Abstract
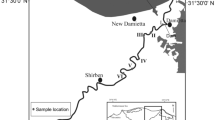
Spatial variations of the water quality in the Haicheng River during April and October 2009 were evaluated for the national monitoring program on water pollution control and treatment in China. The spatial autocorrelation analysis with lower Moran’s I values displayed the spatial heterogeneity of the 12 physicochemical parameters among all the sampling sites of the river. The one-way ANOVA showed that all variables at different sampling sites had significant spatial differences (p < 0.01). Based on the similarity of water quality characteristics, cluster analysis grouped the 20 sampling sites into three clusters, related with less polluted, moderately polluted and highly polluted sites. The factor analysis extracted three major factors explaining 76.4 % of the total variance in the water quality data set, i.e., integrated pollution factor, nitrogen pollution factor and physical factor. The results revealed that the river has been severely polluted by organic matter and nitrogen. The major sources leading to water quality deterioration are complex and ascribed to anthropogenic activities, e.g., domestic and industrial wastewater discharges, agricultural runoff, and animal rearing practices.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anselin L, Syabri L, Kho Y (2006) GeoDa: an introduction to spatial data analysis. Geogr Anal 38:5–22
Bu H, Tan X, Li S, Zhang Q (2010) Water quality assessment of the Jinshui River (China) using multivariate statistical techniques. Environ Earth Sci 60:1631–1639
Bu H, Meng W, Zhang Y (2011) Nitrogen pollution and source identification in the Haicheng River basin in Northeast China. Sci Total Environ 409:3394–3402
Chang H (2008) Spatial analysis of water quality trends in the Han River basin, South Korea. Water Res 42:3285–3304
Environmental Protection Agency of the Haicheng City of Liaoning Province, China (EPAHCLPC) (2010) Environmental quality report in Haicheng City during 2009. Haicheng (in chinese)
Felipe-Sotelo M, Andrade JM, Carlosena A, Tauler R (2007) Temporal characterization of river waters in urban and semi-urban areas using physico-chemical parameters and chemometric methods. Anal Chim Acta 583:128–137
Helena B, Pardo R, Vega M, Barrado E, Fernandez JM, Fernandez L (2000) Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuerga River, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Res 34:807–816
Huang F, Wang X, Lou L, Zhou Z, Wu J (2009) Spatial variation and source apportionment of water pollution in Qiantang River (China) using statistical techniques. Water Res 44:1562–1572
Jain CK (2002) A hydro-chemical study of a mountainous watershed: the Ganga, India. Water Res 36:1262–1274
Jiang Y (2009) China’s water scarcity. J Environ Manage 90:3185–3196
Kannel PR, Lee S, Kanel SR, Khan SP (2007) Chemometric application in classification and assessment of monitoring locations of an urban river system. Anal Chim Acta 582:390–399
Kannel PR, Lee S, Lee YS (2008) Assessment of spatial–temporal patterns of surface and ground water qualities and factors influencing management strategy of groundwater system in an urban river corridor of Nepal. J Environ Manage 86:595–604
Kazi TG, Arain MB, Jamali MK, Jalbani N, Afridi HI, Sarfraz RA, Baig JA, Shah AQ (2009) Assessment of water quality of polluted lake using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:301–309
Liu J, Diamond J (2005) China’s environment in a globalizing world. Nature 435:1179–1186
Mendiguchía C, Moreno C, García-Vargas M (2007) Evaluation of natural and anthropogenic influences on the Guadalquivir River (Spain) by dissolved heavy metals and nutrients. Chemosphere 69:1509–1517
Ongley ED (2004) Non-point source water pollution in China: current status and future prospects. Water Int 29:299–306
Perona E, Bonilla I, Mateo P (1999) Spatial and temporal changes in water quality in a Spanish river. Sci Total Environ 241:75–90
Pillsbury LA, Byrne RH (2007) Spatial and temporal chemical variability in the Hillsborough River system. Mar Chem 104:4–16
Shrestha S, Kazama F (2007) Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environ Model Softw 22:464–475
Simeonov V, Stratis JA, Samara C, Zachariadis G, Voutsa D, Anthemidis A, Sofoniou M, Kouimtzis T (2003) Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Res 37:4119–4124
Singh KP, Malik A, Mohan D, Sinha S (2004) Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)—a case study. Water Res 38:3980–3992
Singh KP, Malik A, Sinha S (2005) Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources of Gomti River (India) using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study. Anal Chim Acta 538:355–374
State Environmental Protection Administration (SEPA) (2002) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, version 4. China Environmental Science Publish Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Wang X (2006) Management of agricultural non-point source pollution in China: current status and challenge. Water Sci Technol 53:1–9
World Health Organization (WHO) (2008) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 3rd edn, incorporating the first and second addenda, Vol 1—Recommendations. Geneva
Wunderlin DA, Diaz MP, Ame MV, Pesce SF, Hued AC, Bistoni MA (2001) Pattern recognition techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variation in water quality—a case study: Suquia River basin (Cordoba Argentina). Water Res 35:2881–2894
Zhu Z, Zhou H, Ouyang T, Deng Q, Kuang Y, Huang N (2001) Water shortage: a serious problem in sustainable development of China. Int J Sustain Dev World 8:233–237
Zilberbran M, Rosenthal E, Shachnai E (2001) Impact of urbanization on hydro-chemical evolution of groundwater and on unsaturated-zone gas composition in the coastal city of Tel Aviv, Israel. J Contam Hydrol 50:175–208
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the “Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment in China” (Grant No. 2008ZX07526-001). The authors express their sincere gratitude to Drs. Weijing Kong and Nan Zhang for their valuable discussion, Xiaobo Jia and Libin Chen for their assistance during the fieldwork, and anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bu, H., Wan, J., Zhang, Y. et al. Spatial characteristics of surface water quality in the Haicheng River (Liao River basin) in Northeast China. Environ Earth Sci 70, 2865–2872 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2348-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2348-5