Abstract
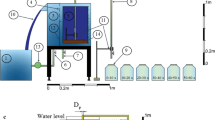
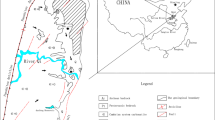
A computational flow analysis was carried out to identify the retention time and flow distribution characteristics depending on the shape and depth of an oxidation pond. To evaluate the flow characteristics and efficiency of the oxidation pond with various shapes, the shape of the oxidation pond was defined by its horizontal and vertical deformation. The flow characteristics of the oxidation pond were found to be independent of the direction of the horizontal deformation angle, but dependent on the magnitude of the vertical deformation angle. The larger the vertical deformation angle, the stronger the short circulation of the mine drainage and the lower the inflow exchange efficiency in the oxidation pond. Moreover, the efficiency of the oxidation pond was increased when the dip angle direction of the pond was the same as that of the flow and the dip angle of the pond was similar to the velocity contour.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
ANSYS (2013) http://www.ansys.com/Products/Simulation+Technology/Fluid+Dynamics/Fluid+Dynamics+Products/ANSYS+Fluent. Accessed 7 October 2013
Hedin RS, Nairn RW, Kleinmann RLP (1994) Passive treatment of polluted coal mine drainage. USBM IC 9389, US Dept of Interior, Washington DC
Hyman DM, Watzlaf GR (1995) Mine drainage characterization for the successful design and evaluation of passive treatment systems. In: Proceedings of the 17th Annual National Association of Abandoned Mine Lands Conference, French Lick
Jage CR, Zipper CE, Noble R (2001) Factors affecting alkalinity generation by successive alkalinity-producing systems: regression analysis. J Environ Qual 30:1015–1022
Laine DM, Jarvis AP (2003) Engineering design aspects of passive in situ remediation of mining effluents. Land Contam Reclam 11(2):113–125
National Coal Board (1982) Technical management of water in the coal mining industry. National Coal Board, London
Skousen J, Rose A, Geidel G, Foreman J, Evans R, Hellier W (1998) Handbook of technologies for avoidance and remediation of acid mine drainage. National Mine Land Reclamation Center, Morgantown
Younger P (2000) The adoption and adaptation of passive treatment technologies for mine waters in the United Kingdom. Mine Water Environ 19:84–97
Ziemkiewicz PF, Skousen JG, Simmons J (2003) Long-term performance of passive acid mine drainage treatment systems. Mine Water Environ 22(3):118–129
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Research Project of the Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources (KIGAM) and Mine Reclamation Corporation (MIRECO) funded by the Ministry of Knowledge Economy of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, DK., Yim, GJ. Computational study on flow characteristics of acid mine drainage in oxidation pond with asymmetric and inclined shape. Environ Earth Sci 72, 757–766 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2999-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2999-2