Abstract
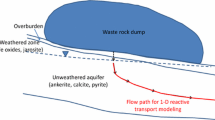
The oxidation of pyrite results in sulphate concentrations from 1,300 to 2,000 mg/l in the dump water of the open cast mine Inden, which is located in Germany. Under near-neutral pH and reduced redox conditions, precipitation of siderite (FeCO3) retains up to 85% of the pre-liberated ferrous iron, so that iron concentrations in the dump water are relatively low as compared to the concentrations of sulphate. The highly mineralised dump water will enter the aquifer system northwards of Inden during the next centuries. This area is used intensely for water extraction. Model calculations show that there will be no problem of acidification in the adjacent aquifer system and, therefore, no problem of high heavy metal concentrations during the next centuries. The most important problem will be high sulphate concentrations in the groundwater. Besides dispersion and diffusion, there are no chemical mechanisms that lower the sulphate concentrations downstream. On the basis of the simulations, sulphate plumes of about 1–2 km in width and up to 15 km in length are expected. Within the core of these plumes, sulphate concentrations will be above the drinking water limits.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appelo CAJ, Postma D (2007) Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution. A.A. Balkema Publishers, London
Bilek F (2004) Beschaffenheitsprognose für den Grundwasser-Abstrom aus Braunkohle-Tagebaukippen auf der Basis von experimentell bestimmten Parametern und geochemisch charakterisierten Sedimenten (Simulation of the groundwater composition in the downstream area of lignite overburden dumps on the basis of experimentally determined parameters and geochemically characterised sediments). Proc des DGFZ 26, Dresden
Brand T (1996) Numerische Simulation dreidimensionaler Strömungs-, Transport- und hydrogeochemischer Reaktionsprozesse im Grundwasserabstrom von Braunkohlentagebaukippen (Numeric simulation of three-dimensional flow-, transport- and hydrogeochemical processes in the downstream area of lignite overburden dumps. Besondere Mitt zum Dtsch Gewässerkdl Jahrb 59
Katzur J, Ziegler H-D (1997) Acidität und Metallgehalte der Tagebaustillgewässer im Südwesten des Niederlauitzer Braunkohlenreviers (Acidity and metal concentrations of residual lakes in the Lusatia mining area). Wasser Boden 49:30–35
Lenk S (2008) Grundwasserbeschaffenheit und hydrogeochemische Prozesse in rheinischen Braunkohlenabraumkippen und in deren Abstrom (Groundwater composition and hydrogeochemical processes in Rhenisch lignite overburden dumps and in the adjacent aquifers). Dissertation, University of Bochum
Lenk S, Wisotzky F (2007) Chemische Beschaffenheit und modellierte Gense von Grundwässern in Braunkohlenabraumkippen des Tagebaues Inden [Groundwater quality and modelled chemical composition of water in lignite overburden dump aquifers (surface mine Inden, Germany)]. Grundwasser 12:301–313
Leuchs W (1988) Vorkommen, Abfolge und Auswirkungen anoxischer Redoxreaktionen in einem pleistozänen Porengrundwasserleiter (Occurence, progression and effects of anoxic redox reactions in a peistocene porous aquifer). Besondere Mitt zum Dtsch Gewässerkdl Jahrb 52
Morin KA, Cherry JA (1986) Trace amounts of siderite near a uranium-tailings impoundment, Elliot Lake, Ontario, Canada, and its implication in controlling contaminant migration in a sand aquifer. Chem Geol 56:117–134
Nixdorf B, Hemm M, Schlundt A, Kapfer M, Krumbeck H (2001) Tagebauseen in Deutschland—ein Überblick (Residual dump lakes in Germany—an overview). Umweltbundesamt, UBA-Texte 35/01, Germany
Parker G, Noller B, Waite TD (1999) Assessment of the use of fast-weathering silicate minerals to buffer AMD in surface waters in tropical australia. Publisher unknown, ISBN 0886670470
Parkhurst DL, Appelo CAJ (1999) User’s guide to PHREEQC (version 2)—a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport and inverse geochemical calculations. Water-Resources Investigations Report 99–4259, USA. Department of the Inter US Geological Survey, Denver
Sanchez J, Pamo EL, Santofimia E, Aduvire O, Reyes J, Barettino D (2005) Acid mine drainage in the Iberian Pyrite Belt (Odiel river watershed, Huelva, SW Spain): geochemistry, mineralogy and environmental implications. Appl Geochem 20:1320–1356
Schöpke R (1999) Erarbeitung einer Methodik zur Beschreibung hydrochemischer Prozesse in Kippengrundwasserleitern (Development of a method to describe hydrochemical processes in dump aquifers). Schriftenreihe Siedlungswasserwirtschaft und Umw. der Brandenbg. Tech. Universität Cottbus 2
Van Berk W, Wisotzky F (1995) Sulfide oxidation in brown coal overburden and chemical modelling of reactions in aquifers influenced by sulfide oxidation. Environ Geol 26:192–196
Walter AL, Frind EO, Blowes DW, Ptacek CJ, Molson JW (1994) Modeling of multicomponent reactive transport in groundwater 2. Metal mobility in aquifers impacted by acidic mine tailings discharge. Water Resour Res 30:3149–3158
Wisotzky F (1994) Untersuchungen zur Pyritoxidation in Sedimenten des Rheinischen Braunkohlenreviers und deren Auswirkungen auf die Chemie des Grundwassers (Pyrite oxidation in sediments of the Rhenish lignite mining area and its impact on the groundwater chemistry). Besondere Mitt zum Dtsch Gewässerkdl Jahrb 58
Wisotzky F (2001) Prevention of acidic groundwater in lignite overburden dumps by addition of alkaline substances: pilot-scale field experiments. Mine Water Environ 20:122–128
Wisotzky F (2003) Saure Bergbauwässer (acid mine drainage) und deren Qualitätsverbesserung durch Zugabe von alkalisch wirkenden Zuschlagstoffen zum Abraum—Untersuchungen im Rheinischen Braunkohlenrevier (Acid mine drainage and its quality improvement through application of alkaline substances to the mine wastes—Investigations in the Rhenisch lignite working area). Besondere Mitt zum Dtsch Gewässerkdl Jahrb 61
Wisotzky F, Obermann P (2001) Acid mine groundwater in lignite overburden dumps and its prevention—the Rhineland lignite mining area (Germany). Ecol Eng 17:115–123
Acknowledgments
The authors express appreciation to the RWE Power AG for their support and Dr. Nils Cremer (Erftverband) for his encouragement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lenk, S., Wisotzky, F. Chemical modelling of the groundwater composition in aquifers affected by lignite mine dumps discharge (surface mine Inden, Germany). Environ Earth Sci 62, 581–591 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0549-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0549-8