Abstract
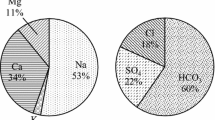
The suitability of groundwater quality for drinking and agricultural purposes was assessed in the rural areas of Delhi based on the various water quality parameters. A total of 50 ground water samples were collected randomly from different sources viz. hand pump, tube well, boring and analyzed for major ion chemistry to understand the operating mechanism of geochemical processes for ground water quality. The quality analysis is performed through the estimation of pH, EC, TDS, total hardness, total alkalinity, Na, K, Cl, NO3, SO4, DO, BOD, Cu, Cr, Cd, Ni, Zn and Pb. Hydrochemical facies were identified using Piper, Durov and Chadha diagram. Chemical data were also used for mathematical calculations (SAR, %Na, RSC, PI, KI, and chloroalkaline indices) for better understanding the suitability of ground water for irrigation purposes. The results of saturation index shows that all the water samples were supersaturated to undersaturated with respect to carbonate minerals and undersaturated with respect to sulphate and chloride minerals. According to USSL diagram, most of the samples fall in the field of C3S1, indicating medium salinity and low sodium water which can be used for almost all types of soil with little danger of exchangeable sodium. Assessment of water samples from various methods indicated that majority of the ground water in the study area is chemically suitable for drinking and agricultural uses.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aastri JCV (1994) Groundwater chemical quality in river basins, hydrogeochemical facies and hydrogeochemical modeling. Bharathidasan University, Thiruchirapalli
APHA (1998) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th edn. Washington
Appelo CAJ, Postma D (1996) Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution. Balkema, Rotterdam, p 536
Back W (1966) Hydrochemical facies and ground-water flow patterns in northern part of Atlantic Coastal Plain, US Geol. Surv. Prof. Paper 498-A, p 42
BIS (1991) Specifications for Drinking Water. IS:10500:1991. Bureau of Indian standards, New Delhi
Brandon C, Homman K (1995) The cost of interaction: valuing the economy- wide cost of environmental degradation in India. Asia Environment Division, World Bank 7, October memo
Census of India (1991) District census Handbook, part XII A & B, Village & Town Director, Village & Town wise, primary Census Abstract, Delhi District, pp 288–294
Central Ground Water Board (2006) Ground water year book of national capital of territory. Delhi. Ministry of Water Resources, Government of India, New Delhi
Chadha DK (1999) A proposed new diagram for geochemical classification of natural water and interpretation of chemical data. Hydrogeol J 7:431–439
Chapell FH (1993) Ground water microbiology and geochemistry. Wiley, New York, p 424
Chilingar GV (1956) Durovs classification of natural water and chemical composition of atmospheric precipitation in U.S.S.R. Transactions - American Geophysical Union 37:193–196
Cidu R, Biddau R, Fanfani L (2009) Impact of past mining activity on the quality of groundwater in SW Sardinia (Italy). J Geochem Explor 100:125–132
Comly HH (1945) Cyanosis in infants caused by nitrates in well water. J Am Med Assoc 129(129):12–144
Davis SN, De Wiest RJM (1966) Hydrogeology, vol 463. Wiley, New York
Edmunds WM, Shand P, Hart P, Ward RS (2003) The natural baseline quality of ground water: a UK pilot study. Sci Total Environ 310:25–35
Foster SSD (1995) Groundwater for development- an overview of quality constraints. In: Nash H, McCall GJH (eds) Groundwater quality. 17th Special report. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 1–3
Freeze RA, Cherry JA (1979) Groundwater. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey
Gilly G, Carrao G, Favilli S (1984) Concentration of nitrates in drinking water and incidence of carcinomas. First descriptive study of the Piemonate Region, Italy. Sci Total Environ 34:35–37
Hem JD (1992) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. U.S.Gov. Print. Office, Washington
Hook Z (2005) An assessment of the water quality of drinking water in rural districts in Zimbabwe. The case of Gokwe South, Nkayi Lupane, and Mwenezi districts. Phys Chem Earth 30:859–866
Hudak PF, Sanmanee S (2003) Spatial patterns of nitrate, chloride, sulfate, and fluoride concentration in the woodbine aquifer of North-Central Texas. Environ Monit Assess 82:311–320
Jahed KGR, Dehghani MH, Mahvi AH, Rafati L, Tavanafar E (2008) Concentration of nitrate and nitrite in groundwater resources of Hamdan Province, Iran. Res J Chem Environ 12(4):56–58
Kelly WP (1940) Permissible composition and concentration of irrigated waters. In: Proceeding of the ASCF 66, pp 607
Kruawal K, Sacher F, Werner K, Mqller J, Knepper TP (2005) Chemical water quality in Thailand and its impacts on the drinking water production in Thailand. Sci Total Environ 340:57–70
Langmuir D (1997) Aqueous environmental geochemistry. Prentice Hall, India, p 601
Lorenzen G, Sprenger C, Taute T, Pekdeger A, Massmann G (2010) Assessment of the potential for bank filteration in a water-stressed megacity (Delhi, India) 61:1419–1434
Ministry of Finance (2008) Economic survey. Government of India, New Delhi
Mor S, Ravindra K, Dahiya RP, Chandra A (2006) Leachate characterization and assessment of groundwater pollution near municipal solid waste landfill site. Environ Monit Assess 118:435–456
Mull R, Harig F, Pielke M (1992) Ground water management in the urban area of Hanover Germany. J Inst Water Environ Manage 6(2):199–206
Nagarajah S, Emerson BN, Abeykoon V, Yogalingam S (1988) Water quality of some wells in Jaffna and killinochchi with special reference to nitrate pollution. Tropical Agriculture 44:61–73
Ophori DU, Toth J (1989) Patterns of groundwater chemistry, Ross Creek basin, Alberta, Canada. Ground Water 27:20–26
Paliwal KV (1967) Effect of gypsum application on the quality if irrigation waters. The madras agricultural journals 59:646–647
Pierre D, Glynn L, Plummer N (2005) Geochemistry and the understanding of ground-water systems. Hydrogeol J 13:263–287
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Trans Am Geophys Union 25:914–923
Raghunath HM (1987) Groundwater, 2nd edn. Wiley Eastern Ltd., New Delhi, pp 344–369
Raju NJ, Ram P, Dey S (2009) Groundwater quality in the lower Varuna River basin, Varanasi district, Uttar Pradesh, India. Journal of Geological Society of India 73:178–192
Rakesh K, Singh RD, Sharma KD (2005) Water resources in India. Curr Sci 89:794–811
Robins NS (2002) Groundwater quality in Scotland: Major ion chemistry of the key groundwater bodies. Sci Total Environ 294:41–56
Saleh A, Al-Ruwih F, Shehata M (1999) Hydrogeochemical process operating within the main aquifers of Kuwait. J Arid Environ 42:195–209
Sawyer GN, McCartly DL (1967) Chemistry of sanitary engineers, 2nd edn. McGraw Hill, New York, p 518
Schilling KE, Wolter CF (2007) A GIS-based groundwater travel time model to evaluate stream nitrate concentration reductions from land use change. Env Geol 53:433–443
Schoeller H (1977) Geochemistry of groundwater. In: Ground water studies-An international Guide for Research & Practice. UNESCO, Paris, pp 1–18
Sett DN (1964) Ground water geology of the Delhi region, Bulletin. Geological survey of India, Series B 16:1–35
Subba Rao N (2006) Seasonal variation of groundwater quality in a part of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Geol 49:413–429
Tiwari TN, Manzoor A (1988) Pollution of Subarnarekha river near Jamshedpur and the suitability of its water for irrigation. Indian journal of environmental protection 8(7):494–497
US Salinity Laboratory (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. Agricultural Handbook, USDA, No 60, pp 160
WHO (1993) Guidelines for drinking water quality, vol.1, recommendations, 2nd edn. WHO, Geneva
WHO/UNICEF (2004) Meeting the MDG drinking water and sanitation target: A mid-term assessment of progress. WHO, Geneva
Wilcox LV (1955) Classification and use of irrigation water. USDA, Circular. Washington, pp 969
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alam, M., Rais, S. & Aslam, M. Hydrochemical investigation and quality assessment of ground water in rural areas of Delhi, India. Environ Earth Sci 66, 97–110 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1210-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1210-x