Abstract
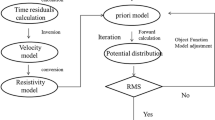
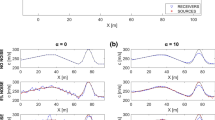
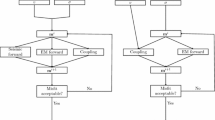
The simultaneous inversion of multiple geophysical data types has been proven to be a powerful tool to both improve subsurface imaging and help in the interpretation process. The main goal of this paper was to develop joint inversion strategies to provide improved resistivity and seismic velocity images for delineating saline water zones in karstic geological formations. The cross-gradient constraint approach was adopted to jointly invert resistivity and seismic first arrival data. The basic idea of this approach is to quantitatively estimate the structural similarity between resistivity and seismic velocity models, using the cross product of their gradients and to achieve a unified geological model which satisfies both data sets. Initially, synthetic data were employed to help develop a joint inversion strategy to be used over such complex geological structures. The proposed strategy uses a weighting factor for the cross-gradient constraints and separate damping factors for the resistivity and seismic data. This strategy was applied successfully on field data from the karstic region of Stilos, Crete, Greece.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul Nassir SS, Loke MH, Nawawi MN (2000) Salt-water intrusion mapping by geoelectrical imaging surveys. Geophys Prospect 48:647–661
Albouy Y, Andrieux P, Rakotonondrasoa G, Ritz M, Descloitres M, Join JL, Rasolomanana E (2001) Mapping coastal aquifers by joint inversion of DC and TEM soundings—three case histories. Groundwater 39:87–97
Athanasiou EA, Tsourlos PI, Papazachos CB, Tsokas GN (2007) Combined weighted inversion of electrical resistivity data arising from different array types. J Appl Geophys 62:124–140
Balia R, Gavaudo E, Ardau F, Ghiglieri G (2003) Geophysical approach to the environmental study of a coastal plain. Geophysics 68:1446–1459
Berge PA, Berryman JG, Bertete-Aguirre H, Bonner P, Roberts J, Wildenschild D (2000) Joint inversion of geophysical data for site characterization and restoration monitoring. LLNL rep. URCL-ID-128343. Proj. 55411, Lawrence Livermore Natl. Lab., Livermore
Constable SC, Parker RL, Constable CG (1987) Occam’s inversion: a practical algorithm for generating smooth models from electromagnetic sounding data. Geophysics 52:289–300
Dey A, Morrison HF (1979) Resistivity modeling for arbitrary shaped three-dimensional shaped structures. Geophysics 44:753780
Dobroka M, Gyulai A, Ormos T, Csokas J, Dresen L (1991) Joint inversion of seismic and geoelectric data recorded in an underground coal mine. Geophys Prospect 39:643–665
Gallardo LA, Meju MA (2003) Characterization of heterogeneous near-surface materials by joint 2D inversion of DC resistivity and seismic data. Geophys Res Lett 30:1658. doi:10.1029/2003GL017370
Gallardo LA, Meju MA (2004) Joint two-dimensional DC resistivity and seismic travel time inversion with cross-gradients constrains. J Geophys Res 109:B03311. doi:10.1029/2003JB002716
Gnanasundar D, Elango L (1999) Groundwater quality assessment of a coastal aquifer using geoelectrical techniques. J Environ Hydrol 7:34113419
Haber E, Oldenburg D (1997) Joint inversion: a structural approach. Inverse Prob 13:63–77
Haeni FP (1986) Application of seismic refraction methods in groundwater modeling studies in New England. Geophysics 51:236–249
Hamdan AH and Vafidis A (2009) Inversion techniques to improve the resistivity images over karstic structures. Proceedings of the 15th European Meeting of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics. 3–5 September 2009, Dublin, Ireland
Hamdan AH, Kritikakis G, Andronikidis N, Economou N, Manoutsoglou E, Vafidis A (2010) Integrated geophysical methods for imaging saline karst aquifers: a case study of Stylos, Chania, Greece. J Balkan Geophys Soc 13:1–8
Hering A, Misiek R, Gyulai A, Ormos T, Dobroka M, Dersen L (1995) A joint inversion algorithm to process geoelectrical and surface wave seismic data. Geophys Prospect 43:135–156
Imhof AL, Guell AE, Villagra SM (2001) Resistivity sounding method applied to saline horizons determination in Colonia Lloveras-San Juan Province-Argentina. Brazilian J Geophys 19(3):263–278
Jarvis KD, Knight RJ (2002) Aquifer heterogeneity from SH-wave seismic impedance inversion. Geophysics 67:1548–1557
Kuras O, Meldrum PI, Ogilvy RD, Gisbert J, Joretto S, Sanchez MF (2005) Imaging sea water intrusion in coastal aquifers with electrical resistivity tomography: initial results from the lower Andarax delta, SE Spain. In: Proceedings, 11th Annual Meeting EAGE-Near-Surface Geophysics Conference, Palermo, Sicily, Italy
Lashkaripour GR (2003) An investigation of groundwater condition by geoelectrical resistivity method: a case study in Korin aquifer, southeast Iran. J Spatial Hydrol 3(1):1–5 (Fall 2003)
Lines LR, Schultz AT, Treitel S (1988) Cooperative inversion of geophysical data. Geophysics 53:8–20
Maier D, Maurer HR, Green AG (1995) Joint inversion of related data sets: DC-resistivity and transient electromagnetic soundings. 1st Annual Symposium Environmental and Engineering, Geophysics Society (European Section), (Exp abst.), pp 461–464
McGillivray P, Oldenburg D (1990) Methods for calculating Frechet derivatives and sensitivities for the non-linear inverse problem: a comparative study. Geophys Prospect 38:499–524
Mela Κ (1997) Viability of using seismic data to predict hydrogeological parameters. Presented at SAGEEP, Reno/Sparks, Nevada
Menke W (1989) Geophysical data analysis: discrete inverse theory. Academic Press, New York
Michalakis I, Economou N, Hamdan H, Vafidis A, Manoutsoglou E, Panagopoulos G, Roubedakis S, Vozinakis C, Lampathakis S, and Dassyra E (2006) Geological and geophysical study of saltwater contamination at Stylos, Crete. Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference Advances in Mineral Resources Management and Environmental Geotechnology (AMIREG), 25–27 September, Chania, Greece
Moser TJ (1991) Shortest path calculation of seismic rays. Geophysics 56:59–67
Ogilvy RD, Kuras O, Meldrum PI, Wilkinson PB, Chambers JE, Sen M, Tsourlos P (2009) Monitoring saline intrusion of a coastal aquifer with automated electrical resistivity tomography. In: Proceedings, 15th Annual Meeting EAGE-Near-Surface Geophysics Conference, Dublin, Ireland
Park SK, Van GP (1991) Inversion of pole–pole data for 3-D resistivity structure beneath arrays of electrodes. Geophysics 56:951–960
Raiche AP, Jupp DLP, Rutters H, Vozof K (1985) The joint use of coincident loop transit electromagnetic and Schlumberger sounding to resolve layered structures. Geophysics 50:1618–1627
Sandberg AK (1993) Examples of resolution improvements in geoelectrical soundings applied to groundwater investigations. Geophys Prospect 41:207–227
Schmutz M, Albouy Y, Guerin R, Maquaire O, Vassal J, Schott JJ, Descloitres M (2000) Joint electrical and time domain electromagnetism (TDEM) data inversion applied to the Super Sauze earthflow (France). Surveys Geophys 21:371–390
Singh UK, Das RK, Hodlur GK (2004) Significance of Dar-Zarrouk parameters in the exploration of quality affected coastal aquifer systems. Environ Geol 45:697–702
Soupios MP, Papazaxoz CP, Johlin C, Tsokas GN (2001) Nonlinear three-dimensional traveltime inversion of crosshole data with an application in the area of Middle Urals. Geophysics 66:627–636
Soupios P, Kalisperi D, Kanta A, Kouli M, Barsukov P, Vallianatos F (2010) Coastal aquifer assessment based on geological and geophysical survey, northwestern Crete, Greece. Environ Earth Sci 61(1):63–77
Sumanovac F, Weisser M (2001) Evaluation of resistivity and seismic methods for hydrogeological mapping in karst terrains. J Appl Geophys 47:13–28
Tillman A, Stocker T (2000) A new approach for the joint inversion of seismic and geoelectric data. Presented at 63th EAGE Conference and Technical Exhibition, European Association of Geoscience and Engineering, Amsterdam
Tsourlos P (1995) Modelling, Interperetation and Inversion of Multielectrode Survey Data. PHD Thesis, University of York
Tsourlos PI, Szymanski JE, Tsokas GN (1998) A smoothness constrained algorithm for the fast 2-D inversion of DC resistivity and induced polarization data. J Balkan Geophys Soc 1:3–13
Vozof K, Jupp DLB (1975) Joint inversion of geophysical data. Geophys J R Astr Soc 42:977–991
Zhang J, Morgan FD (1997) Joint seismic and electrical tomography. Annual Symposium Environmental and Engineering, Geophysics Society (SAGEEP) Exp. Abst., pp 391–395
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. Panayiotis Tsourlos and Dr. Pantelis Soupios for providing their codes. They also wish to thank Mr. Nikos Andronikidis, Dr. Nikos Economou and Dr. George Kritikakis, collaborators at TUC, for the great help during the field data acquisition. This paper is part of the 03ED375 Research Project, implemented within the framework of the “Reinforcement Programme of Human Research Manpower” (PENED) and co-financed by National and Community Funds (25 % from the Greek Ministry of Development General Secretariat of Research and Technology and 75 % from E.U. European Social Fund).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamdan, H.A., Vafidis, A. Joint inversion of 2D resistivity and seismic travel time data to image saltwater intrusion over karstic areas. Environ Earth Sci 68, 1877–1885 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1875-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1875-9