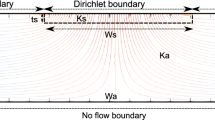
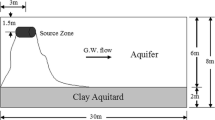
Abstract
Sustainable water quality management requires a profound understanding of water fluxes (precipitation, run-off, recharge, etc.) and solute turnover such as retention, reaction, transformation, etc. at the catchment or landscape scale. The Water and Earth System Science competence cluster (WESS, http://www.wess.info/) aims at a holistic analysis of the water cycle coupled to reactive solute transport, including soil–plant–atmosphere and groundwater–surface water interactions. To facilitate exploring the impact of land-use and climate changes on water cycling and water quality, special emphasis is placed on feedbacks between the atmosphere, the land surface, and the subsurface. A major challenge lies in bridging the scales in monitoring and modeling of surface/subsurface versus atmospheric processes. The field work follows the approach of contrasting catchments, i.e. neighboring watersheds with different land use or similar watersheds with different climate. This paper introduces the featured catchments and explains methodologies of WESS by selected examples.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anibas C, Fleckenstein JH, Volze N, Buis K, Verhoeven R, Meire P, Batelaan O (2009) Transient or steady-state? Using vertical temperature profiles to quantify groundwater-surface water exchange. Hydrol Process 23(15):2165–2177
Barth JAC, Grathwohl P, Jones KC (2007) AquaTerra: pollutant behavior in the soil, sediment, ground, and surface water system. Environ Poll 148(3):693–694
Basu N, Destouni G, Jawitz JW, Thompson SE, Loukinova NV, Darracq A, Zanardo S, Yaeger M, Sivapalan M, Rinaldo A, Rao PSC (2010) Nutrient loads exported from managed catchments reveal emergent biogeochemical stationarity. Geophys Res Lett 37:L23404. doi:10.1029/2010GL045168
Bates BC, Kundzewucz ZW, Wu S, Palutikof JP (eds) (2008) Climate change and water. Technical paper of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. IPCC Secretariat, Geneva, p 210
Bauer HS, Wulfmeyer V, Schwitalla T, Zus F, Grzeschik M (2011) Operational assimilation of GPS slant path delay measurements into the MM5 4DVAR system. Tellus A 63:263–282. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0870.2010.00489.x
Behrendt A, Wulfmeyer V, Di Girolamo P, Kiemle C, Bauer H-S, Schaberl T, Summa D, Whiteman DN, Demoz BB, Browell EV, Ismail S, Ferrare R, Kooi S, Ehret G, Wang J (2007) Intercomparison of water vapor data measured with lidar during IHOP_2002, Part 1: Airborne to ground-based lidar systems and comparisons with chilled-mirror hygrometer radiosondes. J Atmos Oceanic Technol 24(1):3-21. doi:10.1175/JTECH1924.1
Behrendt A, Wulfmeyer V, Riede A, Wagner G, Pal S, Bauer H, Radlach M, Späth F (2009) Three-dimensional observations of atmospheric humidity with a scanning differential absorption Lidar. Proc SPIE 7475:74750L. doi:10.1117/12.835143
Biernath C, Gayler S, Klein C, Bittner S, Högy P, Fangmeier A, Priesack E (2011) Evaluating the ability of four crop models to predict different environmental impacts on spring wheat grown in open-top chambers. Eur J Agron 35:71–82
Bilke (2012) http://www.youtube.com/user/OpenGeoSys
Boano F, Revelli R, Ridolfi L (2010) Effect of streamflow stochasticity on bedform-driven hyporheic exchange. Adv Water Resour 33(11):1367–1374
Bogena et mult (2012) TERENO—Ein langfristiges Beobachtungsnetzwerk für die terrestrische Umweltforschung. Hydrol Wasserbewirt 56(3):138–143
Bonan GB, Lawrence PJ, Oleson KW, Levis S, Jung M, Reichstein M, Lawrence DM, Swenson SC (2011) Improving canopy processes in the Community Land Model version 4 (CLM4) using global flux fields empirically inferred from FLUXNET data. J Geophys Res 116:G02014
Brunner P, Simmons CT (2012) HydroGeoSphere: a fully integrated, physically based hydrological model. Ground Water 50(2):170–175
Caldwell TG, Wöhling T, Young MH, Boyle DP, McDonald EV (2012) Characterization of disturbed desert soils using multi objective parameter optimization. Vadose Zone J. doi:10.2136/vzj2012.0083
Cardenas MB (2009) Stream-aquifer interactions and hyporheic exchange in gaining and losing sinuous streams. Water Resour Res 45(6). doi:10.1029/2008WR007651
Centler F, Shao H, De Biase C, Park C-H, Regnier P, Kolditz O, Thullner M (2010) GeoSysBRNS—a flexible multidimensional reactive transport model for simulating biochemical subsurface processes. Comput Geosci 36:397–405
Cirpka OA, Fienen MN, Hofer M, Hoehn E, Tessarini A, Kipfer R, Kitanidis PK (2007) Analyzing bank filtration by deconvoluting time series of electric conductivity. Ground Water 45(3):318–328
Cook P, Lamontagne S, Berhane D, Clark JF (2006) Quantifying groundwater discharge to Cockburn River, southeastern Australia, using dissolved gas tracers 222Rn and SF6. Water Resour Res 42(10):W10411
Daly GL, Wania F (2005) Organic contaminants in mountains. Critical review. Environ Sci Technol 39:385–398
Delfs J-O, Park C-H, Kolditz O (2009) A sensitivity analysis of Hortonian flow. Adv Water Resour 32(9):1386–1395
Delfs J-O, Blumensaat F, Wang W, Krebs P, Kolditz O (2012) Coupling hydrogeological with surface runoff model in a Poltva case study in Western Ukraine. Environ Earth Sci 65:1439–1459
Delfs J-O, Wang W, Kalbacher T, Maier U, Grathwohl P, Shao H, Kolditz O (2013) Coupling two-phase subsurface flow with overland flow to assess the impact of the gas phase on surface runoff. Environ Earth Sci 69(2) (accepted)
DFG (2012) Strategiepapier “Langzeitperspektiven und Infrastruktur der terrestrischen Forschung Deutschlands—ein systemischer Ansatz”. Arbeitsgruppe “Infrastruktur für die terrestrische Forschung”, Senatskommission für Stoffe und Ressourcen in der Landwirtschaft, Senatskommission für Wasserforschung, Senatskommission für Zukunftsaufgaben der Geowissenschaften, Nationales Komitee für Global Change Forschung
Doro KO, Leven C, Cirpka OA (2013) Delineating subsurface heterogeneity at the Steinlach River Loop using geophysical and hydrogeological methods. Environ Earth Sci (in revision)
EU-WFD (2000) European Water Framework Directive. Eur Off J L327:1–72
Febria CM, Beddoes P, Fulthorpe RR, Williams DD (2012) Bacterial community dynamics in the hyporheic zone of an intermittent stream. ISME J 6(5):1078–1088
Ferguson IM, Maxwell RM (2010) Role of groundwater in watershed response and land surface feedbacks under climate change. Water Resour Res 46: W00F02
Fleckenstein JH, Krause S, Hannah DM, Boano F (2010) Groundwater-surface water interactions: new methods and models to improve understanding of processes and dynamics. Adv Water Resour 33(11):1291–1295
Gayler S, Ingwersen J, Priesack E, Wöhling T, Wulfmeyer V, Streck T (2013) Assessing the relevance of sub surface processes for the simulation of evapotranspiration and soil moisture dynamics with CLM3.5: comparison with field data and crop model simulations. Environ Earth Sci 69(2). doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2309-z
Gocht T, Ligouis B, Hinderer M, Grathwohl P (2007) Accumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rural soils based on mass balances at the catchment scale. Environ Toxicol Chem 26(4):591–600
Gooseff MN, LaNier J, Haggerty R, Kokkeler K (2005) Determining in-channel (dead zone) transient storage by comparing solute transport in a bedrock channel-alluvial channel sequence, Oregon. Water Resour Res 41(6). doi:10.1029/2004WR003513
Grzeschik M, Bauer H-S, Wulfmeyer V (2008) Four-dimensional variational analysis of water-vapor Raman lidar data and their impact on mesoscale forecasts. J Atmos Oceanic Technol 25:1437–1453
Grzeschik M, Schwitalla T, Bauer H-S, Wulfmeyer V (2012) Comparison of WRF 3D-Var with the DART EnKF for a COPS IOP. 6th HyMeX workshop, Primosten, 7–10 May 2012
Haberer CM, Rolle M, Liu S., Cirpka OA, Grathwohl P (2011) A high-resolution non-invasive approach to quantify oxygen transport across the capillary fringe and within the underlying groundwater. J Contam Hydrol 122:26–39. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2010.10.006
Haggerty R, Argerich A, Marti E (2008) Development of a ‘‘smart’’ tracer for the assessment of microbiological activity and sediment-water interaction in natural waters: The resazurin-resorufin system. Water Resour Res 44(6). doi:10.1029/2007WR006670
Haggerty R, Marti E, Argerich A, von Schiller D, Grimm NB (2009) Resazurin as a “smart’’ tracer for quantifying metabolically active transient storage in stream ecosystems. J Geophys Res 114. doi:10.1029/2008JG000942
HVZ Sachsen-Anhalt (2012) Landesbetrieb für Hochwasserschutz und Wasserwirtschaft Hochwasservorhersagezentrale Sachsen-Anhalt. http://www.hochwasservorhersage.sachsen-anhalt.de
Ingwersen J, Steffens K, Högy P, Warrach-Sagi K, Wizemann H-D, Zhunusbayeva D, Poltoradnev M, Gäbler R, Fangmeier A, Wulfmeyer V, Streck T (2011) Comparison of NOAH simulations with eddy covariance and soil water measurements at a winter wheat stand. Agric For Meteorol 151:345–355
Jiménez PA, Dudhia J, González-Rouco JF, Navarro J, Montávez JP, García-Bustamante E (2012) A revised scheme for the WRF surface layer formulation. Mon Weather Rev 140:898–918
Kalbacher T, Delfs JO, Shao H et al (2012) The IWAS-ToolBox: software coupling for an integrated water resources management IWAS SI. Environ Earth Sci 65(5):1367–1380
Kalbus E, Reinstorf F, Schirmer M (2006) Measuring methods for GW-surface water interactions: a review. HESS 10(6):873–887
Köhne JM, Wöhling T, Pot V, Benoit P, Leguédois S, Le Bissonnais Y, Šimrunek J (2011) Coupled simulation of surface runoff and soil water flow using multi-objective parameter estimation. J Hydrol 403:141–156
Kolditz O, Rink K, Shao HB, Kalbacher T, Zacharias S, Kunkel R, Dietrich P (2012) International viewpoint and news: data and modelling platforms in environmental earth sciences. Environ Earth Sci 66:1279–1284
Kunkel R, Sorg J, Eckardt R, Kolditz O, Rink K (2013) TEODOOR—a distributed geodata infrastructure for terrestrial observation data. Environ Earth Sci (in revision)
Lausch A, Pause M, Merbach I, Zacharias S, Doktor D, Volk M, Seppelt R (2012) A new multiscale approach for monitoring vegetation using remote sensing-based indicators in laboratory, field, and landscape. Environ Monit Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-012-2627-8
Lawrence DM, Oleson KW, Flanner MG, Thornton PE, Swenson SC, Lawrence PJ, Zeng X, Yang Z-L, Levis S, Sakaguchi K, Bonan GB, Slater AG (2011) Parameterization Improvements and Functional and Structural Advances in Version 4 of the Community Land Model. J Adv Model Earth Syst 3(27) Art. 2011MS000045:27
Lemke D, Liao Z, Cirpka OA (2012) Ermittlung von hyporheischen Austauschflüssen und deren Verweilzeiten mit Hilfe von reaktiven und konservativen Tracern. Tag der Hydrologie 2012, March 22–23, 2012, Freiburg, Germany, 54–58
Lemke D, Schnegg PA, Schwientek M, Osenbrück K, Cirpka OA (2013) A field fluorometer for the simultaneous online-measurement of conservative (Na-fluorescein) and reactive tracers (resazurin, resorufin). Environ Earth Sci 69(2). doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2305-3
Leube PC, Geiges A, Nowak W (2012) Bayesian assessment of the expected data impact on prediction confidence in optimal sampling design. Water Resour Res 48 W02501. doi:10.1029/2010WR010137
Liao Z, Cirpka OA (2011) Shape-free inference of hyporheic travel-time distributions from conservative and reactive tracer tests in streams. Water Resour Res 47(7). doi:10.1029/2010WR009927
Liu Y, Beckingham B, Rügner H, Li Zhe, Ma Limin, Schwientek M, Xies Huan, Zaoh Jianfu, Grathwohl P (2013) Comparison of sedimentary PAHs in the Rivers of Ammer (Germany) and Liangtan (China): differences between early- and newly-industrialized countries. Environ Sci Technol. doi:10.1021/es3031566
Maier U, Flegr M, Rügner H, Grathwohl P (2013) Long-term solute transport and geochemical equilibria in seepage water and groundwater in a catchment cross section. Envron Earth Sci 69(2) (accepted)
Martin H, Patterson BM, Davis GB, Grathwohl P (2003) Comparative field trial of time-integrated aqueous contaminant monitoring with ceramic dosimeters and conventional water sampling. Environ Sci Technol 37(7):1360–1364
Maxwell RM, Kollet SJ (2008) Interdependence of groundwater dynamics and land-energy feedbacks under climate change. Nature Geosci 1(10):665–669
Maxwell RM, Chow FK, Kollet SJ (2007) The groundwater–land–surface–atmosphere connection: soil moisture effects on the atmospheric boundary layer in fully-coupled simulations. Adv Water Resour 30(12):2447–2466
Maxwell RM, Lundquist JK, Mirocha JD, Smith SG, Woodward CS, Tompson AFB (2011) Development of a coupled groundwater-atmosphere model. Mon Weather Rev 139(1):96–116
Moore CR, Wöhling T, Wolf L (2011) Optimisation of monitoring data for increased predictive reliability of regional water allocation models. In: sustaining our future—Proceedings of the MODSIM11 international congress on modelling and simulation, Perth, 12–16 Dec 2011
News Nature (2008) Enough water to go around? Nature 452(7185):253–310
Niu G-Y, Yang Z-L, Mitchell KE, Chen F, Ek MB, Barlage M, Kumar A, Manning K, Niyogi D, Rosero E, Tewari M, Xia Y (2012) The community Noah land surface model with multiparameterization options (Noah-MP): 1. Model description and evaluation with local-scale measurements. J Geophys Res 116:D12109
Nowak W (2010) Measures of parameter uncertainty in geostatistical estimation and geostatistical optimal design. Math Geosc 42(2):199–221
Nowak W, Rubin YN, de Barros FPJ (2010) Bayesian geostatistical design: Task-driven optimal site investigation when the geostatistical model is uncertain. Water Resour Res 46(W03535), doi:10.1029/2009WR008312
Nowak W, Rubin YN, de Barros FPJ (2012) A hypothesis-driven approach to optimize field campaigns. Water Resour Res. doi:10.1029/2011WR011016
Ollesch G (2008) Erfassung und Modellierung der Schneeschmelzerosion am Beispiel der Kleineinzugsgebiete Schäfertal (Deutschland) und Lubazhinkha (Russland), Habilitationsschrift Fakultät für Geowissenschaften, Geotechnik und Bergbau der TU Bergakademie Freiberg, p 213
Osenbrück K, Wöhling Th, Lemke D, Rohrbach N, Schwientek M, Leven C, Castillo Alvarez C, Taubald H, Cirpka OA (2013) Assessing hyporheic exchange and associated travel times by hydraulic, chemical, and isotopic monitoring at the Steinlach Test Site, Germany. Environ Earth Sci 69(2). doi:10.1007/s12665-012-2155-4
Park C-H, Beyer C, Bauer S et al (2008) Using global node-based velocity in random walk particle tracking in variably saturated porous media: application to contaminant leaching from road constructions. Environ Geol 55(8):1755–1766
Patton EG, Sullivan PP, Moeng CH (2005) The influence of idealized heterogeneity on wet and dry planetary boundary layers coupled to the and surface. J Atmos Sci 62:2078–2097
Pause M, Schulz K, Zacharias S, Lausch A (2012) Near-surface soil moisture estimation by combining airborne L-band brightness temperature observations and imaging hyperspectral data at the field scale. J Appl Rem Sens, accepted
Pause M, Lausch A, Jagdhuber T, Hejnsek I, Denk A (2013) WESS/TERENO Env Sens observations 2011: toward multi-sensor land surface parameter retrieval at the small catchment scale. Environ Earth Sci (in revision)
Reinstorf F, Wollschläger U, John H, Tiedke J (2013) The Schäfertal catchment/Harz Mountains—site description, observation programme and recent runoff modelling results. Environ Earth Sci (in revision)
Rink K, Fischer T, Selle B, Kolditz O (2013) A data exploration framework for validation and setup of hydrological models. Environ Earth Sci 69(2). doi:10.1007/s12665-012-2030-3
Robinson DA, Binley A, Crook N, Lewis FD, Ferré TPA, Grauch VJS, Knight R, Knoll M, Lakshmi V, Miller R, Nyquist J, Pellerin L, Singha K, Slater L (2008) Advancing process-based watershed hydrological research using near-surface geophysics: a vision for, and review of, electrical and magnetic geophysical methods. Hydrol Process 22:3604–3635. doi:10.1002/hyp.6963
Rossi L, Chèvre N, Fankhauser R, Margot J, Curdy R, Babut M, Barry DA (2013) Sediment contamination assessment in urban areas based on total suspended solids. Water Res 47:339–350
Rotach MW, et mult. (2009) MAP D-PHASE: Realtime demonstration of weather forecast quality in the Alpine Region. Bull Amer Meteor Soc 90:1321–1336. doi:10.1175/2009BAMS2776.1
Rügner H, Schwientek M, Beckingham B, Kuch B, Grathwohl P (2013) Turbidity as a proxy for total suspended solids (TSS) and particle facilitated transport in catchments. Environ Earth Sci 69(2). doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2307-1
Samaniego L, Kumar R, Attinger S (2010) Multiscale parameter regionalization of a grid-based hydrologic model at the mesoscale. Water Resour Res 46:W05523, doi:10.1029/2008WR007327
Santanello J, Peters-Lidard C, Kumar S, Alonge C, Tao WK (2009) A modeling and observational framework for diagnosing local land-atmosphere coupling on diurnal time scales. J Hydrom 10(3):577–599
Schmidt C, Bayer-Raich M, Schirmer M (2006) Characterization of spatial heterogeneity of groundwater-stream water interactions using multiple depth streambed temperature measurements at the reach scale. HESS 10:849–859
Schöniger A, Nowak W, Hendricks Franssen H-J (2012) Parameter estimation by ensemble Kalman filters with transformed data: Approach and application to hydraulic tomography. Water Resour Res 48(4). doi:10.1029/2011WR010462
Schwientek M, Rügner H, Beckingham B, Kuch B, Grathwohl P (2013a) Integrated monitoring of transport of persistent organic pollutants in contrasting catchments. Env Poll, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.09.004
Schwientek M, Osenbrück K, Fleischer M (2013b) Investigating hydrological drivers of nitrate export dynamics in two agricultural catchments in Germany using high-frequency data series. Environ Earth Sci (in revision)
Schwitalla T, Bauer H-S, Wulfmeyer V, Aoshima F (2011) High-resolution simulation over central Europe: assimilation experiments during COPS IOP 9c. Q J R Meteorol Soc 137(S1):156–175
Selle B, Rink K, Kolditz O (2013) Recharge and discharge controls on groundwater travel times and flow paths to production wells for the Ammer catchment in south-western Germany. Environ Earth Sci 69(2) (accepted)
Smith JWN, Surridge BWJ, Haxton TH, Lerner DN (2009) Pollutant attenuation at the groundwater-surface water interface: a classification scheme and statistical analysis using national-scale nitrate data. J Hydrol 369:392–402
Spanoudaki K, Stamou AI, Nanou-Giannarou A (2009) Development and verification of a 3-D integrated surface water–groundwater model. J Hydrol 375:410–427
Sudicky E, Jones J, Park Y, Brookfield A, Colautti D (2008) Simulating complex flow and transport dynamics in an integrated surface-subsurface modeling framework. Geosci J 12(2):107–122
Sulis M, Meyerhoff SB, Paniconi C, Maxwell RM, Putti M, Kollet SJ (2010) A comparison of two physics-based numerical models for simulating surface water-groundwater interactions. Adv Water Resour 33(4):456–467
Sulis M, Paniconi C, Rivard C, Harvey R, Chaumont D (2011) Assessment of climate change impacts at the catchment scale with a detailed hydrological model of surface-subsurface interactions and comparison with a land surface model. Water Res. Research 47 W01513. doi:10.1029/2010WR009167
United Nations (2012) World Water Development Report, 4th edition: managing water under uncertainty and risk. United Nations, New York
USGS (2007) Water-quality assessment of the high plains aquifer, 1999–2004 In: McMahon PB, Dennehy KF, Bruce BW, Gurdak JJ, Qi SL (eds) National water-quality assessment program, Professional Paper 1749
Vogt T, Hoehn E, Schneider P, Freund A, Schirmer M, Cirpka OA (2010a) Fluctuations of electrical conductivity as a natural tracer for bank filtration in a losing stream. Adv Water Resour 33(11):1296–1308. doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2010.02.007
Vogt T, Schneider P, Hahn-Woernle L, Cirpka OA (2010b) Estimation of seepage rates in a losing stream by fiber-optic high-resolution vertical temperature profiling. J Hydrol 380(1–2):154–164. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.10.033
Vörösmarty CJ, Green PA, Salisbury J, Lammers RB (2000) Global water resources: vulnerability from climate change and population growth. Science 289:284–288
Vrugt JA, Robinson BA (2007) Improved evolutionary optimization from genetically adaptive multimethod search. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 104:708–711. doi:10.1073/pnas.0610471104
Warrach-Sagi K, Wulfmeyer V (2010) Streamflow data assimilation for soil moisture analysis. Geosci Model Dev 3:1–12
Warrach-Sagi K, Schwitalla T, Wulfmeyer V, Bauer HS (2012) Evaluation of a CORDEX-Europe simulation based on the WRF-NOAH Model System: precipitation in Germany. Clim Dyn (in revision)
Wöhling T, Vrugt JA (2011) Multi-response multi-layer vadose zone model calibration using Markov chain Monte Carlo simulation and field water retention data. Water Resources Research 47:doi:10.1029/2010WR009265
Wöhling T, Bidwell VJ, Barkle GF (2012a) Dual-tracer, non-equilibrium mixing cell modelling and uncertainty analysis for unsaturated bromide and chloride transport. J Cont Hydrol. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2012.08.001
Wöhling T, Gayler S, Ingwersen J, Streck T, Vrugt JA, Priesack E (2012b) Multi-objective calibration of coupled soil–vegetation–atmosphere models. In: Models—repositories of knowledge. Proceedings Model CARE 2011, September 19–22, 2011, Vol 355. IAHS Publ, Leipzig, Germany, pp 357–363
Wöhling T, Samaniego L, Kumar R (2013) Evaluating multiple performance criteria to calibrate distributed hydrological models of the upper Neckar catchment. Environ Earth Sci 69(2). doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2306-2
Wollschläger U, et mult. (2013) The Bode Catchment as part of the TERENO Harz/Central German Lowland Observatory: a platform for integrated interdisciplinary hydrological research. Environ Earth Sci (to be submitted)
World Economic Forum Water Initiative (2009) Managing our future water needs for agriculture, industry, human health and the environment. Draft for Discussion—Meeting of the World Economic Forum, January 2009
Wulfmeyer V, et mult. (2011) The convective and orographically induced precipitation study (COPS): the scientific strategy, the field phase, and first highlights. COPS Special Issue of the Q. J. R. Meteorol Soc 137:3–30
Wulfmeyer V, Bauer H-S, Grzeschik M, Behrendt A, Vandenberghe F, Browell EV, Ismail S, Ferrare R (2006) 4-dimensional variational assimilation of water-vapor differential absorption lidar data: the first case study within IHOP_2002. Mon Wea Rev 134:209–230
Zacharias S, Bogena H, Samaniego L, Mauder M, Fuß R, Pütz T, Frenzel M, Schwank M et al (2011) A network of terrestrial environmental observatories in Germany. Vadose Zone J 10(3):955–973
Zimmermann JB, Mihelcic JR, Smith J (2008) Global stressors on water quality and quantity. Environ Sci Technol 42(12):4247–4254
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Ministry of Science, Research and Arts of Baden-Württemberg (AZ Zu 33-721.3-2) and the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research—UFZ, Leipzig. Research in the Bode Catchment was in addition supported by TERENO (TERrestrial ENvironmental Observatories).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grathwohl, P., Rügner, H., Wöhling, T. et al. Catchments as reactors: a comprehensive approach for water fluxes and solute turnover. Environ Earth Sci 69, 317–333 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2281-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2281-7