Abstract
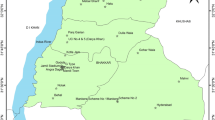
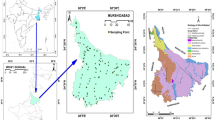
Bardsir plain is located in the central part of Kerman Province of Iran. The relative prevalence of arsenic-related cancers, the high concentration of arsenic in nearby plains, as well as the recharge of this aquifer through the mountains composed of high-sulfide volcanic rocks have been motivations of the authors to study the concentration of this element in Bardsir plain. Arsenic concentration was measured in 63 groundwater samples using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry method. The results were evaluated through iso-concentration maps, correlation diagrams, and multivariate statistical methods. Accordingly, the concentration of arsenic ranges from 1.3 to 464.5 μg/l with an average value of 134.2 μg/l. So, the groundwaters are enriched with arsenic to much higher levels than permitted for than drinking water acceptable level (10 μg/l). The high arsenic levels in groundwaters of Bardsir plain are ascribed to joint influence of decomposition of sulfides present in mountainous volcanic rocks and the mixing with hydrothermal waters in some locations. Supposedly, the prevalence of higher than 8 pH values has enhanced the release of arsenic from Fe-hydroxides generated during sulfide weathering process.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argos M, Kalra T, Pierce BL, Chen Y, Parvez F, Islam T, Ahmed A, Hasan R, Hasan K, Sarwar G, Levy D, Slavkovich V, Graziano JH, Rathouz PJ, Ahsan H (2011) A prospective study of arsenic exposure from drinking water and incidence of skin lesions in Bangladesh. Am J Epidemiol 174(2):185–194
Armienta MA, Rodriguez R, Cruz O, Aguayo A, Ceniceros N, Vilasenor G, Ongley LK, Mango H (2005) Environmental behavior of arsenic in a mining zone: Zimapan, Mexico. In: Bundschuh J, Bhattacharya P, Chndrasekharam D (eds) Natural arsenic in groundwater: occurrence, remediation and management, pp 125–130
Baeyens W, De Brauwere A, Brion N, De Gieter M, Leermakers M (2007) Arsenic speciation in the River Zenne, Belgium. Sci Total Environ 384:409–419
BAMWSP (2005) Bangladesh arsenic mitigation water supply project (BAMWSP). Upazila wise summary results. http://www.bwspp.org/BAMWSPContents/Survey%20Result/Upazila%20Summary.pdf
BGS and DPHE (2001) Arsenic contamination of groundwater in Bangladesh (four volumes). British geological survey (see http://www.bgs.ac.uk/Arsenic)
Bhattacharya P, Claesson M, Bundschuh j, Sracek O, Fagerberg J, Jacks G, Martin RA, Storniolo AD, Thir JM (2006) Distribution and mobility of arsenic in the Rio Dulce alluvial aquifers in Santiago del Estero Province, Argentina. Sci Total Environ 358:97–120
Chakraborti D, Biswas BK, Chowdhury TR, Basu GK, Mandal BK, Chowdhury UK, Mukherjee SC, Gupta JP, Chowdhury SR, Rathore KC (1999) Arsenic groundwater contamination and sufferings of people in Rajnandgaon district, Madhaya Pradesh, India. Curr Sci 77:502–504
Craiud A, Fouillac C (1989) The distribution of arsenic (III) and arsenic (V) in geothermal waters: examples from the Massif Central of France, the Island of Dominica in the Leeward Islands of the Caribbean, the Valles Caldera of New Mexico, USA, and southwest Bulgaria. Chem Geol 76:259–269
Dehghani M (2009) Environmental hydrogeochemistry of groundwaters resources of Anar Plain. M.Sc. Thesis (in Persian), Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, p 176
Dehghani M, Abbasnejad A (2011) Pollution of Anar Plain’s groundwater with respect to Cadmium, Arsenic, Lead and Nitrate. J Environ Stud 36(56):87–100 (in Persian)
DelValls TA, Forja JM, Gonzalez-Mazo E, Gomez-Parra A (1998) Determining contamination sources in marine sediments using multivariate analysis. Trend Anal Chem 17:181–192
Ebrahimi M (2009), Evaluation of Arsenic dispersivity and the survey of the source of Arsenic in Groundwaters of Rafsanjan plain and represent the suitable ways of removal arsenic. M.Sc. Thesis (in Persian), Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, p 203
Fernández MI, López JF, Vivaldi B, Coz F (2012) Long-term impact of arsenic in drinking water on bladder cancer health care and mortality rates 20 years after end of exposure. J Urol 187(3):856–861
Harvey CF, Swartz Ch, Badruzzaman ABM, Keon-Blute N, Yu W, Ali MA, Jay J, Beckie R, Niedan V, Brabander D, Oates PM, Ashfaque KN, Islam S, Hemond HF, Ahmed MF (2002) Arsenic mobility and groundwater extraction in Bangladesh. Science 298:1602–1606
Kaiser HF (1960) The application of electronic computers to factor analysis. Educ Psychol Meas 20:141–151
Khajehpour S (2007) Assessment of the concentration of heavy metals in groundwaters of Southern Rafsanjan Plain, focusing on the likely effects of Sarcheshmeh Copper Complex. M.Sc. Thesis (in Persian), Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, p 154
Klamp S, Kipfer R, Cirpka OA, Harvey CF, Brennwald MS, Ashfaque KN, Badruzzaman ABM, Hug SJ, Imboden DM (2006) Groundwater dynamics and arsenic mobilization in Bangladesh assessed using noble gases and tritium. Environ Sci Technol 40:243–250
Komnitsas K, Xenidis A, Adam K (1995) Oxidation of pyrite and arsenopyrite in sulphidic spoils in Lavrion. Miner Eng 12:1443–1454
Ma HZ, Xia YJ, Wu KG, Sun TZ, Mumford JL (1999) Human exposure to arsenic and health effects in Bayingormen, Inner Mongolia. In: Chappell WR, Abernathy CO, Calderon RL (eds) Arsenic exposure and health effects. Amsterdam, Elsevier, pp 127–131
Medical Geology Atlas of Iran (2009) Geological Survey of Iran (in Persian)
Ning Z, Lobdell DT, Kwok RK, Liu Z, Zhang S, Ma C, Riediker M, Mumford JL (2007) Residential exposure to drinking water arsenic in Inner Mongolia, China. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 222:351–356
Pandey PK, Yadav S, Nair S, Bhui A (2002) Arsenic contamination of the environment—a new perspective from central-east India. Environ Int 28:235–245
Raju NJ (2012) Arsenic exposure through groundwater in the middle Ganga plain in the Varanasi environs, India: a future threat. J Geol Soc India 17:302–314
Regional Water Organization of Kerman (2009) Internal report (in Persian) 1:21–45
Rosenboom JW (2004) Not just red or green. An analysis of arsenic data from 15 upazilas in Bangladesh. APSU, Arsenic Policy Support Unit, Bangladesh
Shojaaheidari R (2008) The effect of agriculture on the quality and quantity of groundwaters in Jiroft area. M.Sc. Thesis (in Persian), Shahid Beheshti University, p 126
Smedley PL (2006) Source and distribution of arsenic in groundwater and aquifers. Proceedings of arsenic in groundwater—a world problem, pp 4–32
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2005) Arsenic in groundwater and the environment. In: Selinus O, Alloway B, Smedley PL, Centeno JA, Finkelman RB, Fuge R, Lindh U (eds) Essentials of medical geology: impacts of the natural environment on public health. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 263–299
Smedley PL, Zhang M-Y, Zhang G-Y, Luo Z-D (2003) Mobilisation of arsenic and other trace elements in fluviolacustrine aquifers of the Huhhot Basin, Inner Mongolia. Appl Geochem 18:1453–1477
Smedley PL, Knudsen J, Maiga D (2007) Arsenic in groundwater from mineralised Proterozoic basement rocks of Burkina Faso. Appl Geochem 22:1074–1092
Smith AH, Goycolea M, Haque R, Biggs ML (1998) Marked increase in bladder and lung cancer mortality in a region of Northern Chile due to arsenic in drinking water. Am J Epidemiol 147(7):660–669
Swedlund PJ, Webster JG (1998) Arsenic removal from geothermal bore waters: the effect of mono-silisic acid. In: Arehart GB, Hulston JR (eds) Water–rock interaction. Balkema Publishers, Rotterdam, pp 947–950
Thornton I (1994) Sources and pathways of arsenic in south-west England: health implications. In: Chappell WR, Abernathy CO and Cothern CR (eds) Arsenic exposure and health. Science and Technology Letters, Northwood, pp 61–69
Van Geen A, Zheng Y, Versteeg R, Stute M, Horneman A, Dhar R, Steckler M, Gelman A, Small C, Ahsan H, Graziano JH, Hussain I, Ahmed KM (2003) Spatial variability of arsenic in 6000 tube wells in a 25 km(2) area of Bangladesh. Water Resources Research, vol. 39, art. No.1140
Wilkie JA, Hering JG (1998) Rapid oxidation of geothermal arsenic (III) in streamwaters of the eastern Sierra Nevada. Environ Sci Technol 32:657–662
Williams M, Fordyce F, Paijitprapapon A, Charoenchaisri P (1996) Arsenic contamination in surface drainage and groundwater in part of the southeast Asian tin belt, Nakhon Si Thammarat Province, southern Thailand. Environ Geol 27:16–33
Yongming H, Peixuan D, Junji C, Posmentier ES (2006) Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Sci Total Environ 355:176–186
Yu GQ, Sun DJ, Zheng Y (2007) Health effects of exposure to natural arsenic in groundwater and coal in China: an overview of occurrence. Environ Health Perspect 115:636–642
Zheng Y, van Geen A, Stute M, Dhar R, Mo Z, Cheng Z, Horneman A, Gavrieli I, Simpson HJ, Versteeg R, Steckler M, Grazioli-Venier A, Goodbred S, Shahnevaz M, Shamsudduha M, Hoque MA, Ahmed KM (2005) Geochemical and hydrogeological contrasts between shallow and deeper aquifers in two villages of Araihazar, Bangladesh: implication for deeper aquifers as drinking water sources. Geochimicla et Cosmochimica Acta 69:5203–5218
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbasnejad, A., Mirzaie, A., Derakhshani, R. et al. Arsenic in groundwaters of the alluvial aquifer of Bardsir plain, SE Iran. Environ Earth Sci 69, 2549–2557 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-2079-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-2079-z