) Review on current status and challenging issues of land subsidence in China. Eng Geol 76(1–2):65–77
Jiang L, Lin H, Ma J, Kong B, Wang Y (2011) Potential of small-baseline SAR interferometry for monitoring land subsidence related to underground coal fires: Wuda (Northern China) case study. Remote Sens Environ 115(2):257–268
Karaman A, Seyhan T, Isik MF (2013) Detecting the footprint of a longwall mine panel claimed to infringe on a permit boundary at the Soma-Darkale coalfield (Manisa, Turkey) using surface fractures and microgravity measurements. Environ Earth Sci 70(4):1895–1902
Lanari R, Casu F, Manzo M, Zeni G, Berardino P, Manunta M, Pepe A (2007) An overview of the small baseline subset algorithm: a DInSAR technique for surface deformation analysis. Pure Appl Geophys 164:637–661
Li XL, Guo J, Hu AY, Chen JX (2006) Analysis and countermeasures on harness of subsidence in Huainan coal mine. Resour Ind 8(2):75–77 [in Chinese]
Liu J (2008) An analysis of the current situation for resource-based cities and the countermeasures for its sustainable development. J Jixi Univ 8(4):41–43 [in Chinese]
Lopez-Quiroz P, Doin MP, Tupin F, Briole P, Nicolas JM (2009) Time series analysis of Mexico city subsidence constrained by radar interferometry. J Appl Geophys 69(1):1–15
Marschalko M, Yilmaz I, Lamich D, Drusa M, Kubeckova D, Penaz T, Burkotova T, Slivka V, Bednarik M, Krcmar D, Duraj M, Sochorkova A (2014) Unique documentation, analysis of origin and development of an undrained depression in a subsidence basin caused by underground coal mining (Kozinec, Czech Republic). Environ Earth Sci 72(1):11–20
Massonnet D, Feigl KL (1998) Radar interferometry and its application to changes in the Earth’s surface. Rev Geophys 36(4):441–500
Massonnet D, Rossi M, Carmona C, Ardagna F, Peltzer G, Feigl K, Rabaute T (1993) The displacement field of Landers earthquake mapped by radar interferometry. Nature 364:138–142
Ng AHM, Ge L, Yan Y, Li X, Chang HC (2010) Mapping accumulated mine subsidence using small stack of SAR differential interferograms in the Southern coalfield of New South Wales, Australia. Eng Geol 115:1–15
Perissin D, Wang Z, Lin H (2012) Shanghai subway tunnels and highways monitoring through cosmo-skymed persistent scatterers. J Photogramm Remote Sens 73:58–67
Perski Z, Hanssen R, Wojcik A, Wojciechowski T (2009) InSAR analysis of terrain deformation near the Wieliczka salt mine, Poland. Eng Geol 106(1–2):58–67
Samsonov S (2010) Topographic correction for ALOS PALSAR intergerometry. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 48(7):3020–3027
Samsonov S, Tiampo K, Gonzalez PJ, Manville V, Jolly G (2010) Ground deformation occurring in the city of Auckland, New Zealand, and observed by Envisat interferometric synthetic aperture radar during 2003–2007. J Geophys Res 115(B8):B08410
Samsonov S, van der Koij M, Tiampo K (2011) A simultaneous inversion for deformation rates and topographic errors of DInSAR data utilizing linear least square inversion technique. Comput Geosci 37(8):1083–1091
Samsonov S, d’Oreye N, Smets B (2013a) Ground deformation associated with post-mining activity at the French–German border revealed by novel InSAR time series method. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 23:142–154
Samsonov S, Gonzalez P, Tiampo K, d’Oreye N (2013b) Spatio-temporal analysis of ground deformation occurring near Rice Lake, Saskatchewan, and observed by Radarsat-2 DInSAR during 2008–2011. Can J Remote Sens 39(1):27–33
Samsonov S, d’Oreye N, Gonzalez PJ, Tiampo KF, Ertolahti L, Clague JJ (2014a) Rapidly accelerating subsidence in the Greater Vancouver region from two decades of ERS-ENVISAT-RADARSAT-2 DInSAR measurements. Remote Sens Environ 143(5):180–191. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2013.12.017. ISSN 0034-4257
Samsonov S, Gonzalez P, Tiampo K, d’Oreye N (2014b) Modeling of fast ground subsidence observed in southern Saskatchewan (Canada) during 2008–2011. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 14:247–257
Sandwell DT, Price EJ (1998) Phase gradient approach to stacking interferograms. J Geophys Res 103:30183–30204
Usai S (2003) A least squares database approach for SAR interferometric data. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 41(4):753–760
Wang GQ, Li YX, Wu DX, Ge XG, Liu Y, Ye CH (2002) Characteristics of groundwater resources and water environmental problems in Anhui Province. J Nat Resour 17(2):234–239 [in Chinese]
Wang ZL, Zhang QB, Li R (2009) Study on flood resources of coal mining depressed area. J Nat Resour 24(7):1156–1162
Wu Q, Pang J, Qi S, Li Y, Han C, Liu T, Huang L (2009) Impacts of coal mining subsidence on the surface landscape in Longkou city, Shandong province of China. Environ Earth Sci 59(4):783–791
Wyss M (2001) Locked and creeping patches along the Hayward fault, California. Geophys Res Lett 28(18):3537–3540
Xu L (2009) Study on water quality influence factor and pollution comprehensive assessment method of coal mine subsided water area, Anhui University of Science and Technology, Anhui, China
Yang M, Liu G, Sun R, Chou CL, Zheng L (2012) Characterization of intrusive rocks and REE geochemistry of coals from the Zhuji Coal Mine, Huainan Coalfield, Anhui, China. Int J Coal Geol 94:283–295
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key Technology R & D Program of China (No. 2012BAC10B02), National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC: 41372353), China Scholarship Council (CSC) and Huainan Mining Group (No. HNKY-JT-JS-(2013)-004). The ALOS PALSAR data were provided by the Global Earth Observation Grid (GEO Grid, http://www.geogrid.org/en/index.html). ASTER GDEM was provided by METI and NASA. Images were plotted with GMT software. We would like to thank four anonymous reviewers for their comments that helped us improve our paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, S., Samsonov, S., Yin, H. et al. Spatio-temporal analysis of ground subsidence due to underground coal mining in Huainan coalfield, China. Environ Earth Sci 73, 5523–5534 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3806-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3806-4