Abstract
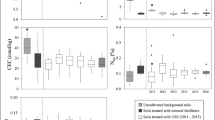
The toxicity and potential bioavailability of heavy metals were studied in sewage sludge-amended ferralsols and chernosols, using bioassays with earthworms (Eisenia andrei). Acute toxicity tests and avoidance assays were performed according to standard protocols. Potentially bioavailable concentrations of heavy metals were estimated by quantifying their concentrations in tissues of survival earthworms. The results revealed that soil properties played an important role in the toxicity and bioavailability of heavy metals. In this respect, higher levels of toxicity were detected for the ferralsol. The abundance of 2:1 clay minerals, high fertility and more basic values of pH seem to be very important in the reduction of toxicity levels for earthworms. Organisms exposed to the chernosols were able to uptake higher amount of metals. In that case, higher contents of nutrients in chernosols may have influenced such bioavailability processes. Avoidance responses were the most sensible indicator of toxicity. In the near future, such data can subsidize the establishment of toxic reference concentrations able to reflect the characteristics of important tropical pedological occurrences, supporting the definition of sustainable indicators for using sewage sludge in the tropical agriculture.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alamino RCJ, Polivanov H, Campos TMPC, Silva VHG, Santos LV, Mendes JC (2007) Biodisponibilidade de cádmio em latossolo acrescido de lodo de esgoto. Anuário do Inst de Geociências 30(2):45–54
American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) (2004) Standard guide for conducting laboratory soil toxicity or bioaccumulation tests with the Lumbricid Earthworm Eisenia fetida and the enchytraeid potworm enchytraeus albidus
Baun A, Justesen KB, Nyholm N (2002) Algal tests with soil suspensions and elutriates: a comparative evaluation for PAH-contaminated soils. J Soils Sediments 46(2):251–258
Borges MR, Coutinho ELM (2004) Metais pesados do solo após aplicação de biossólido II—disponibilidade. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo 28:557–568
Bright DA, Healey N (2003) Contaminant risks from biosolids land application: contemporary organic contaminant levels in digested sewage sludge from five treatment plants in Greater Vancouver, British Columbia. Environ Poll 126:39–49
Burton DT, Turley SD, Fisher DJU, Green DJ, Shedd TR (2006) Bioaccumulation of total mercury and monomethylmercury in the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Water Air Soil Pollut 170:37–54
Cai Q, Mo C, Wu Q, Zeng Q, Katsoyaiannis A (2007) Occurrence of organic contaminants in sewage sludges from eleven wastewater treatment plants, China. Chemos 68:1751–1762
Carbonell G, Gómez JPN, Babín MM, Fernández C, Alonso E, Tarazona JV (2009) Sewage sludge applied to agricultural soil: ecotoxicological effects on representative soil organisms. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 72:1309–1319
Cesar RG, Egler SG, Alamino RCJ, Polivanov H, Silva RC, Castilhos ZC, Araújo P (2008) Avaliação do potencial tóxico de latossolos e chernossolos acrescidos de lodo de esgoto utilizando bioensaios com oligoquetas da espécie Eisenia andrei. Anuário do Inst de Geociências 31(2):53–60
CH Serviços Ambientais (2008) Relatório ambiental simplificado: programa de gestão sócio-ambiental e avaliação de risco à saúde humana do programa de revitalização, urbanização e recuperação ambiental dos canais do Fundão e do Cunha. Relatório Técnico, pp 234–240
Cocking D, Hayes R, King ML, Rohrer MJ, Thomas R, Ward D (1991) Compartmentalization of mercury in biotic components of terrestrial flood plain ecosystems adjacent to the South River at Waynesboro, Va.’ Water Air Soil Pollut 57–58:159–170
Companhia de Tecnologia de Saneamento Ambiental (CETESB) (2005) Decisão de Diretoria no. 195/2005 de 23 de novembro de 2005. http://www.cetesb.sp.gov.br/Solo/relatorios/tabela_valores_2005.pdf. Accessed March 2009
Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente (CONAMA) (2006) Resolução nº 375 de 29 de agosto de 2006, p 25. http://www.mma.gov.br/port/conama/legiabre.cfm?codlegi=506. Accessed Aug 2009
Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente (CONAMA) (2009) Resolução nº 420 de 28 de dezembro de 2009, p 16. http://www.mma.gov.br/port/conama/legiabre.cfm?codlegi=506. Accessed Feb 2010
Crouau Y, Gisclard C, Perotti P (2002) The use of Folsomia candida (Collembola, Isomidae) in bioassays of waste. Appl Soil Ecol 19:65–79
Fjällborg B, Li B, Nilsson E, Dave G (2006) Toxicity identification evaluation of five metals performed with two organisms (Daphnia magna and Lactuca sativa). Arch Environ Cont Toxicol 50:196–204
Garcia M (2004) Effects of pesticides on soil fauna: development of ecotoxicology test methods for tropical regions. In: Vlek PLG et al (eds) Ecology and development series, vol 19. Cuvillier Verlag, Gottingen, p 282
Hall NE, Fairchild JF, Point TW, Heine PH, Ruessler DS, Ingersoll CG (1996) Problems and recommendations in using algal toxicity testing to evaluate contaminated sediments. J Great Lakes Res 22(3):545–556
Hinton J, Veiga MM (2008) The influence of organic acids on mercury bioavailability: insight from an earthworm assessment protocol. Environ Bioindic 3:47–67
Hund-Rinke K, Wiechering H (2001) Earthworm avoidance test for soil assessments: an alternative for acute and reproduction tests. J Soils Sediments 1(1):15–20
ISO (2008) Soil quality—avoidance test for determining the quality of soils and effects of chemicals on behaviour—Part 1: test with earthworms (Eisenia fetida and Eisenia andrei). Geneva, ISO 17512-1
Katz SA, Salem H (1993) The toxicology of chromium with respect to its chemical speciation: a review. Appl Toxicol 13:217–224
Liu X, Chengxiao H, Zhang S (2005) Effects on earthworm activity on fertility and heavy metals bioavailability in sewage sludge. Environ Int 31:874–879
Lukkari T, Astsinki M, Väisänen A, Haimi J (2005) Toxicity of copper and zinc assessed with three different earthworms tests. Appl Soil Ecol 30:133–146
Matzke M, Stolte S, Arning J, Uebers U, Filser J (2008) Imidazolium based ionic liquids in soils: effects of the side chain length on wheat (Triticum aestivum) and cress (Lepidium sativum) as affected by different clays and organic matter. Green Chem 10:584–591
Miyasaki A, Amano T, Saito H, Nakano Y (2002) Acute toxicity of chlorophenols to earthworms using a simple paper contact method and comparison with toxicities to fresh water organisms. Chemos 47:65–69
Morgan JE, Richards SPG, Morgan AJ (2001) Stable strontium accumulation by earthworms: A paradigm for radiostrontium interactions with its cation analogue, calcium. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:1236–1243
Nahmani J, Lavelle P (2002) Effects of heavy metal pollution on soil macrofauna in a grassland of Northern France. Eur J Soil Biol 38:297–300
Nahmani J, Hodson ME, Black S (2007) A review of studies performed to assess metal uptake by earthworms. Environ Pollut 145:402–424
Nahmani J, Hodson ME, Devin S, Vijver MG (2009) Uptake kinetics of metals by the earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to field-contaminated soils. Environ Pollut 157:2622–2628
Natal-da-Luz T, Ribeiro R, Sousa JP (2004) Avoidance tests with collembola and earthworms as early screening tool for site-specific assessment of polluted soils. Environ Toxicol Chem 23(9):2188–2193
Natal-da-Luz T, Tidona S, Jesus B, Morais PV, Sousa JP (2009) The use of sewage sludge as soil amendment: the need for an ecotoxicological evaluation. J Soils Sediments 9:246–260
Neuhauser EF, Cukic ZV, Malecki MR, Loehr RC, Durkin PR (1995) Bioconcentration and biokinetics of heavy metals in the earthworm. Environ Pollut 89:293–301
Obbard JP (2001) Ecotoxicological assessment of heavy metals in sewage sludge-amended soils. Appl Geochem 15:1405–1411
OECD (1984) Earthworm, acute toxicity tests. In: OECD guideline for testing of chemicals No. 207, OECD, Paris
Paoliello MMB, Capitani EM, Cunha FG, Matsuo T, Carvalho MF, Sakuma A, Figueiredo BR (2002) Exposure of children to lead and cadmium from a mining area of Brazil. Environ Geochem Health 88:120–128
Parkpian O, Klankrong K, DeLauna R, Jugsujínda A (2002) Metal leachability from sewage sludge amended Thai soils. J Environ Sci Health 37:765–791
Roberts LB, Dorough HW (1984) Relative toxicities of chemicals to the earthworm Eisenia foetida. Environ Toxicol Chem 3:67–78
Schnaak W, Küchler T, Kujawa M, Henschel KP, Süssenbach D, Donau R (1997) Organic contaminants in sewage sludge and their ecotoxicological significance in the agricultural utilization of sewage sludge. Chemos 35:5–11
Selivanovskaya SY, Latypova VZ (2003) The use of bioassays for evaluating the toxicity of sewage sludge and sewage sludge-amended soil. J Soils Sediments 3(2):85–92
Smith PN, Cobb GP, Gobard-Codding C, Hoff D, McMurry CT, Rainwater TR, Reynolds KD (2007) Contaminant exposure in terrestrial invertebrates. Environ Pollut 150:41–64
Spurgeon DJ, Hopkin SP (2000) The development of genetically inherited resistance to zinc in laboratory-selected generations of the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Environ Pollut 109:193–201
Straalen NM, Donker MH, Vijver MG, Gestel CAM (2005) Bioavailability of contaminants estimated from uptake rates into soil invertebrates. Environ Pollut 136:409–417
Suthar S, Singh S (2008) Bioconcentrations of metals (Fe, Cu, Zn, Pb) in earthworms (Eisenia fetida), inoculated in municipal sewage sludge: do earthworms pose a possible risk of terrestrial food chain contamination? Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 24(1):25–32
Tsutya MT (2000) Alternativas de disposição final de biossólidos gerados em estações de tratamento de esgotos. In: Bettiol W, Camargo OA (eds) Impacto Ambiental do Uso Agrícola do Lodo de Esgoto. Embrapa Meio Ambiente, Jaguariúna, p 69-105
Vijver MG, Vink JPM, Miermans CJH, Gestel CAM (2003) Oral sealing using glue: a new method to distinguish between intestinal and dermal uptake of metals in earthworms. Soil Biol Biochem 35:125–132
WHO (World Health Organization) (1990) Environmental health criteria for Methylmercury, Geneva, p 34
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the colleagues from the Mineral Analysis Group (COAM) of the Centre for Mineral Technology (CETEM/MCT) for their help in the chemical determinations. Ricardo Cesar, Marianna Silva and Juan Colonese were supported by grants from the National Brazilian Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq). Without such financial help, this research could not be executed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cesar, R., Silva, M., Colonese, J. et al. Influence of the properties of tropical soils in the toxicity and bioavailability of heavy metals in sewage sludge-amended lands. Environ Earth Sci 66, 2281–2292 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1449-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1449-2