Abstract
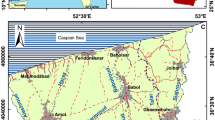
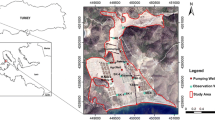
A salinization of groundwater by oilfield brine and seawater intrusion was detected in the plain of Wadi Al Ayn and Darouda in CapBon, northeast of Tunisia. The objective of this work is to simulate the historical trends of saltwater distribution in the study area and to predict its future dynamics under some proposed countermeasures for remediation. Based on the developed model with SEAWAT, the oilfield brine plume needs at least 5 years to be naturally reduced to less than the half of its actual size, while the seawater–freshwater interface can reach an inland extent of 1.3 km with a TDS of 10 g/L if no countermeasures will be taken until the next three decades. The tested remediation plan by model demonstrated that the artificial recharge with treated wastewater is the best solution to stop seawater intrusion just after 2 years of percolating 1 m/day with TDS of 1.5 g/L of recharge water. The natural remediation of the oilfield brine plume can be enhanced by imposing optimized pumping rates and installation of a restricted pumping perimeter.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen RG, Pereira LS, Raes D, Smith M (1998) Crop evapotranspiration. Guidelines for computing crop water requirements. FAO Irrigation Drainage Paper No. 56, FAO, Rome, Italy
Al-Maktoumi A, Lockington DA, Volker RE (2007) SEAWAT 2000: modeling unstable flow and sensitivity to discretization levels and numerical schemes. Hydrogeol J 15:1119–1129
Bakker M, Oude Essink GHP, Langevin CD (2004) The rotating movement of three immiscible fluids––a benchmark problem. J Hydrol 287:270–278
Bauer P, Held RJ, Zimmermann S, Linn F, Kinzelbach W (2006) Coupled flow and salinity transport modelling in semi-arid environments: the Shashe River Valley, Botswana. J Hydrol 316:163–183
Ben Hammouda MF, Tarhouni J, Leduc C, Zouari K (2011) Understanding the origin of salinization of the Plio-Quaternary eastern coastal aquifer of CapBon (Tunisia) using geochemical and isotopic investigations. Environ Earth Sci 63(5):889–901
Ben Salem H (1992) Contribution a la connaissance de la geologie du CapBon: stratigraphie, tectonique et sedimentologie. Thesis (Ph.D.), Faculty of Sciences of Tunis
CCI CapBon (2011) Chambre de Commerce et d’Industrie du CapBon, Tunisia [online]. Available from: http://www.ccicapbon.org.tn. Accessed 4 December 2011
Chekirbane A (2013) Interaction between groundwater and saline surface water in alluvial aquifers of ephemeral coastal streams, north-east of Tunisia. Thesis (Ph.D.), University of Tsukuba, Japan
Chekirbane A, Tsujimura M, Kawachi A, Isoda H, Tarhouni J, Yamada W, Takahashi M, Amri F (2012) Mapping of groundwater salinization using time domain electromagnetic induction in a small coastal semi-arid aquifer in CapBon, North-eastern of Tunisia. In: Proceeding of 22nd salt water intrusion meeting, 17–22 June 2012, Armaçao dos Buzios, Brazil
Chekirbane A, Tsujimura M, Kawachi A, Isoda H, Tarhouni J, Benalaya A (2013) Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater salinization in an ephemeral coastal flood plain: Cap Bon, Tunisia. Hydrol Sci J 58(5):1097–1110
Chkirbene A (2008) Hydrogéochimie et indices de pollution des eaux du système aquifère phréatique de la plaine d’oued Al Ayn au Cap-Bon. Thesis (Master), Higher School of Agriculture of Mograne, Zaghouan, Tunisia
Cobaner M, Yurtal R, Dogan A, Motz LH (2012) Three dimensional simulation of seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: a case study in the Goksu Deltaic Plain. J Hydrol 465:262–280
Colleuil B (1976) Étude stratigraphique et néotectonique des formations néogènes et quaternaires de la région Nabeul – Hammamet (CapBon, Tunisie). Thesis (Ph.D.), Nice University, France
CRDA of Nabeul (2004) Projet de recharge des nappes du CapBon à partir des eaux usées traitées. Project report, CRDA of Nabeul
Ennabli M (1980) Étude hydrogéologique des aquifères du Nord-Est de la Tunisie pour une gestion intégrée des ressources en eau. Thesis (Ph.D.), Nice University, France
Guo W, Langevin CD (2002) User’s guide to SEAWAT: a computer program for simulation of threedimensional variable-density ground-water flow. U.S. Geological Survey Techniques of Water-Resources Investigations, book 6, Chapter A7, p 77
Harbaugh AW, Banta ER, Hill MC, McDonald MG (2000) MODFLOW-2000, the U.S. Geological survey modular ground-water model––user guide to modularization concepts and the ground-water flow process: U.S. Geological Survey
Hudak FH, Wachal DJ (2001) Effects of brine injection wells, dry holes, and plugged oil/gas wells on chloride, bromide, and barium concentrations in the Gulf Coast Aquifer, southeast Texas, USA. Environ Int 26(7–8):497–503
Jemai S (1996) Evolution de l’état de la nappe de Korba: Étude hydrogéochimique et modélisation numérique. Thesis (Master), Agronomical National Institute of Tunisia (INAT), Tunisia
Jin L, Blake S, Zheng C, Wu J (2009) A modeling study of seawater intrusion in Alabama Gulf Coast, USA. Environ Geol 57:119–130
Kerrou J (2008) Deterministic and probabilistic numerical modelling towards sustainable groundwater management: application to seawater intrusion in the Korba aquifer (Tunisia). Thesis (Ph.D.), Neuchâtel University, Switzerland
Khlaifi I (1998) Contribution à l’étude de l’intrusion marine par un modèle de transport tridimensionnel: interfaçage avec des systèmes d’information géographique. Thesis (Master), University of Tunis El Manar
Kouzana L, Ben Mammou A, Sfar Felfoul M (2009) Seawater intrusion and associated processes: case of the Korba aquifer (CapBon, Tunisia). CR Geosci 341(1):21–35
Kouzana L, Benassi R, Ben Mammou A, Sfar Felfoul M (2010) Geophysical and geochemical study of the seawater intrusion in Mediterranean semi arid zones. Case of the Korba coastal aquifer (CapBon, Tunisia). J Afr Earth Sci 58(2):242–254
Langevin CD (2003) Simulation of submarine ground water discharge to a marine estuary: Biscayne Bay, Florida. Ground Water 41(6):758–771
Langevin CD, Shoemaker WB, Guo W (2003) MODFLOW-2000, the U.S. Geological survey modular ground-water model-documentation of the SEAWAT-2000 version with the variable-density flow process (VDF) and the integrated MT3DMS transport process (IMT). US Geological Survey, Open-File Report 03-426, p 43
Langevin CD, Thorne DT Jr, Dausman AM, Sukop MC, Guo W (2008) SEAWAT version 4: a computer program for simulation of multi-species solute and heat transport. U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods Book 6, Chapter A22, p 39
Lecca G (2000) Implementation and testing of the CODESA-3D model for density-dependent flow and transport problems in porous media. Environment Area, CRS4, Pula, Italy (Internal report)
Lin HJ, Rechards DR, Talbot CA, Yeh GT, Cheng JR, Cheng HP, Jones NL (1997) A three-dimensional finite-element computer model for simulating density-dependent flow and transport in variable saturated media: version 3.1. US Army Engineering Research and Development Center, Vicksburg, MS
Mastrocicco M, Colombani N, Sbarbati C, Petitta M (2012) Assessing the effect of saltwater intrusion on petroleum hydrocarbon plumes via numerical modeling. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:4417–4427
Narayan KA, Schleeberger C, Bristow KL (2007) Modelling seawater intrusion in the Burdekin delta irrigation area, North Queensland, Australia. Agric Water Manag 89:217–228
Nazoumou Y (2002) Impact des barrages sur la recharge des nappes en zone aride : Etude par modélisation numérique sur le cas de Kairouan (Tunisie centrale). Thesis (Ph.D.). Ecole Nationale d’Ingénieurs de Tunis
Paniconi C, Khlaifi I, Lecca G, Giacomelli A, Tarhouni J (2001) A modeling study of sea water intrusion in the Korba coastal plain, Tunisia. Phys Chem Earth (B) 26(4):345–351
Paniconi C, Khlaifi I, Lecca G, Giacomelli A, Tarhouni J (2004) Modeling and analysis of seawater intrusion in the coastal aquifer of eastern CapBon, Tunisia. Transp Porous Media 43(1):3–28
Qahman K, Larabi A (2006) Evaluation and numerical modeling of seawater intrusion in the Gaza aquifer (Palestine). Hydrogeol J 14:713–728
Rekaya M (1989) Le contexte hydrogéologique de la nappe aquifère de la côte orientale du CapBon (Tunisie) et les problèmes causés par la surexploitation. General Direction of Water Resources, Tunis
Rouatbi R (1968) Étude hydrogéologique primaire de la région Tafelloune, CapBon oriental. Bureau of Hydraulic Resources Inventory (BIRH), Tunis
Saidi S, Bouri S, Ben Dhia H (2013) Groundwater management based on GIS techniques, chemical indicators and vulnerability to seawater intrusion modelling: application to the Mahdia–Ksour Essaf aquifer, Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci 70(4):1551–1568
Sanford WE, Konikow LF (1985) A two-constituent solute transport model for ground water having variable density. US Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 85-4279, p 89
Simmons CT, Fenstemaker TR, Sharp JM Jr (2001) Variable-density groundwater flow and contaminant transport in heterogeneous porous media: approaches, resolutions and future challenges. J Contam Hydrol 52(1–4):245–275
Slama F (2010) Field experimentation and modeling of salt transfer in Korba coastal plain: impact of seawater intrusion and irrigation practices. Thesis (Ph.D.), Neuchâtel University, Switzerland
Trabelsi F, Tarhouni J, Ben Mammou A, Ranieri G (2013) GIS-based subsurface databases and 3-D geological modeling as a tool for the set up of hydrogeological framework: Nabeul–Hammamet coastal aquifer case study (Northeast Tunisia). Environ Earth Sci 70(5):2087–2105
Voss CI (1984) SUTRA: a finite-element simulation model for saturated–unsaturated, fluid-density-dependent ground-water flow with energy transport or chemically reactive single-species solute transport. US Geological Survey, Water-Resources Investigation Report 84-4369, p 409
Zghibi A, Zouhri L, Tarhouni J (2011) Groundwater modelling and marine intrusion in the semi-arid systems (CapBon, Tunisia). Hydrol Process 25(11):1822–1836
Zheng C (2006) MT3DMS v5.2 supplemental user’s guide: Technical report to the U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center, Department of Geological Sciences, University of Alabama, p 24
Zheng C, Wang PP (1999) MT3DMS—a modular three-dimensional multispecies transport model for simulation of advection, dispersion and chemical reactions of contaminants in ground-water systems: documentation and user’s guide: U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Contract Report SERDP-99-1
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Research Partnership for Sustainable Development (SATREPS) program, funded by the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) and the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA), Japan. The authors would also like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chekirbane, A., Tsujimura, M., Kawachi, A. et al. 3D simulation of a multi-stressed coastal aquifer, northeast of Tunisia: salt transport processes and remediation scenarios. Environ Earth Sci 73, 1427–1442 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3495-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3495-z