Abstract
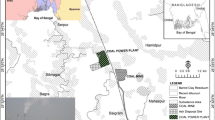
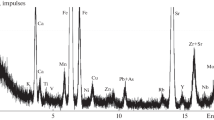
The natural radiological characteristics and their respective annual effective dose (AED) rates, produced by 226Ra, 232Th and 40K in coal, fly ash and bottom ash from two large coal-fired power plants (CFPPs) of Xi’an were determined by means of γ-ray spectrometry. The average activity concentrations of 226Ra, 232Th and 40K in all ash samples (fly ash and bottom ash samples) from the two CFPPs were 67.6, 74.3 and 225.3 Bq kg−1, respectively. The results are compared with data from other locations. To evaluate the radiological hazards of the natural radioactivity, the radium equivalent activity (Raeq), air absorbed dose rate (D), AED and external hazard index (H ex) are compared with internationally accepted values. Raeq and H ex of all samples except three fly ash samples were less than the limits of 370 Bq kg−1 and unity, respectively. The average D and AED for ash samples were 86.8 nGy h−1 and 0.11 mSv y−1, respectively, which exceed the world average and Xi’an average values.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alencar AS, Freitas AC (2005) Reference levels of natural radioactivity for the beach sands in a Brazilian southeastern coastal region. Radiat Meas 40:76–83
Ayçik GA, Ecran A (1997) Radioactivity measurements of coal and ashes from coal-fired power plants in the southwestern part of Turkey. J Environ Radioact 35:23–35
Baba A (2002) Assessment of radioactive contaminants in by-products from Yatagan (Mugla, Turkey) coal-fired power plant. Environ Geol 41:916–921
Bem H, Wieczorkowski P, Budzanowski M (2002) Evaluation of technologically enhanced natural radiation near the coal-fired power plants in the Lodz region of Poland. J Environ Radioact 61:191–201
Beretka J, Mathew PJ (1985) Natural radioactivity of Australian building materials, industrial wastes and by-products. Health Phys 48:87–95
Cevik U, Damla N, Nezir S (2007) Radiological characterization of Cayirhan coal-fired power plant in Turkey. Fuel 86:2509–2513
Faheem M, Mujahid SA, Matiullah (2008) Assessment of radiological hazards due to the natural radioactivity in soil and building material samples collected from six districts of the Punjab province-Pakistan. Radiat Meas 43:1443–1447
Flues M, Camargo IMC, Figueiredo FPM, Silva PSC, Mazzilli BP (2007) Evaluation of radionuclides concentration in Brazilian coals. Fuel 86:807–812
Flues M, Camargo IMC, Silva PSC, Mazzilli BP (2006) Radioactivity of coal and ashes from Figueira coal power plant in Brazil. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 270:597–602
Flues M, Moraes V, Mazzilli BP (2002) The influence of a coal-fired power plant operation on radionuclide concentrations in soil. J Environ Radioact 63:285–294
Karangelos DJ, Petropoulos NP, Anagnostakis MJ, Hinis EP, Simopoulos SE (2004) Radiological characteristics and investigation of the radioactive equilibrium in the ashes produced in lignite-fired power plants. J Environ Radioact 77:233–246
Lalit BY, Ramachandran TV, Mishra UC (1986) Radiation exposures due to coal-Fired power stations in India. Radiat Prot Dosim 15:197–202
Lu X, Jia X, Wang F (2006) Natural radioactivity of coal and its by-products in the Baoji coal-fired power plant, China. Curr Sci 91:1508–1511
Lu X, Luo K, Wang L, Wang W (2003) The content of trace elements of coals in Weibei area, Shaanxi Province. J Jinlin Univ (Earth Science Edition) 33:178–182 (in Chinese)
Lu X, Wang F, Jia X, Wang L (2007) Radioactive analysis and radiological hazards of lime and cement fabricated in China. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 54:327–332
Lu X, Zhang X (2006) Measurement of natural radioactivity in sand samples collected from the Baoji Weihe Sands Park, China. Environ Geol 50:977–982
Mahur AK, Kumar R, Sengupta D, Prasad R (2008) Estimation of exhalation rate, natural radioactivity and radiation doses in fly ash samples from Durgapur thermal power, West Bengal, India. J Environ Radioact 99:1289–1293
Mandal A, Sengupta D (2003) Radioelemental study of Kolaghat, thermal power plant, West Bengal, India: possible environmental hazards. Environ Geol 44:180–186
Mishra UC, Lalit BY, Ramachandran TV (1980) Radioactivity release to the environment by thermal power stations using coal as fuel. Sci Total Environ 14:77–83
Mishra UC (2004) Environmental impact of coal industry and thermal power plants in India. J Environ Radioact 72:35–40
Mondal T, Sengupta D, Mandal A (2006) Natural radioactivity of ash and coal in major thermal power plants of Bengal, India. Curr Sci 91:1387–1392
Nisnevich M, Sirotin G, Schlesinger T, Eshel Y (2008) Radiological safety aspects of utilizing coal ashes for production of lightweight concrete. Fuel 87:1610–1616
Nowina-Konopka M (1993) Radiological hazard from coal-fired power plants in Poland. Radiat Prot Dosim 46:171–180
Papastefanou C (1996) Radiation impact from lignite burning due to 226Ra in Greek coal-fired power plants. Health Phys 70:187–191
Rahman S, Mujahid SA, Hussain S (2008) Assessment of radiological hazards due to the presence of natural radionuclides in samples of building materials collected from the northwestern areas of Pakistan. J Radiol Prot 28:205–212
Ramachandran TV, Mishra UC (1989) Radiological impact of airborne releases from coal-fired power plants in India. Ecology 4:23–35
Realo E, Realo K, Jogi J (1996) Releases of natural radionuclides from oil-shale-fired power plants in Estonia. J Environ Radioact 33:77–89
Tso MYW, Leung JKC (1996) Radiological impact of coal ash from the power plants in Hong Kong. J Environ Radioact 30:1–14
UNSCEAR (1993) Sources and effects of ionizing radiation. UNSCEAR, New York
UNSCEAR (2000) Sources and effects of ionizing radiation. UNSCEAR, New York
Varinlioğlu A, Akyüz T, Köse A (1998) The radioactivity measurement of Turkish lignites. J Environ Radioact 41:381–387
Yu Q (1996) Investigation on the radioactivity concentration of coal and ash from Shanghai coal-fired power plant. Chin J Radiol Med Prot 16:374–375 (in Chinese)
Zhang CF, Li J (1994) Investigation of environmental natural penetrating radiation level in Shaanxi province. Radiat Prot 14:276–283 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Provincial Natural Sciences Foundation of Shaanxi Province under Grant 2006D14 and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant GK200901008. We are grateful to the authorities of the Baqiao and Xijiao coal-fired power plants for permission to carry out fieldwork and for providing samples. We also thank Editor-in-Chief Dr, James W. LaMoreaux and anonymous reviewers for their insightful suggestions and critical reviews of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, X., Li, L.Y., Wang, F. et al. Radiological hazards of coal and ash samples collected from Xi’an coal-fired power plants of China. Environ Earth Sci 66, 1925–1932 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1417-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1417-x