Abstract
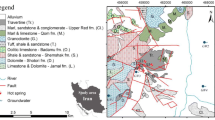
The Kharaqan hot springs are located in the historic city of Abe-Garm, famous for its hot springs, in Qazvin province, in northwestern Iran. Thermal waters with temperatures ranging from 28.7 to 52 °C vary in chemical composition and TDS contents. Those waters generally are enriched in Na–Cl–HCO3 and suggest deep water circulation. Chemistry of all of the water samples are graphed in the Cl–SO4–HCO3 ternary diagram. There is a trend of mixing along a line of constituent proportions between recently recharged water and older water. The trend toward the chloride corner is mainly the result of contact in the subsurface with evaporite-bearing formations and/or mixing with brines. Relatively high concentrations of Na, Ca, K, Cl, and SO4 resulted from rock/water interactions. These hot spring waters show high concentrations of arsenic (0.14–0.95 mg L−1). The diffusion of As-bearing spring waters into shallow aquifers could contaminate the groundwater which is used for drinking purposes. Also discharges of this As-enriched water into streams and rivers could affect irrigated crops in downstream fields. In both cases, the health of local residents could be at risk.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghanabati A (2004) Geology of Iran. GSI Publication, Tehran
Ahmad SA, Bandarnayake D, Khan AW, Hadi SA, Uddin G, Halim MA (1997) Arsenic in ground water and arsenicosis in Bangladesh. Int J Environ HealthRes 7:271–276
Ahmad SA, Sayed MHSU, Barua S, Khan MH, Faruquee MH, Jalil A, Hadi SA, Talukder HK (2001) Arsenic in drinking water and pregnancy outcomes. Environ Health Perspect 109:629–631
Back W (1966) Hydro chemical facies and groundwater flow patterns in northern part of Atlantic Coastal Plain. US Geological Survey Professional Paper 498–A:42
Bates MN, Smith AH, Hopenhayn-Rich C (1992) Arsenic ingestion and internal cancers: a review. Am J Epidemiol 135:462–476
Berberian M (1971) Preliminary report on structural analysis of Ipak Active Fault, internal report. Geological Survey of Iran, Tehran
Bolourchi MH, Hajian J, Ohanian T, Vahdati F (1979) Explanatory text of Kabudar Ahang Quadrangle map 1:250,000 (D5). Geological and Mineral Survey of Iran, Tehran
Bowen HJM (1979) Environmental Geochemistry of the Elements. Academic Press, London
Bundschuh J, Maity JP, Nath B, Baba A, Gunduz O, Kulp TR, Jean JS, Kar S, Yang HJ, Tseng YJ, Bhattacharya P, Chen CY (2013) Naturally occurring arsenic in terrestrial geothermal systems of western Anatolia, Turkey: potential role in contamination of freshwater resources. J Hazard Mater 262:951–959
Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (CCME) (1999) Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for the Protection of agricultural water uses/Arsenic. http://ceqg-rcqe.ccme.ca/
Caporale AG, Pigna M, Azam SMGG, Sommella A, Rao MA, Violante A (2013) Effect of competing ligands on the sorption/desorption of arsenite on/from Mg–Fe layered double hydroxides (Mg–Fe-LDH). Chem Eng J 225:704–709
Carmen Blanco M, Paoloni J, Morrás H, Fiorentino C, Sequeira M, Amiotti N, Bravo O, Diaz S, Espósito M (2012) Partition of arsenic in soils sediments and the origin of naturally elevated concentrations in groundwater of the southern pampa region (Argentina). Environ Earth Sci 66:2075–2084
Charlet L, Polya DA (2006) Arsenic hazard in shallow reducing groundwaters in southern Asia. Elements 2:91–96
Chen CJ, Chen CW, Wu MM, Kuo TL (1992) Cancer potential in liver, lung, bladder and kidney due to ingested inorganic arsenic in drinking water. Br J Cancer 66:888–892
Chen CJ, Chiou HY, Chiang MH, Lin LJ, Tai TY (1996) Dose response relationship between ischemic heart disease mortality and longterm arsenic exposure. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 16:504–510
Chiou HY, Hsueh YM, Liaw KF et al (1995) Incidence of internal cancers and ingested inorganic arsenic: a seven-year follow-up-study in Taiwan. Cancer Res 55:1296–1300
Choong TSY, Chuah TG, Robiah Y, Gregory Koay FL, Azni I (2007) Arsenic toxicity, health hazards and removal techniques from water: an overview. Desalination 217:139–166
Chudaev O, Chudaeva V, Sugimori K, Kuno A, Matsuo M (2006) Geochemistry of recent hydrothermal systems of Mendeleev Volcano, Kuril Islands, Russia. J Geochem Explor 88:95–100
Duker AA, Carranza EJM, Hale M (2005) Arsenic geochemistry and health. Environ Int 31:631–641
Eleni I, Aletrari M, Eftychia C (2006) Risk assessment of the dietary intake of lead, cadmium, mercury and nitrates in cyprus and the relevant uncertainty. In: proceedings of the AOAC Europe Section, International Workshop, November 6-7, Limassol
Erfurt-Cooper P, Cooper M (2009) Health and wellness tourism: spas and hot springs. Aspects of tourism, vol 40. Channel View Publications, Bristol
Freeze RA, Cherry JA (1979) Groundwater. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Ghafouri MR (2003) Mineral water and mineral springs of Iran. University of Tehran, Tehran
Giggenbach WF (1988) Geothermal solute equilibria. Derivation of Na–K–Ca–Mg geoindicators. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:2749–2765
Guha Mazumder DN, Haque R, Ghosh N et al (2000) Arsenic in drinking water and the prevalence of respiratory effects in West Bengal, India. Int J Epidemiol 29:1047–1052
Hindmarsh JT, McCurdy RF (1986) Clinical and environmental aspects of arsenic toxicity. CRC Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 23:315–347
Karimi H, Moore F (2008) The source and heating mechanism for the Ahram, Mirahmad and Garu thermal springs, Zagros mountains, Iran. Geothermics 37:84–100
Krauskopf KB, logue K (2002) Environmental geochemistry, environmental science, encyclopedia of physical science and technology, 3rd edn. Academy Press, London, pp 519–545
Leybourne MI, Goodfellow WD, Boyle DR (1998) Hydro geochemical, isotopic and rare earth element evidence for contrasting water–rock interactions at two undisturbed Zn–Pb massive sulphide deposits, Bathurst Mining Camp, NB, Canada. J Geochem Exp 64:237–261
Marini L (2000) Geochemical techniques for the exploration and exploitation of geothermal energy, Università degli Studi di Genova. Dipartimento per lo Studio del Territorio e delle sue Risorse, Genova, Italia
McArthur JM, Banerjee DM, Hudson-Edwards KA, Mishra R, Purohit R, Ravenscroft P, Cronin A, Howarth RJ, Chatterjee A, Talukder T, Lowry D, Houghton S, Chadha DK (2004) Natural organic matter in sedimentary basins and its relation to arsenic in anoxic ground water: the example of West Bengaland its worldwide implications. Appl Geochem 19:1255–1293
Milton AH, Hasan Z, Rahman A (2001) Chronic arsenic poisoning and respiratory effects in Bangladesh. J Occup Health 43:136–140
Minissale A (1991) Thermal springs in Italy: their relation to recent tectonics. Appl Geochem 6:201–212
Modabberi S, Jahromi Yekta SS (2014) Environmental geochemistry and sources of potentially toxic elements in thermal springs in the Sabalan volcanic field, NW Iran. Environ Earth Sci 71:2821–2835
Mroczek EK (2005) Contributions of arsenic and chloride from the Kawerau geothermal field to the Tarawera River, New Zealand. Geothermics 34:218–233
Mukherjee SC, Rahman MM, Chowdhury UK et al (2003) Neuropathy in arsenic toxicity from groundwater arsenic contamination in West Bengal-India. J Environ Sci Health Part A Environ Sci Eng 38:165–183
Mukherjee A, Bhattacharya P, Savage K, Foster A, Bundschuh J (2008) Distribution of geogenic arsenic in hydrologic systems: controls and challenges. J Contam Hydrol 99:1–7
Mukherjee A, Fryar AE, Scanlon BR, Bhattacharya P, Bhattacharya A (2011) Elevated arsenic in deeper groundwater of western Bengal basin, India: extents and controls from regional to local-scale. Appl Geochem 26:600–613
Mutlu H (1998) Chemical geothermometry and fluid–mineral equilibria for the Ömer-Gecek thermal waters, Afyon area, Turkey. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 80:303–321
Navi P, Taheri M, Yazdi M (2012) Introduction of Kharaqan Hot springs for Health Tourism. In: Proceedings of 1st Symposium on Irans Geoheritage, January 23, The Geological Survey and Mineral Exploration of Iran, 13 p
Nicolli HB, Suriano JM, Gomez Peral MA, Ferpozzi LH, Baleani OA (1989) Groundwater contamination with arsenic and other trace elements in an area of the Pampa, Province of Cordoba, Argentina. Environ Geol Water Sci 14:3–16
Nicolli HB, Bundschuh J, Blanco MC, Tujchneider OC, Panarello HO, Dapeña C, Rusansky JE (2012) Arsenic and associated trace-elements in groundwater from the Chaco-Pampean plain, Argentina: results from 100 years of research. Sci Total Environ 429:36–56
Pearcy CA, Chevis DA, Haug TJ, Jeffries HA, Yang N, Tang J, Grimm DA, Johannesson KH (2011) Evidence of microbially mediated arsenic mobilization from sediments of the Aquia aquifer, Maryland, USA. Appl Geochem 26:575–586
Pehlivan R (2002) The effects on human health and hydro geochemical characteristics of the Kirkgeçit and Ozancik hot springs, Çanakkale, Turkey. Environ Geochem Health 25:205–217
Pentecost A, Jones B, Renaut RW (2003) What is a hot spring? Can J Earth Sci 40:1443–1446
Piper AM (1944) A graphical interpretation of water analysis. Trans Am Geophys Union 25:914–928
Pitkanen P, Kaija J, Blomqvist R, Smellie JAT, Frape SK, Laaksoharju M, Negral PH, Casanova J, Karhu J (2002) Hydro geochemical interpretation of groundwater at Palmottu. Paper EUR 19118 EN, European Commission, Brussels, pp 155–167
Polya DA, Gault AG, Diebe N, Feldman P, Rosenboom JW, Gilligan E, Fredericks D, Milton AH, Sampson M, Rowland HAL, Lythgoe PR, Jones JC, Middleton C, Cooke DA (2005) Arsenic in shallow Cambodian groundwaters. Miner Mag 69:807–823
Rahman MM, Tondel M, Ahmad SA, Axelson O (1998) Diabetes mellitus associated with arsenic exposure in Bangladesh. Am J Epidemiol 148:198–203
Rahman MM, Chowdhury UK, Mukherjee SC et al (2001) Chronic arsenic toxicity in Bangladesh and West Bengal, India—a review and commentary. Clin Toxicol 39:683–700
Rahman M, Naidu R, Bhattacharya P (2009) Arsenic contamination in groundwater in the Southeast Asia region. Environ Geochem Health 31:9–21
Ravenscroft P, Brammer H, Richards K (2009) Arsenic pollution: a global synthesis. Wiley, UK
Raychowdhury N, Mukherjee A, Bhattacharya P, Johannesson K, Bundschuh J, Bejarano Sifuentes G, Nordberg E, Martin RA, Rosario Storniolo AD (2013) Provenance and fate of arsenic and other solutes in the Chaco-Pampean Plain of the Andean foreland, Argentina: from perspectives of hydrogeochemical modeling and regional tectonic setting. J Hydrol. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.07.003
Robinson B, Duwig C, Bolan N, Kannathasan M, Saravanan A (2003) Uptake of arsenic by New Zealand watercress (Lepidium sativum). Sci Total Environ 301:67–73
Scanlon BR, Nicot JP, Reedy RC, Kurtzman D, Mukherjee A, Nordstrom DK (2009) Elevated naturally occurring arsenic in a semiarid oxidizing system, Southern High Plains aquifer, Texas, USA. Appl Geochem 24:2061–2071
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2002) A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl Geochem 17:517–568
Smith AH, Goycolea M, Haque R et al (1998) Marked increase in bladder and lung cancer mortality in a region of northern Chile due to arsenic in drinking water. Am J Epidemiol 147:660–669
Taheri M, Yazdi M, Navi P (2012a) Health hazards and arsenic pollutants in Kharaqan Hot springs, Qazvin. In: proceedings of 4th Symposium of Iranian Society of Economic Geology, August 30–31, Birjand university
Taheri M, Yazdi M, Navi P, Sadati N (2012b) Application of remote sensing for alteration mapping in Avaj area. In: proceedings of 16th Symposium of geological society of Iran, September 4–6, Shiraz University, p 8
Taylor SR (1964) Abundance of elements in the continental crust. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 28:1273–1286
Thakur JK, Thakur RK, Ramanathan A, Kumar M, Singh SK (2011) Arsenic contamination of groundwater in Nepal—an overview. Water 3:1–20
Tondel M, Rahman M, Magnuson A, Chowdhury IA, Faruquee MH, Ahmad SA (1999) The relationship of arsenic levels in drinking water and the prevalence rate of skin lesions in Bangladesh. Environ Health Perspect 107:727–729
USNRC (1999) Arsenic in drinking water. DC, United States National Research Council, National Academy Press, Washington
Vaughan DJ (2006) Arsenic. Elem (Int Mag Miner Geochem Petrol) 2(2):71–75
Wang CH, Hsiao CK, Chen CL et al (2007) A review of the epidemiologic literature on the role of environmental arsenic exposure and cardiovascular diseases. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 222:315–326
Webster JG (1999) The source of arsenic (and other elements) in the Marbel-Matingao river catchment, Mindanao, Philippines. Geothermics 28:95–111
Wedepohl KH (eds) (1969–1974) Handbook of Geochemistry. Springer, Berlin
Welch AH, Westjohn DB, Helsel DR, Wanty RB (2000) Arsenic in ground water of the United States: occurrence and geochemistry. Ground Water 38(4):589–604
Woolson EA (1983) Emissions, cycling and effects of arsenic in soil ecosystems. In: Fowler BA (eds) Biological and environmental effects of arsenic. Elsevier, New York, pp 51–139
World Health Organization (2003) Total dissolved solids in drinking water. Background document for preparation of WHO guidelines for drinking-water quality. World Health Organization, Geneva
World Health Organization (2006) Guidelines for safe recreational water environments. Swimming pools and similar environments. World Health Organization, Geneva
World Health Organization (2011) Arsenic in drinking-water. World Health Organization, Geneva
Yazdi M, Taheri M, Navi P, Sadati N (2013) Landsat ETM+ imaging for mineral potential mapping: application to Avaj area, Qazvin, Iran. Int J Remote Sens 34(16):5778–5795
Yoshizuka K, Nishihama S, Sato H (2010) Analytical survey of arsenic in geothermal waters from sites in Kyushu, Japan, and a method for removing arsenic using magnetite. Environ Geochem Health 32:297–302
Yousefi H, Noorollahi Y, Ehara S, Itoi R, Yousefi A, Fujimitsu Y, Nishijima J, Sasaki K (2010) Developing the geothermal resources map of Iran. Geothermics 39:140–151
Zhang G, Liu CQ, Liu H, Jin Z, Han G, Li L (2008) Geochemistry of the Rehai and Ruidian geothermal waters, Yunnan Province, China. Geothermics 37:73–83
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their thanks to the Geological Survey of Iran and Shahid Beheshti University for providing the funds for this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yazdi, M., Taheri, M. & Navi, P. Environmental geochemistry and sources of natural arsenic in the Kharaqan hot springs, Qazvin, Iran. Environ Earth Sci 73, 5395–5404 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3794-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3794-4