Abstract
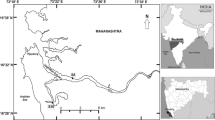
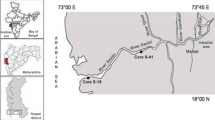
Two mudflat sediment cores collected from a sub-channel (S-61) and the main channel (S-60) of a tropical wetland, along central west coast of India, were investigated for recent changes in depositional environment using geochemical (sediment grain size, total organic carbon, total nitrogen, carbon/nitrogen ratio (TOC/TN), selected metals and pH) and diatom records. The sub-channel (S-61) represents river environment which opens into main channel (S-60) which represents marine environment being close to the sea. We report a transition from river-dominated to marine-dominated depositional environment over the years. The relatively higher sand percentage together with elevated carbon/nitrogen ratio and predominance of freshwater diatoms suggested greater river runoff in the past while marine influence is supported by decrease in TOC/TN ratio and increased dominance of marine diatoms in recent years. In the main channel (S-60), distribution of metals is regulated by organic matter (total nitrogen and total organic carbon) while in the sub-channel (S-61), Fe–Mn oxyhydroxides play a significant role in trace metal distribution. The highest numbers of diatoms were recorded in the sub-channel (S-61) which is also characterized by higher total nitrogen concentration. Geochemical and diatom signatures thus have helped to infer spatial and temporal variations in depositional environment.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida SFPD, Gil MCP (2001) Ecology of freshwater diatoms from the central region of Portugal. Cryptogamie Algol 22(1):109–126
Aloupi M, Angelidis MO (2002) The significance of coarse sediments in metal pollution studies in the coastal zone. Water Air Soil Pol 133:121–131
Ayyamperumal T, Jonathan MP, Srinivasalu S, Armstrong-Altrin JS, Ram-Mohan V (2006) Assessment of acid leachable trace metals in sediment cores from River Uppanar, Cuddalore, Southeast coast of India. Environ Pollut 143:34–45
Battarbee RW (1986) Diatom analysis. In: Berglund BE (ed) Handbook of holocene palaeoecology and palaeohydrology. Wiley, Chichester, pp 527–570
Bianchi TS (2007) Biogeochemistry of estuaries. Oxford University Press, New York
Borole DV (1988) Clay sediment accumulation rates on the Monsoon-dominated western continental shelf and slope region of India. Mar Geol 82:285–291
Chapman PM, Wang F (2001) Assessing sediment contamination in estuaries. Environ Toxicol Chem 20(1):3–12
Chatterjee M, Filho-Silva EV, Sarkar SK, Sella SM, Bhattacharya A, Satpathy KK, Prasad MVR, Chakraborty S, Bhattacharya BD (2007) Distribution and possible source of trace elements in the sediment cores of a tropical macrotidal estuary and their ecotoxicological significance. Environ Int 33:346–356
Clarke SJ, Wharton G (2001) Using macrophytes for the environmental assessment of rivers: the role of sediment nutrients R&D technical report E1-S01/TR
D’Costa PM, Anil AC (2010) Diatom community dynamics in a tropical, monsoon-influenced environment: west coast of India. Cont Shelf Res 30:1324–1337
Dalrymple RW, Choi K (2007) Morphologic and facies trends through the fluvial-marine transition in tide-dominated systems: a schematic framework for environmental and sequence-stratigraphic interpretation. Earth-Sci Rev 81:135–174
Das AK, Mukherjee S (2002) Study of weathering and erosional status of Basaltic rocks using remote sensing data. J Indian Soc Remote Sensing 30:3
Desikachary TV (1986) Atlas of diatoms 1–6. Madras Science Foundation Madras 809 plates
Federico II, Marcela E (2009) Stratigraphy, tectonic and paleogeography of the Loberia coastline, southeastern Buenos Aires. Rev Asoc Geol Argent 64(4):557–568
Fernandes L (2011) Enrichment and bioavailability of metals in sediments with time in Thane creek, Mumbai, India. In: National seminar on Modern and Palaeo sediments: implication to climate, water resources and environment changes & XXVIII. Conven Indian Assoc Sedimentologists 124–139
Folk RL (1968) Petrology of sedimentary rocks. Austin, Hemphills, p 177
Gajbhiye SN, Mustafa S, Metha P, Nair VR (1995) Assessment of biological characteristics on coastal environment of Murud (Maharashtra) during the oil spill (17 May 1993). Indian J Mar Sc 24:196–202
Gandhi HP (1956) A preliminary account of the soil diatom flora of Kolhapur. J Indian Bot Soc 35(4):402–408
Gattuso JP, Frankignoulle M, Wollast R (1998) Carbon and carbonate metabolism in coastal aquatic ecosystems. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 29:405–433
Gaudette HE, Flight WR, Toner L, Folger DW (1974) An inexpensive titration method for the determination of organic carbon in recent sediments. J Sediment Petrol 44:249–253
Gonzalves EA, Gandhi HP (1952) A systematic account of the diatoms of Bombay and Salsette-I. Ibid 31:117–151
Gonzalves EA, Gandhi HP (1953) A systematic account of the diatoms of Bombay and Salsette-II. Ibid 32:239–263
Gonzalves EA, Gandhi HP (1954) A systematic account of the diatoms of Bombay and Salsette-III. Ibid 33:239–263
Gopinathan CP (1975) On new distributional records of plankton diatoms from the Indian Seas. J Mar Biol Assoc India 17(1):223–240
Gopinathan CP (1984) A systematic account of the littoral diatoms of the southwest coast of India. J Mar Biol Assoc India 26(1):1–31
Hedges JI, Clark WA, Quay PD, Richey JE, Devol AH, De-Santos UM (1986) Compositions and fluxes of particulate organic material in the Amazon river. Limnol Oceanogr 31:717–738
IPCC (2007) The physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change
Jarvis IJ, Jarvis K (1985) Rare earth element geochemistry of standard sediments: a study using inductively coupled plasma spectrometry. Chem Geol 53:335–344
Kennish MJ (2002) Environmental threats and environmental future of estuaries. Environ Conserv 29:78–107
Kumar SP, Edward JKP (2009) Assessment of metal concentration in the sediment cores of Manakudy estuary, south west coast of India. Indian J Mar Sci 38(2):235–248
Maeda L, Kawahata H, Nohara M (2002) Fluctuation of bio-genic and abiogenic sedimentation on the Shatsky rise in the western North Pacific during the late Quaternary. Mar Geol 189:197–214
Meyers PA (1997) Organic geochemical proxies of paleoceanographic, paleolimnologic, and paleoclimatic processes. Org Geochem 27:213–250
Meyers PA, Ishiwatari R (1993) Lacustrine organic geochemistry—an overview of indicators of organic matter sources and diagenesis in lake sediments. Org Geochem 20:867–900
Meyers PA, Teranes JL (2001) Sediment organic matter in tracking environmental change using lake sediments. Phys Geochem Methods 2:239–269
Milliman JD, Syvitski JPM (1992) Geomorphic/tectonic control of sediment discharge to the oceans: the importance of small mountain rivers. J Geol 100:525–544
Millward GE, Moore RM (1982) The adsorption of Cu, Mn and Zn by iron oxyhydroxides in model estuarine solutions. Water Res 16:981–985
Mishra JN (1956) A systematic account of some littoral marine diatoms from the West Coast of India. J Bomb Nat Hist Soc 53:537–568
Muller G (1979) Schwermwtalle in den sedimentation des Rheins–Veranderungen seit 1971. Umschau 79:778–783
Pande A (2013) Depositional environments and processes within mudflats and mangroves along central west coast of India. Goa University, India
Passos EA, Alves JC, Dos Santos IS, Alves JPH, Garcia CAB, Spinola Costa A (2010) Assessment of trace metals contamination in estuarine sediments using a sequential extraction technique and principal component analysis. Microchem J 96:50–57
Patil JS, Anil AC (2008) Temporal variation of diatom benthic propagules in a monsoon influenced tropical estuary. Cont Shelf Res 28(17):2404–2416
Pejrup M (1988) The triangular diagram used for classification of estuarine sediments: a new approach. In: de Boer PL, van Gelder A, Nios SD (eds) Tide-influenced sedimentary environments and facies. Reidel, Dordrecht, pp 289–300
Reineek HE (1972) Tidal flats. In: Rigby JK, Hamblin WK (eds) Recognition of ancient sedimentary environments Tulsa Okla. Soc Econ Paleontol Mineral Spec Publ 16:146–159
Ribeiro FCP, Cristina DSFS, Lezilda CT (2010) The use of diatoms for paleohydrological and paleoenvironmental reconstructions of Itupanema beach, Pará state, Amazon region, during the last millennium. Rev Bras Paleontolog 13(1):21–32
Ruiz-Fernández AC, Marrugo-Negrete JL, Paternina-Uribe R, Pérez-Bernal LH (2011) 210Pb-derived sedimentation rates and corg fluxes in soledad lagoon (Cispatá Lagoon System, NW Caribbean Coast of Colombia). Estuar Coast 34:1117–1128
Santschi PH, Hohener P, Benoit G, Bucholtz-ten BM (1990) Chemical processes at the sediment–water interface. Mar Chem 30:269–315
Semeniuk V (1981) Sedimentology and the stratigraphic sequence of a tropical tidal flat, north-western Australia. Sediment Geol 29:195–221
Sharma P, Borole DV, Zingde MD (1994) 210Pb based trace element fluxes in the nearshore and estuarine sediments off Bombay, India. Mar Chem 47:227–241
Shindikar M (2006) Ecological studies on Mangroves of Maharashtra coast, University of Poona, India
Simenstad CA (1983) The ecology of estuarine channels of the Pacific Northwest coast: a community profile. Fish Wild, US, p 9
Singh KT, Nayak GN, Fernandes LL, Borole DV, Basavaiah N (2013) Changing environmental conditions in recent past—reading through the study of geochemical characteristics, magnetic parameters and sedimentation rate of mudflats, central west coast of India. Palaeogeogr, Palaeoclimatol, Palaeoecol. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.04.008
Soto MCM, Martı´nez G (2012) Organic carbon, phosphorus and nitrogen in surface sediments of the marine–coastal region north and south of the Paria Peninsula, Venezuela. Environ Earth Sci 65:429–439
Spencer KT (2002) Spatial variability of metals in the inter-tidal sediments of the Medway Estuary, Kent, UK. Marine Poll Bull 44:933–944
Stephens JA, Uncles RJ, Barton ML, Fitzpatrick F (1992) Bulk properties of intertidal sediments in a muddy, macrotidal estuary. Mar Geol 103:445–460
Stevenson JR, Pan Y (1999) Assessing environmental conditions in rivers and streams with diatoms. In: Stoermer EF, Smol JP (eds) The diatoms: applications for the environmental and earth science. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 11–40
Subramanya KR (1987) Evolution of western Ghats, India—A simple model. J Geol Soc India 29(4):446–449
Suto I (2006) The explosive diversification of the diatom genus Chaetoceros across the Eocene/Oligocene and Oligocene/Miocene boundaries in the Norwegian Sea. Mar Micropaleontol 58:259–269
Sylvestre F, Guiralb D, Debenaya JP (2004) Modern diatom distribution in mangrove swamps from the Kaw Estuary (French Guiana). Mar Geol 208:281–293
Temmerman S, Govers G, Wartel S, Meire P (2003) Spatial and temporal factors controlling short term sedimentation in a salt and freshwater tidal marsh, Scheldt estuary, Belgium, SW, Netherlands. Earth Surf Proc Land 28:739–755
Turekian KK, Wedepohl KH (1961) Distribution of the elements in some major units of the Earth’s crust. Geol Soc American Bull 72:175–192
Turner A (2000) Trace metal contamination in sediments from UK estuaries: an empirical evaluation of the role of hydrous iron and manganese oxides. Est Coast Shelf Sci 50:355–371
Venkatramanan S, Ramkumar T, Anithamary I, Vasudevan S (2014) Heavy metal distribution in surface sediments of the Tirumalairajan river estuary and the surrounding coastal area, east coast of India. Arab J Geosci 7:123–130
Virkanen J (1998) Effect of urbanization on metal deposition in the Bay of T6616nlahti Southern Finland. Marine Poll Bull 36(9):729–738
Volvoikar SP, Nayak GN (2013a) Depositional environment and geochemical response of mangrove sediments from creeks of northern Maharashtra coast, India. Marine Poll Bull 69:223–227
Volvoikar SP, Nayak GN (2013b) Factors controlling the distribution of metals in intertidal mudflat sediments of Vaitarna estuary. Arab J Geosci, North Maharashtra coast, India. doi:10.1007/s12517-013-1162-4
Volvoikar SP, Nayak GN, Mazumdar A, Peketi A (2014) Reconstruction of depositional environment of a tropical estuary and response of d13Corg and TOC/TN signatures to changing environmental conditions. Est Coast Shelf Sci 139:137–147
Weikert H (1987) Plankton and the pelagic environment. In: Edwards AJ, Head SM (eds) Key Environments: Red Sea. Oxford Press, Pergamon, pp 90–111
Wilson GP, Lamb AL, Leng MJ, Gonzalez S, Huddart D (2005) Variability of organic d13C and C/N in the Mersey estuary, UK and its implications for sea-level reconstruction studies. Est Coast Shelf Sci 64:685–698
Xia P, Meng X, Yin P, Cao Z, Wang X (2011) Eighty-year sedimentary record of heavy metal inputs in the intertidal sediments from the Nanliu river estuary, Beibu Gulf of South China Sea. Environ Pollut 159:92–99
Yu F, Zong Y, Lloyd JM, Huang G, Leng MJ, Kendrick C, Lamb AL, Yim WWS (2010) Bulk organic d13C and C/N as indicators for sediment sources in the Pearl River delta and estuary, southern China. Est Coast Shelf Sci 87:618–630
Zhou H, Peng X, Pan J (2004) Distribution, source and enrichment of some chemical elements in sediments of the Pearl river estuary, China. Cont Shelf Res 24:1857–1875
Zong Y (1997) Implications of Paralia sulcata abundance in Scottish Isolation Basins. Diatom Res 12:125–150
Zourarah B, Maanan M, Robin M, Carruesco C (2009) Sedimentary records of anthropogenic contribution to heavy metal content in Oum Er Bia estuary (Morocco). Environ Chem Lett 7:67–78
Zwolsman JJG, Berger GW, VanEck GTM (1993) Sediment accumulation rates, historical input, postdepositional mobility and retention of major elements and trace metals in salt marsh sediments of the Scheldt estuary, SW Netherlands. Mar Chem 44:73–94
Acknowledgments
Authors thank Dr. Bishwajit Thakur, scientist, Birbal Sahni Institute of Paleobotany (BSIP), Lucknow, for the help in diatom analysis. We are grateful to Dr. Rahul Mohan, scientist, National center for Antarctic and ocean research (NCAOR), Goa, for providing microscope facility. Our sincere thanks to Dr. Rajeev Saraswat, scientist, National Institute of Oceanography (NIO), Goa, for his valuable suggestions on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pande, A., Nayak, G.N., Prasad, V. et al. Geochemical and diatom records of recent changes in depositional environment of a tropical wetland, central west coast of India. Environ Earth Sci 73, 5447–5461 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3799-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3799-z