Abstract
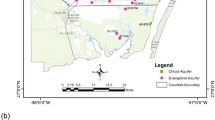
The quality of the Upper Cheliff groundwater, located in North West Algeria, has in recent years undergone serious deterioration due to uncontrolled discharge of urban wastewaters, intensive use of chemical fertilizers in agriculture as well as to overexploitation. This study aims at analyzing the flow pattern of the Upper Cheliff groundwater, determining its current hydrochemical status and understanding the mineralization processes involved in its chemical quality. Two piezometric and sampling campaigns were carried out in 2008 in high water (April) and low water (October) periods. The major chemical ions (Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, K+, Cl−, HCO3 −, NO3 −, SO4 2−) were analyzed in all samples. The piezometric data were mapped and allowed to analyze the groundwater flow conditions, in particular at the boundaries of the aquifer. The interpretation of hydrochemical data was made using various methods (Piper diagram, Stabler classification, base exchanges index, bi-elements scatter diagrams, saturation indices, mapping and multivariate principal component analysis). The results provide a better understanding of this aquifer hydrogeology and hydrochemistry. Several hydrochemical types (chloride-calcium, chloride-sodium and bicarbonate-calcium) characterize the groundwater. Mineralization processes and the origin of salinity are determined by the lithology of the aquifer (dissolution, base exchanges), and by climatic (evaporation) and anthropogenic factors (agricultural and urban wastes). The groundwater in the Upper Cheliff is currently of poor quality. This status is worrying, as this groundwater is an important natural resource for the socio-economic development of this region. Urgent measures must be taken to preserve this resource.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abderamane H, Razack M, Vassolo S (2012) Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characterization of the groundwater in the Chari-Baguirmi depression Republic of Tchad. Environ Earth Sci 69(7):2337–2350
Aboubaker M, Jalludin M, Razack M (2013) Hydrochemistry study of a volcano-sedimentary aquifer using major ion and environmental isotope data. Dalha basalts aquifer, southwest of Republic of Djibouti. Environ Earth Sci 70(7):3335–3349
Achour F, Bouzelboudjen M (1998) Variabilité spatio-temporelle des ressources en eau en région semi-aride: application au bassin du Cheliff, Algérie. Spatio-temporal variability of water resources in semi-arid region: application to the Cheliff basin, Algeria. Water resources variability in Africa during XXth Century. Proceedings Abidjan’98 Conference, Abidjan, Cote d’Ivoire, IAHS Publ. 252, (In French)
Adams S, Titus R, Pietersen K, Tredoux G, Harris C (2000) Hydrochemical characteristics of aquifers near Sutherland in the Western Karoo, South Africa. J Hydrol 241:91–103
ANRH Agence Nationale des Ressources Hydrauliques (2004) Annuaire Hydrogéologique de la nappe alluviale du Haut et Moyen Cheliff. Hydrogeological Yearbook of the alluvial aquifer of the Upper and Middle Cheliff. Unpublished report, Alger, (In French)
Appelo CAJ, Postma D (1993) Geochemistry. Groundwater and Pollution, Balkema
Ashley RP, Lloyd JW (1978) An example of the use of factor analysis and cluster analysis in ground water chemistry interpretation. J Hydrol 39:355–364
Bettahar N, Ali Benamara A, Kettab A, Douaoui A (2009) Risque de pollution nitratée des zones semi-arides : cas de la vallée du moyen Cheliff occidental (Nord Algérien). Risk of nitrate pollution in semi-arid areas: case of the valley of the Middle Western Cheliff (North Algerian). Revue Sciences Eau 22(1):69–78 (In French)
Boulaine J (1957) Étude des sols des plaines du Cheliff. Study of the soils of the Cheliff plains. Unpublished report. University of Alger, (In French)
Cerling TE, Pederson BL, Damm KLV (1989) Sodium-Calcium ion exchange in the weathering of shales: implications for global weathering budgets. Geology 17:552–554
Datta PS, Tyagi SK (1996) Major ion chemistry of groundwater in Delhi area: chemical weathering processes and groundwater regime. J Geol Soc India 47:179–188
Davis JC (2002) Statistics and data analysis in geology. Wiley (ASIA) Ltd, Singapore, New York, pp 526–540
Dawdy DR, Feth JH (1967) Application of factor analysis in study of chemistry of groundwater quality, Mojaveriver Valley California. Water Resour Res 3(2):505–510
De Fulvio S, Olori L (1976) Definitions and classification of naturally soft and naturally hard waters. In: Proc. Hardness of drinking water and public health. European Scientific Colloquium, Luxembourg 1975, Pergamon Press, New York, p 95
Diaw M, Faye S, Stichler W, Maloszewski P (2012) Isotopic and geochemical characteristics of groundwater in the Senegal River delta aquifer: implication of recharge and flow regime. Environ Earth Sci 66(4):1011–1020
Domenico PA, Schwartz FW (1990) Physical and chemical hydrology. Wiley, New York
EPA (1983) Methods for the chemical analysis of water and wastes. EPA/600/4-79/020, USA, p 491
Esteller MV, Andreu JM (2004) Anthropic effects on hydrochemical characteristics of the Valle de Toluca aquifer (central Mexico). Hydrogeol J 13:378–390
Fisher RS, Mulican WF III (1997) Hydrochemical evolution of sodium-sulfate and sodium-chloride groundwater beneath the Northern Chihuahuan desert, Trans-Pecos, Rexas, USA. Hydrogeol J 10:455–474
Gouaidia L, Boudoukha A, Djabri L, Guefaifia O (2011) Évaluation de la vulnérabilité d’une nappe en milieu semi-aride et comparaison des méthodes appliquées : cas de la nappe de Meskiana (Est Algérien). Vulnerability assessment of groundwater in semi-arid and comparison of methods: Meskiana groundwater (Eastern Algeria). Revue Sécheresse 22(1):35–42
Gupta S, Mahato A, Roy P, Datta JK, Saha RN (2008) Geochemistry of groundwater, Burdwan District, West Bengal, India. Environ Geol 53:1271–1282
Harman HH (1960) Modern factor analysis. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Hitchon B, Billings GK, Klovan JE (1971) Geochemistry and origin of formation waters in the western Canada sedimentary basin-III factors controlling chemical composition. Geochim Cosmochim 35:567–598
Hounslow A (1995) Water quality data: analysis and interpretation. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Hussein MT (2004) Hydrochemical evaluation of groundwater in the Blue Nile Basin, eastern Sudan, using conventional and multivariate techniques. Hydrogeol J 12:144–158
Jalali M (2009) Geochemistry characterization of groundwater in an agricultural area of Razan, Hamadan, Iran. Environ Geol 56:1479–1488
Jayakumar R, Siraz L (1997) Factor analysis in hydrogeochemistry of coastal aquifers—a preliminary study. Environ Geol 31:174–177
Jayaprakash M, Giridharan L, Venugopal T, Krishna Kumar SP, Periakali P (2008) Characterization and evaluation of the factors affecting the geochemistry of groundwater in Neyveli, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ Geol 54:855–867
Kaiser HF (1958) The Varimax criteria for analytical rotation in factor analysis. Psychometrika 23:187–200
Karanth KR (1997) Groundwater assessment, development and management. Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi
Kuldip S, Hundal H, Dhanwinder S (2011) Geochemistry and assessment of hydrogeochemical processes in groundwater in the southern part of Bathinda district of Punjab, northwest India. Environ Earth Sci 64:1823–1833
Lawrence FW, Upchurch SB (1976) Identification of geochemical patterns in ground water by numerical analysis. In: Zaleem EA (ed) Advances in Groundwater Hydrology. America Water Resources Association, pp 199–214
Lawrence FW, Upchurch SB (1983) Identification of recharge areas using factor analysis. Ground Water 20:680–687
Llamas MR, Martínez-Santos P (2005) Intensive groundwater use: a silent revolution that cannot be ignored. Water Sci Technol Ser 51(8):167–174
Mania J, Djeda F (1990) Hydrogéologie de la plaine alluviale du Haut Cheliff de la région de Khemis–Miliana (Algérie). Hydrogeology of the alluvial plain of the High Cheliff. Region of -Khemis Miliana (Algeria). Bull Soc Géol France 8-VI(3): 505–513, (In French)
Mattauer M (1958) Etude géologique de l’Ouarsenis oriental (Algérie). Geological study of the eastern Ouarsenis (Algeria). Publ Serv Carte Géol Algérie, Alger, Bull 17, (In French)
Meghraoui M, Cisternas A, Philip H (1986) Seismotectonics of the lower Cheliff basin: structural background of the El Asnam (Algeria) earthquake. Tectonics 5:809–836
Moussa A, Zouari K, Oueslati N (2008) Geochemical study of groundwater mineralization in the Grombalia shallow aquifer, north-eastern Tunisia: implication of irrigation and industrial waste water accounting. Environ Geol. doi:10.1007/s00254-008-1530-7
Nandimandalam JR (2011) Evaluation of hydrogeochemical processes in the Pleistocene aquifers of Middle Ganga Plain, Uttar Pradesh, India. Environ Earth Sci 65(4):1291–1308
Narasimhan TN (2005) Hydrogeology in North America: past and future. Hydrogeol J 13:7–24
Parkhurst DL, Appelo CAJ (1999) User’s guide to PHREEQC (Version 2)—A Computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. United States Geological Survey, Water Resources Investigations Report 99-4259, Washington, p 326
Perrodon A (1957) Etude géologique des bassins néogènes sublittoraux de l’Algérie Nord Occidentale. Geological survey of sublittoral Neogene basins of Western North Algeria. Publ Serv Carte Géol Algérie, Alger, Bull 12, (In French)
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analyses. Trans Am Geophys Union 25:914–923
Plummer L, Back W (1980) The mass balance approach: application to interpreting the chemical evolution of hydrologic systems. Amer J of Sci 280:130–142
Rajmohan N, Elango L (2004) Identification and evolution of hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment in an area of the Palar and Cheyyar River Basins, Southern India. Environ Geol 46:47–61
Razack M, Dazy J (1990) Hydrochemical characterization of groundwater mixing in sedimentary and metamorphic reservoirs with combined use of Piper’s principle and factor analysis. J Hydrol 114:371–393
Rodier J, Legube B, Merlet M, Brunet R (2009) L’analyse de l’eau. Ed. Dunod, Paris, p 1600
Scanlon BR, Jolly I, Sophocleous M, Zhang L (2007) Global impacts of conversions from natural to agricultural ecosystems on water resources: quantity versus quality. Water Resour Res 43(3):W3437
Schoeller H (1977) Geochemistry of groundwater. In: Brown RH et al (eds) Groundwater studies—an international guide for research and practice. UNESCO, Paris, pp 1–18
Seyhan EV, Van de Caried AA, Engelen GB (1985) Multivariate analysis and interpretation of the hydrochemistry of a dolomite reef aquifer, Northern Italy. Water Resour Res 21:1010–1024
Simler R (2009). Diagrammes software. Downloadable at http://www.lha.univ-avignon.fr/LHA-Logiciels.htm
Sujatha D, Reddy RB (2003) Quality characterization of groundwater in the south-eastern part of the Ranja Reddy district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Geol 44(5):579–586
Swan ARH, Sandilands M (1995) Introduction to geological data analysis. Blackwell, Oxford
UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme) (2010) Clearing the Waters. A Focus in Water Quality Solutions. Nairobi, UNEP. http://www.unep.org/PDF/Clearing_the_Waters.pdf
Usunoff EJ, Guzman AG (1989) Multivariate analysis in hydrochemistry. An example of the use of factor and correspondence analysis. Ground Water 17:27–34
WHO World Health Organization (2008) Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 2nd edn. Geneva. http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/2edvol1i.pdf
WWAP (World Water Assessment Programme) (2009) United Nations World Water development report 3: water in a changing world. UNESCO, Paris
WWAP (World Water Assessment Programme) (2012) The United Nations World water development report 4: managing water under uncertainty and risk. UNESCO, Paris
Yidana S, Ophori D, Yakubo B (2008) Hydrochemical evaluation of the Voltaian system.The Afram Plains area, Ghana. J Environ Manag 88:697–707
Yitbarek A, Razack M, Ayenew T, Zemedagegnehu E, Azagegn T (2012) Hydrogeological and hydrochemical framework of Upper Awash River basin, Ethiopia: with special emphasis on interbasins groundwater transfer between Blue Nile and Awash Rivers. J Afr Earth Sc 65:46–60
Yuce G (2007) A Geochemical study of the groundwater in the Misli basin and environmental implications. Environ Geol 51:857–868
Zaporozec A (1972) Graphical interpretation of water quality data. Groundwater 10(2):32–43
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge three anonymous reviewers, for their critical evaluation and suggestions, which greatly helped to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Touhari, F., Meddi, M., Mehaiguene, M. et al. Hydrogeochemical assessment of the Upper Cheliff groundwater (North West Algeria). Environ Earth Sci 73, 3043–3061 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3598-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3598-6