Abstract
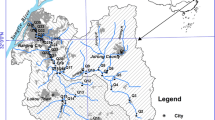
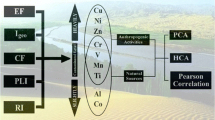
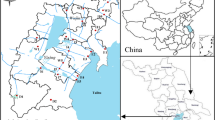
Rivers in metropolitan areas are often highly polluted with materials that pose a threat to a large number of residents. Human influences lead to contaminants in metropolitan rivers having more complex sources than those in rural rivers. This complexity results in contamination that is unstable and rapidly changing. Here, the contents and chemical fractionation patterns of eleven toxic elements (As, Cd, Co, Cu, Cr, Mn, Ni, Pb, Zn, Y, and Hg) were evaluated in 13 samples collected from along the Beiyunhe River in Beijing, China. The results revealed that the metal contents were unevenly distributed along the river, with higher levels being observed in the downriver sites and the rendezvous sites. Additionally, more than 80% of the metals were found to be in the residual phase. The organic and sulfide phases were the most important extractable phases of most metals, with Ni, Co, Cu, and Cr primarily being associated with these phases and As, Cd, and Zn having a strong association with the iron/manganese oxide and hydroxide phases. Additionally, Mn was associated with the exchangeable and carbonate phases, with the lowest concentrations being observed in the organic and sulfide phases. Conversely, the metal exchangeable and carbonate phases were uniformly distributed throughout the river. Analysis of the metal sources revealed that particles input from the atmosphere comprised a considerable amount of the metals in the Beiyunhe River. However, these metals likely do not enter the sediment via atmospheric deposition directly, but rather through rainwater runoff into the river. The methods used in the present study will be useful in other studies that require analysis of complex data.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abollino O, Aceto M, Malandrino M, Mentasti E, Sarzanini C, Barberis R (2002) Distribution and mobility of metals in contaminated sites Chemometric investigation of pollutant profiles. Environ Pollut 119(2):177–193. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(01)00333-5
Baruah NK, Kotoky P, Bhattcharyya KG, Borah GC (1996) Metal speciation in Jhanji River sediments. Sci Total Environ 193:1–12. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(96)05318-1
Blom G, Winkels HJ (1998) Modeling sediment accumulation and dispersion of contaminants in ljsselmeer (the Netherlands). Water Sci Tech 37(6–7):17–24. doi:10.1016/S0273-1223(98)00177-2
Bordas F, Bourg ACM (1998) A critical evaluation of sample pretreatment for storage of contaminated sediments to be investigated for the potential mobility of their heavy metal load. Water Air Soil Pollut 103(1–4):137–149. doi:10.1023/A:1004952608950
Boughriet A, Proix N, Billon G, Recourt P, Ouddane B (2007) Environmental impacts of heavy metal discharges from a smelter in Deûle-canal sediments (Northern France): concentration levels and chemical fractionation. Water Air Soil Pollut 180:83–95. doi:10.1007/s11270-006-9252-5
Brereton RG (2003) Chemometrics: data analysis for the laboratory and chemical plant. Wiley, Bristol, pp 183–255
Bro R, Smilde A (2003) Centering and scaling in component analysis. J Chemom 17:16–33. doi:10.1002/cem.773
Chavagnac V, German CR, Milton JA, Palmer MR (2005) Sources of REE in sediment cores from the Rainbow vent site (36°14′N, MAR). Chem Geol 216(3–4):329–352. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.11.015
Chen ZL, Zhang YH, Ma CG, He FZ (1989) Regional contaminant features of suspended particulates in Beijing-Tianjin area. Environ Sci 10(4):24–27
Chen TB, Zheng YM, Chen H, Zheng GD (2004) Background concentrations of soil heavy metals in Beijing. Environ Sci 25:117–122
Cobelo-García A, Prego R (2004) Influence of point sources on trace metal contamination and distribution in a semi-enclosed industrial embayment: the Ferrol Ria (NW Spain). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 60(4):695–703. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2004.03.008
Cong Y, Chen YL, Yang ZF, Hou QY, Wang HC (2008) Dry and wet atmospheric deposition fluxes of elements in the Plain area of Beijing Municipality, China. Geol Bull China 27(2):257–264
Davidson CM, Thomas RP, Mcvey SE, Perala R, Littlejohn D, Ure AM (1994) Evaluation of a sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of heavy metals in sediments. Anal Chim Acta 291:277–286. doi:10.1016/0003-2670(94)80023-5
Davidson CM, Urquhart GJ, Ajmone-Marsan F et al (2006) Fractionation of potentially toxic elements in urban soils from five European cities by means of a harmonized sequential extraction procedure. Anal Chim Acta 565:63–72. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2006.02.014
Deletic AB, Maksimovie CT (1998) Evaluation of water quality factors in storm runoff from paved areas. J Environ Eng 124(9):869–879. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(1998)124:9(869)
DelValls TÁ, Forja JM, González-Mazo E, Gómez-Parra A, Blasco J (1998) Determining contamination sources in marine sediments using multivariate analysis. Trends Anal Chem 17(4):181–192. doi:10.1016/S0165-9936(98)00017-X
Duran C, Soylak M, Bulut VN et al (2007) Speciation of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) in environmental samples after solid phase extraction on amberlite XAD-2000. J Chin Chem Soc 54:625–634. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.08.074
EPA USA (1990) Meeting the environmental challenge. EPA, USA, p 46
Forstner U (1993) Metal speciation-general concepts and applications. Int J Environ Anal Chem 51:5–23. doi:10.1080/03067319308027608
Gao QX, Su FQ, Ren ZH, Zhang ZG, Wang YT (2002) The dust weather of Beijing and its impact. China Environ Sci 22(5):468–471
Glasby GP, Szefer P (1998) Marine pollution in Gdansk Bay, Puck Bay and the Vistula Lagoon, Poland: an overview. Sci Total Environ 212:49–57. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(97)00333-1
Guevara-Riba A, Sahuquillo A, Rubio R et al (2004) Assessment of metal mobility in dredged harbor sediments from Barcelona, Spain. Sci Total Environ 321(1–3):241–255. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2003.08.021
Hakanson L (1980) An ecology risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14(8):975–1001
Henrion R (1994) N-way principal component analysis: theory, algorithms and applications. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 25:1–23. doi:10.1016/0169-7439(93)E0086-J
Hjorth T (2004) Effects of freeze-drying on partitioning patterns of major elements and trace metals in lake sediments. Anal Chim Acta 526:95–102. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2004.08.007
Ianni C, Magi E, Rivaro P, Ruggieri N (2000) Trace metals in Adriatic coastal sediments: distribution and speciation pattern. Toxicol Environ Chem 78:73–92. doi:10.1080/02772240009358961
Jain CK, Malik DS, Yadav R (2004) Metal fractionation study on bed sediments of River Yamuna, India. Water Res 38:569–578. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2003.10.042
Jain CK, Malik DS, Yadav R (2007) Metal Fractionation study on bed sediments of lake Nainital, Uttaranchal, India. Environ Monit Assess 130:129–139. doi:10.1007/s10661-006-9383-6
Jain CK, Gurunadha Rao VVS, Prakash BA et al. (2009) Meal fractionation study on bed sediments of Hussainsagar Lake, Hyderbad, India. Environ Monit Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-0984-8
Jenne EA (1968) Controls on Mn, Fe, Co, Ni and Zn concentrations in soils and water: the significant role of hydrous Mn and Fe oxides. Adv Chem Ser Am Chem Soc 73:337–388
Jordao CP, Hickless G (1989) Chemical associations of Zn, Cd, Pb and Cu in soils and sediments determined by the sequential extraction technique. Environ Technol Lett 10:743–752. doi:10.1080/09593338909384793
Korfali SI, Davies BE (2004) Speciation of metals in sediment and water in a river underlain by limestone: Role of carbonate species for purification capacity of rivers. Adv Environ Res 8:599–612. doi:10.1016/S1093-0191(03)00033-9
Larner BL, Seen AJ, Townsend AT (2006) Comparative study of optimized BCR sequential extraction scheme and acid leaching of elements in the certified reference material NIST 2711. Anal Chim Acta 556:444–449. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2005.09.058
Leardi R, Armanino C, Lanteri S, Alberotanza L (2000) Three-mode principal component analysis of monitoring data from Venice lagoon. J Chemom 14(3):187–195. doi:10.1002/1099-128X(200005/06)14:3
Li ZG, Feng XB, He TR, Yan HY (2005) Determination of total mercury in soil and sediment by aqua regia digestion in the water bath coupled with cold vapor atom fluorescence spectrometry. Bull Mineral Petrol Geochem 24(2):140–143
Li LF, Zeng XB, Li GX et al (2007) Heavy metal pollution of Wenyu River sediment and its risk assessment. Acta Scientiae Circum Stantiae 27(2):289–297
Loska K, Wiechula D (2003) Application of principal component analysis for the estimation of source of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments from the Rybnik Reservoir. Chemosphere 51:723–733. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00187-5
Morgan JJ, Stumm W (1964) The role of multivalent metal oxides in limnological transformations as exemplified by iron and manganese. In: Jaag O (ed) Advances in water pollution research Bol. 1. Proceedings of the Second international conference held in Tokyo. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 103–131
Muller G (1969) Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of Rhine River. Geol J 2:108–118
Murray KS, Cauvet D, Lybeer M, Thomas JC (1999) Particle size and chemical control of heavy metals in bed sediment from the Rouge River, Southeast Michigan. Environ Sci Technol 33(7):987–992. doi:10.1021/es9807946
Nilsson O, Sternbeck J (1999) A mechanistic model for calcite growth using surface speciation. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63(2):217–255. doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00026-5
Nowak B (1995) Sequential extraction of metal forms in the soil near a roadway in southern Poland. Analyst 120:737–739. doi:10.1039/an9952000737
Nriagu JO (1998) History, production, and uses of thallium. In: Nriagu JO (ed) Thallium in the environment. Wiley, New York, pp 7–8
Pardo R, Barrado E, Perez L, Vega M (1990) Determination and speciation of heavy metals in sediments of the Pisuerga river. Water Res 24(3):373–379. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(90)90016-Y
Pardo R, Helena BA, Cazurro C, Guerra C, Debán L, Guerra CM, Vega M (2004) Application of two- and three-way principal component analysis to the interpretation of chemical fractionation results obtained by the use of the B.C.R. procedure. Anal Chim Acta 523(1):125–132. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2004.07.015
Pardo R, Vega M, Debán L, Cazurro C, Carretero C (2008) Modelling of chemical fractionation patterns of metals in soils by two-way and three-way principal component analysis. Anal Chim Acta 606:26–36. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2007.11.004
Qian J, Wang ZJ, Shan XQ, Tu Q, Wen B, Chen B (1996) Evaluation of plant availability of soil trace metals by chemical fractionation and multiple regression analysis. Environ Pollut 91(3):309–315
Quevauviller P (2002) Operationally defined extraction procedures for soil and sediment analysis. Part 3: new crms for trace element extractable contents. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 21(11):774–785. doi:10.1016/S0165-9936(02)01105-6
Ranu G, Tandon SN, Mathur RP, Singh OV (1993) Speciation of metals in Yamuna river sediments. Sci Total Environ 136:229–242
Rauret G, López-Sánchez JF, Sahuquillo A et al (1999) Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J Environ Monitor 1:57–61. doi:10.1039/a807854h
Reeder RJ (1996) Interaction of divalent cobalt, zinc, cadmium, and barium with the calcite surface during layer growth. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 60:1543–1552. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(96)00034-8
Sahuquillo A, Rigol A, Rauret G (2003) Overview of the use of leaching/extraction tests for risk assessment of trace metals in contaminated soils and sediments. Trends Anal Chem 22:152–159. doi:10.1016/S0165-9936(03)00303-0
Singh KP, Malik A, Singh VK, Sinha S (2006) Multi-way data analysis of soils irrigated with wastewater–A case study. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 83(1):1–12. doi:10.1016/j.chemolab.2006.01.001
Smilde AK (1992) Three-way analyses problems and prospects. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems 15(2–3):143–157. doi:10.1016/0169-7439(92)85005-N
Stanimirova I, Zehl K, Massart DL, Heyden Y, Einax JW (2006) Chemometric analysis of soil pollution data using the Tucker N-way method. Anal Bioanal Chem 385(4):771–779. doi:10.1007/s00216-006-0445-y
Sutherland RA (2000) Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ Geol 39(6):611–627. doi:10.1007/s002540050473
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1985) The continental crust: its composition and evolution. Blackwell Scientific Pub., Palo Alto, CA
Templeton DM, Ariese F, Cornelis R et al (2000) IUPAC guidelines for terms related to chemical speciation and fractionation of elements. Pure Appl Chem 72:1453–1470. doi:10.1351/pac200072081453
Terrado M, Barceló D, Tauler R (2006) Identification and distribution of contamination sources in the Ebro river basin by chemometrics modelling coupled to geographical information systems. Talanta 70(4):691–704. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2006.05.041
Tessier A, Campbell PGC, Bisson M et al (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51(7):844. doi:10.1021/ac50043a017
Tessier A, Campbell PGC, Bisson M (1980) Trace metal speciation in the Yamaska and St. Francois Rivers (Quebec). Can J Earth Sci 71:90–105. doi:10.1139/e80-008
Ure AM (1996) Single extraction schemes for soil analysis and related applications. Sci Total Environ 178(1–3):3–10. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(95)04791-3
Vandeginste BGM, Massart DL, De Jong S et al (1998) Handbook of chemometrics and qualimetrics: Part B. Elsevier, Amsterdam. doi:10.1023/B:EGAH.0000039594.19432.80
Wang W, Yue X, Liu HJ, Pan Z, Tang DG, Wang Y, Du RG, Su HM, Qian F (2002) Study on pollution characteristics of aerosols during sand-dust storm weather in Beijing. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae 22(4):494–498
Wang H, Wang CX, Wang ZJ et al (2004) Fractionation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Taihu Lake, East China. Environ Geochem Health 26(2):303–309
Wen X, Allen HE (1999) Mobilization of heavy metal from Le An River sediment. Sci Total Environ 227:101–108. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00002-9
Yang ZS (1988) Mineralogical assemblages and chemical characteristics of clays from sediments of the Huanghe, Changjiang, Zhujiang Rivers and their relationship to the climate environment in their sediment source areas. Oceanologia Et Limnologia Sinica 19(4):336–346
Yang AL, Zhu YM (1999) The study of nonpoint source pollution of surface water environment. Tech Equip Environ Pollut Control 5:60–66
Yang C, Chen Y, Peng P, Li C, Chang X, Xie C (2005) Distribution of natural and anthropogenic thallium in the soils in an industrial pyrite slag disposing area. Sci Total Environ 341:159–172. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.09.024
Yuan H, Wang Y, Gu S, Lu J, Zhou H, Wan X (2008) Chemical forms and pollution characteristics of heavy metals in Yellow River sediments. Chin J Ecol 27(11):1966–1971
Zhang CS, Zhang S, Wang LJ, Wang LZ (1998a) Geochemistry of metals in sediments from Changjiang River and Huanghe River and their comparison. Acta Geographica Sinica 53(4):314–322
Zhang TH, Shan XQ, Li FL (1998b) Comparison of two sequential extraction procedures for speciation analysis of metals in soils and plant availability. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 29:1023–1034. doi:10.1080/00103629809370004
Zhang RJ, Wang MX, Pu YF, Liu Q, Fu JZ, Zhang W (2000) Analysis on the chemical and physical properties of “2000.4.6” super dust storm in Beijing. Clim Environ Res 5(3):259–266
Zhou GH, Qin XW, Dong YX (2005) Soil environmental quality standards: principle and method. Geol Bull China 24:721–727
Zhuang GS, Guo JH, Yuan H, Zhao CY (2001) The composition, sources and size distribution of Chinese sandstorm in 2000 and its global environment impacts. Chin Sci Bull 46(3):191–196
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Prof. Gong Huili and Prof. Zhao Wenji for their input and suggestions regarding this study. The authors also thank Dr. Jiang Yongbin and Chen Qilong (MSc), Fan Yang (MSc), Wang Lijun (MSc), Xue Yanshan (MSc) for assistance with field sampling. This study was jointly supported by the Beijing Education Committee, Talent Programs of Beijing (2005IA05016012) and the New Century Multi-hundred Talent Programs of Beijing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, H., Ji, H. Application of chemometric methods to analyze the distribution and chemical fraction patterns of metals in sediment from a metropolitan river. Environ Earth Sci 61, 641–657 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0379-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0379-8