Abstract
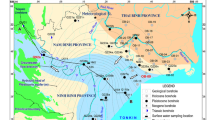
Hydrogeochemistry of the Koyna River basin, famous for the Koyna earthquake (magnitude 7) of 1967, has been studied. Basalt is the primary aquifer; laterites, alluvium, and talus deposits form aquifers of secondary importance. Groundwater generally occurs under water table conditions in shallow aquifers. Deeper aquifers are associated only with basalts. One hundred and 87 water samples were collected from various sources, such as dugwells, borewells, springs, and surface water, including 40 samples for analysis of iron. Only major constituents were analyzed. Analyses show that the concentrations of Ca2+ exceed that of Mg2+ in almost all water samples; the concentrations of Na+ are generally next to Ca2+ and are always higher than that of K+; and CO3 2– and SO4 2– are very low and are often negligible. Groundwater in borewells tapping deeper aquifers has higher mineralization compared to that in dugwells representing shallow aquifers. Majority of the water samples are dominated by alkaline earths (Ca2+, Mg2+) and weak acids (HCO3 −, CO3 2–). Groundwater from shallow aquifers is generally calcium-bicarbonate type (53%) and calcium-magnesium-bicarbonate type (27%). In case of deeper aquifer, it is mostly calcium-magnesium-bicarbonate type (29%), sodium-bicarbonate type (24%), calcium-bicarbonate type (19%), calcium-magnesium-sodium-bicarbonate type (19%) and sodium-calcium-bicarbonate type (9%). Groundwater water is generally fit for drinking and irrigation purposes, except in the lower reaches of the Koyna River basin, which is affected by near water logging conditions.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal PK, Naik PK (1992) Impact of large reservoirs on groundwater recharge in Western Ghats of Maharashtra: a gain to hydrogeological environment. In: Proceedings, national seminar on large reservoirs: environmental loss or gain? Nagpur, India, February 1992, pp 301–304
Agrawal PN (1970) Structural response results from the October 29, 1968, earthquake in the Koyna–Pophali region, India. Bull Seismol Soc Am 60:79–88
Agrawal PN (1971) Observations of earth surface tilting in Koyna–Pophali region, Maharashtra, India. Bull Seismol Soc Am 61:975–982
Agrawal PN (1972) December 11, 1967 Koyna earthquake and reservoir filling. Bull Seismol Soc Am 62:661–662
Angadi KS (1986) Hydrogeological studies of the lower parts of Ghataprabha basin, Belgaum and Bijapur districts, Karnataka, India. PhD Thesis, University of Roorkee
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Athavale RN (1975) Induced seepage along a coastal parallel system of faults as a possible cause of the Koyna earthquakes. Bull Seismol Soc Am 65:183–191
Auden JB (1975) Report on the problem of seismicity associated with the Koyna reservoir, Maharashtra. Irrigation Department, Koyna Dam and Design Circle, Poona
Balsundaram MS, Srinivasan PB (1971) Koyna earthquake and its effects on the Koyna hydro-electric project. In: Proceedings Koyna Earthquake of 11 December 1967 and related problems symp, pp 11–14
Bhattacharya SN (2007) Moment tensor solutions and triggering environment for earthquakes in Koyna–Warna water reservoirs region, India. Pure Appl Geophys 164(5):909–928
BIS (Bureau of Indian Standards) (2003) Indian standard drinking water specifications IS 10500:1991, edition 2.2 (2003–2009). Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi
CGWB (Central Ground Water Board) (1984) Ground water resources of the upper Betwa River basin, India. Indo-British Ground Water Project Bull no 1. Central Ground Water Board, Ministry of Water Resources, Nagpur
Bramham NK, Negi TG (1973) Rift valleys beneath Deccan Traps, India. Geophys Res Bull 2:207–237
Chadha RK, Gupta HK, Kumpel HJ, Mandal P, Nageswara Rao A, Kumar N, Radhakrishna I, Rastogi BK, Raju IP, Sarma CSP, Satyamurthy C, Satyanarayana HVS (1997) Delineation of active faults, nucleation process and pore pressure measurements at Koyna (India). Pure Appl Geophys 150(3–4):551–562
Chandra U (1976) Focal mechanism of the Koyna, India Earthquake of 1967, December 10. Geophys J Int 46(2):247–251
Chopra AK, Chakrabarti P (1973) The Koyna earthquake and the damage to Koyna Dam. Bull Seismol Soc Am 63:381–397
Collins UD (1923) Graphical representation of analysis. Ind Eng Chem 15:394
Das A, Krishnaswami S, Sarin MM, Pande K (2005) Chemical weathering in the Krishna basin and Western Ghats of the Deccan Traps, India: rates of basalt weathering and their controls. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69(8):2067–2084
Dube RK (1986) Relocation of the Koyna earthquakes with a new velocity model. Bull Seismol Soc Am 76:395–407
Fetter CW (1988) Applied hydrogeology. Charles E. Merrill, Columbus
Gahalaut VK, Kalpana, Singh SK (2004) Fault interaction and earthquake triggering in the Koyna–Warna region, India. Geophysical Research Letters, 31, L11614, 2004
Garrels RM, Christ CL (1967) Solutions, minerals and equilibria. Harper and Row, New York
Geological Survey of India (1974) A summary and review of the geological, geophysical and geoseismological studies relating to Koyna earthquakes of 1967 carried out by GSI during the period 1968–1974. Geological Survey of India, Maharashtra Circle (West)
Guha SK, Padale JG (1981) Seismicity and structure of the Deccan Trap region. In: Deccan volcanism and related basalt provinces in other parts of the world. Geol Soc India Mem 3:153–164
Guha SK, Patil DN (1990) Large water-reservoir related induced seismicity. Gerlands Beitr Geophys 99:265–288
Guha SK, Gosavi PD, Padale JG, Marwadi SC (1971) An earthquake cluster at Koyna. Bull Seismol Soc Am 61:297–315
Guha SK, Agarwal SP, Gosavi PD (1972) Accelerogram of Koyna earthquake of December 11, 1967. Bull Seismol Soc Am 62:413–414
Guha SK, Gosavi PD, Nand K, Padale JG, Marwadi SC (1974) Koyna earthquake (Oct 1963 to Dec 1973). Central Water Power Research Station, Poona
Gupta HK (1983) Induced seismicity hazard mitigation through water level manipulation at Koyna, India: a suggestion. Bull Seismol Soc Am 73:679–682
Gupta ID, Rambabu V (1993) Source parameters of some significant earthquakes near Koyna dam, India. Pure Appl Geophys 140(3):403–413
Gupta HK, Narain BK, Mohan I (1969) A study of the Koyna earthquake of December 10, 1967. Bull Seismol Soc Am 59:1149–1162
Gupta HK, Rastogi BK, Narain H (1971) The Koyna earthquake of December 10 1967: a multiple seismic event. Bull Seismol Soc Am 61:167–176
Gupta HK, Rastogi BK, Narain H (1972) Some discriminatory characteristics of earthquakes near the Kariba, Kremasta, and Koyna artificial lakes. Bull Seismol Soc Am 62:493–507
Gupta HK, Rama Krishna Rao CV, Rastogi BK, Bhatia SC (1980) An investigation of earthquakes in Koyna region, Maharashtra, for the period October 1973 through December 1976. Bull Seismol Soc Am 70:1833–1847
Gupta HK, Rastogi BK, Chadha RK, Mandal P, Sarma CSP (1997) Enhanced reservoir-induced earthquakes in Koyna region, India, during 1993–95. J Seismol 1(1):47–53
Gupta SC, Teotia SS, Rai SS, Gautam N (1998) Coda Q estimates in the Koyna region, India. Pure Appl Geophys 153(2–4):713–731
Gupte RB (1968) The Koyna earthquake. J Geol Soc India 9(1):97–105
Hem JD (1970) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. Water Supply Paper-1473, US Geological Survey, pp 363
Hem JD (1985) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. Water Supply Paper-2254, US Geological Survey, pp 263
Jain R, Rastogi BK, Sarma CSP (2004) Precursory changes in source parameters for the Koyna–Warna (India) earthquakes. Geophys J Int 158(3):915–921
Kaila KL, Reddy PR, Dixit MM, Lazarenko MA (1981) Deep crustal structure at Koyna, Maharashtra, indicated by deep seismic sounding. J Geol Soc India 22(1):1–16
Kailasam LN, Murthy BGK (1969) Geophysical investigations in earthquake affected areas of Koyna, Satara district, Maharashtra. Mem Geol Surv India 100:117–122
Kailasam LN, Pant PR, Lahiri SM (1969) Seismic investigations in the earthquake affected areas of Koyna and neighbourhood, Satara district, Maharashtra. Mem Geol Surv India 100:123–126
Karanth KR (1999) Ground water assessment, development and management. Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi, p 720
Krishna J, Chandrasekaran AR, Saini SS (1969) Analysis of Koyna accelerogram of December 11, 1967. Bull Seismol Soc Am 59:1719–1731
Langston CA (1976) A body wave inversion of the Koyna, India earthquake of December 10, 1967 and some implications for body wave focal mechanism. J Geophys Res 81:2517–2529
Langston CA (1981) Source inversion of seismic waveforms: the Koyna, India, earthquakes of 13 September 1967. Bull Seismol Soc Am 71:1–24
Langston CA, Franco-Spera M (1985) Modeling of the Koyna, India, aftershock of 12 December 1967. Bull Seismol Soc Am 75:651–660
Lee W, Rayleigh CB (1969) Fault-plane solution of the Koyna (India) earthquake. Nature 233:172–173
Lloyd JW, Heathcote JA (1985) Natural inorganic hydrochemistry in relation to groundwater: an introduction. Clarendon, Oxford
Mandal P, Rastogi BK (1998) A Frequency-dependent relation of Coda Qc for Koyna–Warna Region, India. Pure Appl Geophys 153(1):163–177
Mandal P, Rastogi BK, Sarma CSP (1998) Source parameters of Koyna earthquakes, India. Bull Seismol Soc Am 88:833–842
Mandal P, Rastogi BK, Sarma CSP, Raju PS, Kousalya M (2002) Magnitude estimation of Koyna–Warna earthquakes, India. J Seismol 6(4):447–458
Mandal P, Mabawonku AO, Dimri VP (2005) Self-organized fractal seismicity of reservoir triggered earthquakes in the Koyna–Warna seismic zone, Western India. Pure Appl Geophys 162(1):73–90
Mathess G, Havery JC Jr (1982) The properties of groundwater. Wiley, New York
Naik PK (1990a) Drinking water problem in parts of Western Ghats, Maharashtra. In: Proceedings, national seminar on challenging problems in water supply engineering, Nagpur, India, October 1990, pp 39–41
Naik PK (1990b) Possibilities of surface water development and artificial recharge of aquifers in parts of Western Ghats, Maharashtra. In: Proceedings, all India seminar on appropriate methods of artificial recharge of groundwater in hard rock areas, Hyderabad, India, July 1990, pp 1.7.1–1.7.4
Naik PK (1993a) Systematic hydrogeological studies in parts of Satara, Sangli, Kolhapur and Ratnagiri districts, Maharashtra. Central Ground Water Board, Central Region, Nagpur, India, pp 147
Naik PK (1993b) On harnessing the springs in the Western Ghats, Maharashtra. Bhujal News, Q J Central Ground Water Board, Ministry of Water Resources, Government of India 8(2):13–18
Naik PK (1999) Reappraisal hydrogeological studies in parts of the Krishna basin. Central Ground Water Board, Central Region, Nagpur, p 78
Naik PK, Awasthi AK (2003a) Groundwater resources estimation of the Koyna River basin, India. Hydrogeol J 11(5):582–594
Naik PK, Awasthi AK (2003b) Groundwater resources development in the Deccan trap country of the Western Ghats, India. In: Krasny J, Hrkal Z, Bruthans J (eds) Groundwater in fractured rocks. IHP-VI, Series on Groundwater No. 7, UNESCO, Paris, ISBN 92-9220-002-X, 377–378
Naik PK, Awasthi AK (2003c) Neotectonic activities in the Koyna River basin—a synopsis. Gondwana Geol Mag Spec Publ 5:157–163
Naik PK, Awasthi AK (2005) Ground water resources development in the Koyna River basin—implications for the Western Ghats region, Maharashtra. J Indian Water Resour Soc 25(3):25–32
Naik PK, Awasthi AK (2006) Role of springs in regeneration of forests in the Western Ghats, India. Paper presented at the international workshop on impacts of reforestation of degraded land on landscape hydrology in the Asian region, Roorkee, India, 6–10 March 2006 (paper in CD)
Naik PK, Awasthi AK (2007) Estimation of shallow aquifer parameters from large-diameter wells in basalts. J Geol Soc India 69:949–958
Naik PK, Awasthi AK, Agarwal PK (1995) On the origin and classification of springs in the Western Ghats, Maharashtra. Gondwana Geol Mag 10:55–62
Naik PK, Awasthi AK, Anand AVSS, Mohan PC (2001) Hydrogeologic framework of the Deccan terrain of the Koyna River basin, India. Hydrogeol J 9(3):243–264
Naik PK, Awasthi AK, Mohan PC (2002) Springs in a headwater basin the Deccan Trap Country of the Western Ghats, India. Hydrogeol J 10(5):553–565
Naik PK, Lamsoge B, Sirsikar DY (2004) Planning conjunctive use practices—a prerequisite for irrigation development in India. In: Proceeding, 20th national convention of civil engineers and national seminar on irrigation development in India, Nagpur, India, October 2004, pp 94–100
Naik PK, Prakash D, Awasthi AK (2007) Thickness estimation of Deccan Flood Basalt of the Koyna area, Maharashtra (India) and implications for recurring seismic activity. Curr Sci 92(7):877–878
Patil DN, Thorat SK, Chavan VS, Guha SK (1992) Seismic hazards due to reservoir-impoundment in Maharashtra, India. In: Proceedings large reservoirs: environmental loss or gain? National Seminar, Nagpur
Pawar NJ, Pondhe GM, Patil SF (1998) Groundwater pollution due to sugar-mill effluent at Sonai, Maharashtra, India. Env Geol 34(213):151–158
Pawar NJ, Pawar JB, Kumar S, Supekar A (2008) Geochemical eccentricity of ground water allied to weathering of basalts from the Deccan Volcanic Province, India: insinuation on CO2 consumption. Aquat Geochem 14:41–71. doi:10.1007/s10498-007-9025-9
Piper AM (1944) A graphical procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Trans Am Geophys Union 25:914–923
Powar KB (1981) Lineament fabric and dyke pattern in the western part of the Deccan Volcanic Province. In: Deccan volcanism and related basalt provinces in other parts of the world. Geol Soc India Mem 3:45–57
Ram A, Singh RP (1971) A note on the seismicity of the Koyna region, Maharashtra, (India). Bull Seismol Soc Am 61:473–477
Ramana DV, Chadha RK, Singh C, Shekar M (2007) Water level fluctuation to earthquakes in Koyna–Warna region, India. Nat Hazards 40(3):585–592
Rao BR, Rao PS (1984) Historical seismicity of Peninsular India. Bull Seismol Soc America 74:2519–2533
Rao BSR, Prakasa Rao TKS, Rao VS (1975) Focal mechanism study of an aftershock in the Koyna region of Maharastra State, India. Pure Appl Geophys 113(1):483–488
Rastogi BK, Mandal P (1999) Foreshocks and nucleation of small- to moderate-sized Koyna earthquakes (India). Bull Seismol Soc America 89:829–836
Rastogi BK, Talwani P (1980) Relocation of Koyna earthquakes. Bull Seismol Soc Am 70(5):1849–1868
Raval U (1995) Seismicity of the Koyna region and regional tectonomagmatism of the Western Margin (India). Pure Appl Geophys 145(1):175–192
Romani S (1981) A new diagram for classification of natural waters and interpretation of chemical analysis data. In: Proc Quality of Ground Water Int Symp, Noordwijkerhout. Studies in environmental science 17. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Sarma PR, Srinagesh D (2007) Improved earthquake locations in the Koyna–Warna seismic zone. Nat Hazards 40(3):563–571
Schoeller H (1959). Arid zone hydrology, recent developments. UNESCO, Paris
Schoeller H (1967) Methods and techniques of groundwater investigation and development. Water Resources Series-33, UNESCO, Paris
Sharma B, Teotia SS, Kumar D (2007) Attenuation of P, S, and coda waves in Koyna region, India. J Seismoly 11(3):327–344
Singh DD, Rastogi BK, Gupta HK (1975) Surface-wave radiation pattern and source parameters of Koyna earthquake of December 10, 1967. Bull Seismol Soc America 65:711–731
Singh C, Bhattacharya PM, Chadha RK (2008) Seismicity in the Koyna–Warna reservoir site in Western India: fractal and b-value mapping. Bul Seismol Soc Am 98:476–482
Sunmonu LA, Dimri VP (2000) Fractal geometry of faults and seismicity of Koyna–Warna region, West India using LANDSAT images. Pure Appl Geophys 157(9):1393–1405
Talwani P (1995) Speculation on the causes of continuing seismicity near Koyna reservoir, India. Pure Appl Geophys 145(1):167–174
Talwani P (1997) Seismotectonics of the Koyna–Warna Area, India. Pure Appl Geophys 150(3–4):511–550
USSL (US Salinity Laboratory Staff) (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. US Department of Agriculture, Washington, DC
Wilcox LV (1955) Classification and use of irrigation waters. Circ 969. US Department of Agriculture, Washington
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the people of the Koyna River basin for their cooperation in the field studies. Thanks are also due to Central Ground Water Board, Ministry of Water Resources, Government of India, for providing necessary field support and facilities. All the analyses were carried out in the chemical laboratory of Central Ground Water Board, Central Region, Nagpur, India. Views expressed in the paper are the authors’ own and do not necessarily reflect the opinions of their affiliated departments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naik, P.K., Awasthi, A.K., Anand, A.V.S.S. et al. Hydrogeochemistry of the Koyna River basin, India. Environ Earth Sci 59, 613–629 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0059-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0059-8