Abstract
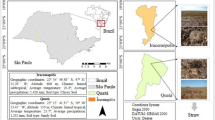
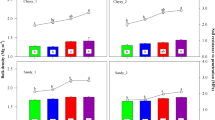
The study described here involved evaluating the effects that the application of one by-product (sugar foam waste) has upon red soils in the region of La Mancha (Central Spain). In view of the fact that this is a location where this type of soil abounds, this technique has been a common practice for many years. The principal goal was to investigate the impact of this approach on some of the soil properties and, secondly, on its level of fertility. As a result, this represents an investigation into the effects that this type of waste has on some soil quality parameters. The results showed that, after the addition of by-products over 25 years, sugar foam waste is of agricultural interest mainly due to the increase in organic matter concentration (about 2%) and, to a lesser extent, by increases in calcium carbonate (more than 30%) and P (four times more). The soil pH was also found to increase slightly (1.4), while the electrical conductivity almost did not change. The properties associated with these pedological qualities therefore had a positive effect by improving nutrient availability. As a result, foams arising from sugar industries have a positive effect on soil quality and the application of such foams to soils is beneficial since the need to dispose this residue is also removed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad F, Tan KL (1986) Effect of lime and organic matter on Soybean seeding grown in Aluminium-oxic soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50:656–661
Alonso FP, Arias JS, Fernandez RO, Fernandez PG, Serrano RE (2006) Agronomic implications of the supply of lime and gypsum by-products to palexerults from western Spain. Soil Sci 171(1):65–81
Anne A (1945) Sur le dosage rapid du carbone organique de sols. Ann Agro 2:161–172
Bending GD, Putland C, Rayns F (2000) Changes in microbial community metabolism and labile organic matter fractions as early indicators of the impact of management on soil biological quality. Biol Fertil Soils 31:78–84
Bremner JM, Mulvaney CS (1982) Nitrogen total, pp 621–622. In: Page AL (ed) Methods of soil analysis Part 2 chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd edn. American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI
Carbonell A, Porthouse JD, Mulbah CK, DeLaune RD, Patrick JWH (1999) Metal solubility in phosphogypsum-amended sediment under controlled pH and redox conditions. J Environ Qual 28:232–242
Cegarra J, Paredas C, Roig A, Bernal MP, García D (1996) Use of olive mill wastewater compost for crop production. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 38:193–203
Chaney K, Swift RS (1984) The influence of organic matter on aggregate stability in some British soils. J Soil Sci 35:415–420
Clark MS, Horwath WR, Shennan C, Scow KM (1998) Changes in soil properties resulting from organic and low-input farming practices. Agrn J 90:662–671
Diaz MJ, Madejon E, Lopez R, Ron-Vaz MD, Cabrera F (1996) Chemical characterization of three composts of (sugar-beet) vinasse with other agroindustrial residues. In: de Bertoldi M, Sequi P, Lemmes B, Papi T (eds) The science of composting vol 2. Blackie Academic and Professional, Glasgow, pp 1138–1141
Drouineau G (1942) Dosage rapide du calcaire actif de sols. Ann Agron 12
Espejo R (2001) El uso de la espuma de azucarería, fosfoyeso y residuos dolomíticos de convertidor (RCD) como enmendantes de suelos ácidos. Actas I encuentro internacional sobre gestión de residuos en el ámbito rural mediterráneo. Pamplona, pp 377–386
FAO (2006) Guidelines for soil description. FAO/UNESCO. Rome, 4th edn
FAO ISRIC ISSS (2006) World reference base for soil resources. A framework for international classification, correlation and communication. World soil resources reports 103, FAO, Rome, 132 p
Fauziah I, Zayah S, Jamal T (1996) Characterization and land application or red gypsum: a waste product from the titanium disoxide industry. Sci Total Environ 188:243–251
Garrido F, Illera V, Vizcayno C, Garcia-Gonzalez MT (2003) Evaluation of industrial by-products as soil acidity amendments: chemical and mineralogical implications. Eur J Soil Sci 54(2):411–422
Gee GW, Bauder JW (1986) Particle-size analysis. In: Klute A (ed) Methods of soil analysis. Part 1. Physical and mineralogical methods, 2nd edn. Agronomy Monograph No.9, ASA-SSSA, Madison, pp 383–411
González Martín J, Rubio Fernández V, García Giménez R, Jiménez Ballesta R (2007) Red palaeosols sequence in a semiarid Mediterranean environment region. Env Geol 51(7):1093–1102
Gunn J, Sein R, Keller B, Beckett P (2001) Liming of acid and metal contaminated catchments for the improvement of drainage water quality. Water Air Soil Pollut 130:1439–1444
Karaka A (2004) Effect of organic wastes on the extractability of cadmium, copper, nickel and zinc in soil. Geoderma 122:297–303
Levi-Minzi R, Riffaldi R, Guidi G, Poggio G (1985) Chemical characterization of soil organic matter in a field study with sewage sludge and composts. In: Williams JH, Guidi G, L’Hermite P (eds) Long term effects of sewage sludge and farm slurries applications. Elsevier, London, pp 151–160
López A, Vidal M, Blázquez R, Urbano P (2001) Differential effects of lime and sugar foam waste on the mineral composition and forage productivity of an acid soil. Agrochimica 45(3–4):89–98
Madejon E, Diaz MJ, Lopez R, Murillo JM, Cabrera F (1996) Cotton fertilization with composts of (sugar-beet) vinasse and agricultural residues. Fertil Res 43:179–182
Madejon E, Lopez R, Murillo JM, Cabrera F (2001) Agricultural use of three (sugar-beet) vinasse composts: effect on crops and chemical properties of a Cambisol soil in the Guadalquivir river valley (SW Spain). Agric Ecosyst Environ 84:53–65
McBride MB (1994) Environmental chemistry of soils. Oxford University Press, New York
Mennch MJ, Manceau A, Vangronsveld J, Clijsters H, Mocquot B (2000) Capacity of soil amendments in lowering the phytoavailabitlity of sludge borne zinc. Agronomie 20:383–397
Moore DM, Reynolds RC Jr (1989) X-ray diffraction and the identification and analysis of clay minerals. Oxford University Press, Oxford, p 332
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. US Department of Agriculture Circ. 939
Ros M (2000) “Recuperación de suelos agrícolas abandonados mediante reciclaje en los mismos de residuos orgánicos de origen urbano”. Tesis Doctoral, Universidad de Murcia
SCS-USDA (1972) Soil Survey investigations report no. 1. Soil survey laboratory methods and procedures for collecting soil samples. US Govt. Printing Office, Washington
Sikora LJ, Azad MI (1993) Effect of compost-fertilizer combinations on wheat yields. Compost Sci Util 1:93–96
Singer MJ, Ewing S (2000) Soil Quality. In: Sumner ME (ed) Handbook of Soil Science, chap 11. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 271–298
Soil Survey Staff (2006) Keys to soil taxonomy, 10th edn. USDA-NCRS
Tejada M, Gonzalez JL (2003) Application of a byproduct of the two-step olive oil mill process on rice yield. Agrochimica 47:94–102
Thomas GW (1982) Exchangeable cations. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis, Part 2. Am Soc Agron Soil Sci Soc Am, Madison, WI, pp 159–165
Tomati U, Galli E, Pasetti L, Volterra E (1995) Bioremediation of olive-mill wastewaters by composting. Waste Manag Res 13:509–518
Vangronsveld J, Cunningham SD (1998) Introduction to the concepts. In: Vangronsveld J, Cunningham SD (eds) Metal contaminated soils: in situ inactivation and phytorestoration. Springer, Berlin and R.G. Landes Company, Georgetown, pp 1–15
Vidal M, Garzon E, Garcia V, Ontanon A, Villa E (2004) Models for predicting composition and temporal structure of chemical parameters for leachates from amended acid soils. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 35(11–12):1517–1542
Vidal M, Garzon E, Garcia V, Ontanon A, Villa E (2006) Differentiating the amending effects of calcareous materials applied to acid soils by use of optimal scaling procedures. Agrochimica 50(3–4):132–147
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García Navarro, F.J., Amorós Ortiz-Villajos, J.A., Sánchez Jiménez, C.J. et al. Application of sugar foam to red soils in a semiarid Mediterranean environment. Environ Earth Sci 59, 603–611 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0058-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0058-9