Abstract
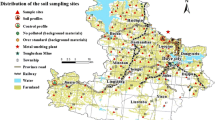
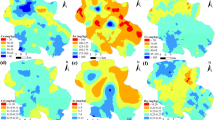
In a typical modern agricultural Zone of southeastern China, Haining City, 224 topsoil samples were collected from paddy fields to measure the total concentrations of copper (Cu), lead (Pb), zinc (Zn), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), mercury (Hg), arsenic (As) and cobalt (Co). The total concentrations ranged from 15.30 to 78.40 mg kg−1 for Cu, 20.10 to 41.40 mg kg−1 for Pb, 54.98 to 224.4 mg kg−1 for Zn, 0.04 to 0.24 mg kg−1 for Cd, 54.90 to 197.1 mg kg−1 for Cr, 0.03 to 0.61 mg kg−1 for Hg, 3.44 to 15.28 mg kg−1 for As, and 7.17 to 19.00 mg kg−1 for Co. Chemometric techniques and geostatistics were utilized to quantify their spatial characteristics and define their possible sources. All eight metals had a moderate spatial dependency except that Pb had a strong spatial dependency. Both factor analysis and cluster analysis successfully classified the eight metals into three groups or subgroups, the first group included Cu, Zn and Cr, the second group included Cd, As and Co, and the last group included Pb and Hg. The Cu, Zn and Cr concentrations in majority samples were higher than their local background concentrations and they were highly correlated (r > 0.80), indicating that they had similar pollution source and anthropic factor controlled their spatial distribution; the Cd, As and Co concentrations in majority samples were lower than their local background concentrations, indicating that the source of these elements was mainly controlled by natural factors; the mean concentration of Pb exhibited generally low level, close to its local background concentration, the Hg concentration in about half of samples was higher than its local background concentration, and they were poor correlated with the other metals, indicating that the source of Pb and Hg was common controlled by natural factor and anthropic factor.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agricultural Chemistry Committee of China (1983) Conventional methods of soil and agricultural chemistry analysis (in Chinese). Science Press, Beijing, pp 70–165
Arrouays D, Mench M, Amans V, Gomez A (1996) Short-range variability of fallout Pb in a contaminated soil. Can J Soil Sci 76:73–81
Atteia O, Dubois JP, Webster R (1994) Geostatistical analysis of soil contamination in the Swiss Jura. Environ Pollut 86:315–327. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(94)90172-4
Benvenuti M, Mascaro I, Corsini F, Lattanzi P, Parrini P, Tanelli G (1995) Mine waste dumps and heavy metal pollution in abandoned mining district of Boccheggiano southern Tuscany, Italy. Environ Geol 30:238–243. doi:10.1007/s002540050152
Bloemen ML, Markert B, Lieth H (1995) The distribution of Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn in topsoils of Osnaruck in relation to land uses. Sci Total Environ 166:137–148. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(95)04520-B
Box GEP, Cox DR (1964) An analysis of transformations. J R Stat Soc B 26:1–78
Boyer DG, Wright RJ, Feldhake CM, Bligh DP (1991) Soil spatial variability in steeply sloping acid soil environment. Soil Sci 161:278–287. doi:10.1097/00010694-199605000-00003
Cahn MD, Hummel JW, Brouer BH (1994) Spatial analysis of soil fertility for site-specific crop management. Soil Sci Soc Am J 58:1240–1248
Cambardella CA, Moorman TB, Nocak JM, Parkin TB, Karlen DL, Turco RF, Konopka AE (1994) Field-scale variability of soil properties in central Iowa soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 58:1501–1511
Carlon C, Critto A, Marcomini A, Nathanail P (2001) Risk based characterisation of contaminated industrial site using multivariate and geostatistical tools. Environ Pollut 111:417–427. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00089-0
Chang AC, Page AL (2000) Trace elements slowly accumulating, depleting in soils. Calif Agr 54(2):49–55
Chen T, Liu XM, Zhu MZ, Zhao KL, Wu JJ, Xu JM, Huang PM (2008) Identification of trace element sources and associated risk assessment in vegetable soils of the urban-rural transitional area of Hangzhou, China. Environ Pollut 151:67–78. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2007.03.004
Cheng JL, Shi Z, Zhu YW, Liu C, Li HY (2006) Differential characteristics and appraisal of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Zhejiang Province (in Chinese). J Soil Water Conserv 20(1):103–107
Cheng JL, Shi Z, Zhu YW (2007) Assessment and mapping of environmental quality in agricultural soils of Zhejiang Province, China. J Environ Sci China 19:50–54. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(07)60008-4
Cressie N (1993) Statistics for spatial data (revised edition). Wiley, New York
Cui Y, Zhu YG, Zhai R, Huang Y, Qiu Y, Liang J (2005) Exposure to metal mixtures and human health impacts in a contaminated area in Nanning, China. Environ Int 31:784–790. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2005.05.025
Cullbard EB, Thornton I, Wheatley M, Moorcroft S, Thompson M (1988) Metal contamination in British urban dusts and soils. J Environ Qual 17(2):226–234
Dudka S (1992) Factor analysis of total element concentrations in surface soils of Poland. Sci Total Environ 121:39–52. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(92)90305-C
Einax JW, Soldt U (1999) Geostatistical and multivariate statistical methods for the assessment of polluted soils: merits and limitations. Chemometr Intell Lab 46:79–91. doi:10.1016/S0169-7439(98)00152-X
Facchinelli A, Sacchi E, Mallen L (2001) Multivariate statistical and GIS based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environ Pollut 114:313–324. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00243-8
Gallego JLR, Ordonez A, Loredo J (2002) Investigation of trace element sources from an industrialized area (Aviles, northern Spain) using multivariate statistical methods. Environ Int 27:589–596. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(01)00115-5
Goovaerts P (1997) Geostatistics for natural resources evaluation. Oxford University Press, New York
He M, Wang Z, Tang H (1997) Spatial and temporal patterns of acidity and heavy metals in predicting the potential for ecological impact on the Le An river polluted by acid mine drainage. Sci Total Environ 206:67–77. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(97)00217-9
Hopke PK (1992) Factor and correlation analysis of multivariate environmental data. In: Hewitt CN (ed) Methods of environmental data analysis. Elsevier Applied Science, London, pp 139–180
Jobson JD (1991) Applied multivariate data analysis. Springer, New York
Jung MC (2001) Heavy metal contamination of soils and waters in and around the Imcheon Au–Ag mine, Korea. Appl Geochem 16:1369–1375. doi:10.1016/S0883-2927(01)00040-3
Kelly J, Thornton I, Simpson PR (1996) Urban geochemistry: a study of the influence of anthropogenic activity on the heavy metal content of soil in traditionally industrial and no-industrial areas of Britain. Appl Geochem 11:363–370. doi:10.1016/0883-2927(95)00084-4
Kowalkowski T, Zbytniewski R, Szpejna J, Buszewski B (2006) Application of chemometrics in river water classification. Water Res 40:744–752. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2005.11.042
L’Herroux L, Le Roux S, Appriou P, Martinez J (1997) Behaviour of metals following intensive pig slurry applications to a natural field treatment process in Brittany France. Environ Pollut 97:119–130. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(97)00072-9
Li X, Lee SL, Wong SC, Shi W, Thornton I (2004) The study of metal contamination in urban soils of Hong Kong using a GIS-based approach. Environ Pollut 129:113–124. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2003.09.030
Li BG, Ran Y, Cao J, Liu WX, Shen WR, Wang XJ, Coveney RM, Tao S (2007) Spatial structure analysis and kriging of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane residues in topsoil from Tianjin, China. Geoderma 141(1–2):71–77. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2007.05.004
Lucho-Constantino CA, Álvarez-Suárez M, Beltrán-Hernández RI, Prieto-García F, Poggi-Varaldo HM (2005) A multivariate analysis of the accumulation and fractionation of major and trace elements in agricultural soils in Hidalgo State, Mexico irrigated with raw wastewater. Environ Int 31:313–323. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2004.08.002
Luo W, Wang T, Lu Y, Giesy JP, Shi Y, Zheng Y, Xing Y, Wu G (2007) Landscape ecology of the Guanting Reservoir, Beijing, China: multivariate and geostatistical analyses of metals in soils. Environ Pollut 146:567–576. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.08.001
Manta DS, Angelone M, Bellanca A, Neri R, Sprovieri M (2002) Heavy metals in urban soils: a case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Sci Total Environ 300:229–243. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00273-5
Meuli R, Schulin R, Webster R (1998) Experience with the replication of regional survey of soil pollution. Environ Pollut 101:311–320. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(98)00064-5
Micó C, Recatalá L, Peris M, Sánchez J (2008) Discrimination of lithogenic and anthropogenic metals in calcareous agricultural soils: a case study of the Lower Vinalopó Region (SE Spain). Soil Sediment Contam 17:467–485. doi:10.1080/15320380802304367
Mukherjee AB, Zevenhoven R (2006) Mercury in coal ash and its fate in the Indian subcontinent: a synoptic review. Sci Total Environ 368:384–392. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.08.022
Nicholson FA, Smith SR, Alloway BJ, Smith CC, Chambers BJ (2003) An inventory of heavy metal input to agricultural soil in England and Wales. Sci Total Environ 311(1–3):205–219. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(03)00139-6
Paz González A, Taboada Castro MT, Vieira SR (2001) Geostatistical analysis of heavy metals in a one-hectare plot under natural vegetation in a serpentine area. Can J Soil Sci 81(4):469–479
Raghunath R, Tripathi RM, Kumar AV, Sathe AP, Khandekar RN, Nambi KSV (1999) Assessment of Pb, Cd, Cu, and Zn exposures of 6 to 10-year-old children in Mumbai. Environ Res 80:215–221. doi:10.1006/enrs.1998.3919
Romic M, Romic D (2003) Heavy metals distribution in agricultural topsoils in urban area. Environ Pollut 43:795–805
Rui YK, Qu LC, Kong XB (2008) Effects of soil use along Yellow River Basin on the pollution of soil by heavy metals (in Chinese). Spectrosc Spect Anal 28(4):934–936
Saito H, McKenna A, Zimmerman DA, Coburn TC (2005) Geostatistical interpolation of object counts collected from multiple strip transects: ordinary Kriging versus finite domain kriging. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 19:71–85. doi:10.1007/s00477-004-0207-3
Shen Z, Chen HM (2000) Bioremediation of heavy metal polluted soils. Rural Eco Environ 16(2):39–44
Shi JC, Wang HZ, Xu JM, Wu JJ, Liu XM, Zhu HP, Yu CL (2007) Spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils: a case study of Changxing, China. Environ Geol 52:1–10. doi:10.1007/s00254-006-0443-6
Tuncer GT, Tuncel SG, Tuncel G, Balkas TI (1993) Metal pollution in the Golden Horn, Turkey-contribution of natural and anthropogenic components since 1913. Water Sci Technol 28:59–64
von Steiger B, Webster R, Schulin R, Lehmann R (1996) Mapping heavy metals in polluted soil by disjunctive kriging. Environ Pollut 94:205–215. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(96)00060-7
Wang XJ, Tao S (1998) Spatial structures and relations of heavy metal content in wastewater irrigated agricultural soil of Beijing’s eastern farming regions. B Environ Contam Tox 61:261–268. doi:10.1007/s001289900757
Wang D, Shi X, Wei S (2003) Accumulation and transformation of atmospheric mercury in soil. Sci Total Environ 304:209–214. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00569-7
Webster R, Oliver MA (1990) Statistical methods in soil and land resource survey. Oxford University Press, London
Webster R, Oliver MA (2001) Geostatistics for environmental scientists. Wiley, Chichester, pp 37–103
Zhang CS (2006) Using multivariate analyses and GIS to identify pollutants and their spatial patterns in urban soils in Galway, Ireland. Environ Pollut 142:501–511. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.10.028
Zhang C, McGrath D (2004) Geostatistical and GIS analyses on soil organic carbon concentrations in grassland of southeastern Ireland from two different periods. Geoderma 119:261–275. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2003.08.004
Zhejiang Soil Survey Office (1994) Zhejiang soils (in Chinese). Zhejiang Technology Press, Hangzhou, pp 556–562
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the grants by the National Basic Research Priorities Program (973 Program) (2002CB410810). We appreciate all the colleagues who collected and analyzed the soil samples. We also extend great appreciation to Dr. Jiaping Wu and Dr. Huiqing Huang of the Zhejiang University, for their aids in auxiliary data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, C., Zhang, L. Heavy metal concentrations and their possible sources in paddy soils of a modern agricultural zone, southeastern China. Environ Earth Sci 60, 45–56 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0168-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0168-4