Abstract
Background
The clinical profile varies in patients with Wilson’s disease (WD). There is paucity of data regarding adult and pediatric patients with hepatic WD.
Methods
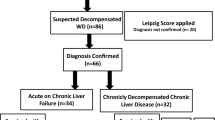
As many as 140 consecutive patients diagnosed with hepatic WD between December 2006 and January 2021 were included in the study. Data was collected regarding the demographic parameters, clinical presentation, extrahepatic organ involvement, liver histology and laboratory investigations. Adult and children (0–14 years) with hepatic WD were compared regarding these features.
Result
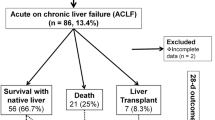
Eighty-eight adults and 52 children were included in the study. The median age of presentation was 17 years (range: 1.1–42 years). Male preponderance was seen (adult 68/88, 69%; children 40/52, 77%). Adults as compared to children presented more commonly as cirrhosis (52/88 vs. 15/52, p = 0.0005) and with hepatic decompensation (35/88 vs. 9/52, p = 0.005). Presentation with acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) was more common in children (10/52 vs. 2/88, p = 0.0005). Twenty-eight-day mortality was 50% (5/10) in children and none in adults presenting with ACLF. Nazer’s Prognostic Index (≥ 7) and New Wilson Index were more accurate in predicting mortality among children with ACLF with AUROC 1, while AARC (APASL ACLF Research Consortium) was less accurate with AUROC 0.45. Liver histology findings were similar in adults and children. Extrahepatic involvement was also similar. (8/88 in adults vs. 3/52 children, p value 0.48).
Conclusion
Most patients with WD present as cirrhosis in adulthood. ACLF is more common in children. Nazer’s prognostic index and new Wilson Index score are accurate in predicting mortality in children with ACLF.
Graphical Abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Yes.
References
Wilson SAK. Progressive lenticular degeneration: a familial nervous disease associated with cirrhosis of liver. Brain. 1912;34:295–507.
Sass-Kortsak A. Wilson’s disease A treatable liver disease in children. Pediatr Clin N Am. 1975;22:963–84.
Pandit AN, Bhave SA. Problems in diagnosis and management of Wilson’s disease in India. Indian Pediatr. 1996;33:807–11.
Pandit A, Bavdekar A, Bhave S. Wilson’s disease. Indian J Pediatr. 2002;69:785–91.
Nagral A, Sarma MS, Matthai J, et al. Wilson’s disease: Clinical Practice Guidelines of the Indian National Association for Study of the Liver, the Indian Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, and the Movement Disorders Society of India. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019;9:74–98.
Steindl P, Ferenci P, Dienes PH, Grimm GH. Wilson’s disease in patients presenting with liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1997;113:212–8.
Guindi M. Wilson disease. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2019;36:415–22.
Ferenci P, Caca K, Loudianos G, et al. Diagnosis and phenotypic classification of Wilson disease. Liver Int. 2003;23:139–42.
Roberts AE. Wilson’s disease. In: Sleisenger and Fordtran’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease, Eleventh Edition, pp. 1180–1188. 2020.
EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Acute (Fulminant) Liver Failure. J Hepatol. 2017; 66:1047–81.
Squires RH Jr, Shneider BL, Bucuvalas J, et al. Acute liver failure in children: the first 348 patients in the pediatric acute liver failure study group. J Pediatr. 2006;148:652–8.
Sarin SK, Choudhury A, Sharma MK, et al. Acute on chronic liver failure: Consensus Recommendations of the Asian Pacific Association for the study of the liver (APASL): an update. Hepatol Int. 2019;13:353–90.
Roberts E, Schilsky ML. A practice guideline on Wilson disease. Hepatology. 2008;47:2089–111.
Kim JW, Kim JH, Seo JK, et al. Genetically confirmed Wilson disease in a 9-month-old boy with elevations of aminotransferases. World J Hepatol. 2013;5:156–9.
Abuduxikuer K, Li LT, Qiu YL, Wang NL, Wang JS. Wilson disease with hepatic presentation in an eight-month-old boy. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:8981–4. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i29.8981.
Dhawan A, Taylor RM, Cheeseman P, et al. Wilson’s disease in children: 37-year experience and revised King’s score for liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2005;11:441–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/lt.20352.
Penon-Portmann M, Lotz-Esquivel S, Chavez Carrera A, et al. Wilson disease in Costa Rica: pediatric phenotype and genotype characterization. JIMD Rep. 2020;52:55–62. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmd2.12098.
Bayes F, Karim AB, Helaly L, et al. Spectrum of hepatic presentation of Wilsons disease in children attending a tertiary care centre of Dhaka city. Bangladesh J Child Health. 2014;38:86–93.
Sokol RJ. Copper metabolism and copper storage disorders. In: Suchy F, Sokol R, Balistreri W, editors. Liver Disease in Children. 4th ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2014. p. 465–92.
Prashanth LK, Taly AB, Sinha S, et al. Wilson’s disease: Diagnostic errors and clinical implications. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004;75:907–9.
Mieli-Vergani G. Value of urinary copper excretion after penicillamine challenge in the diagnosis of Wilson’s disease. Hepatology. 1992;15:609–15.
Giacchino R, Marazzi MG, Barabino A, et al. Syndromic variability of Wilson’s disease in children. Clinical study of 44 cases. Ital J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1997;29:155–61.
Medici V, Trevisan CP, D’Inca R, et al. Diagnosis and management of Wilson’s disease: results of a single center experience. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2006;40:936–41.
Thanapirom K, Treeprasertsuk S, Komolmit P, et al. Comparison of long-term outcome of patients with Wilson’s disease presenting with acute liver failure versus acute-on- chronic liver failure. J Med Assoc Thai. 2013;96:150–6.
Sanchez-Albisua I, Garde T, Hierro L, et al. A high index of suspicion: the key to an early diagnosis of Wilson’s disease in childhood. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999;28:186–90.
Cauza E, Maier-Dobersberger T, Polli C, et al. Screening for Wilson’s disease in patients with liver diseases by serum ceruloplasmin. J Hepatol. 1997;27:358–62.
Walshe JM. Wilson’s disease presenting with features of hepatic dysfunction: a clinical analysis of eighty-seven patients. Q J Med. 1989;70:253–63.
Lau JY, Lai CL, Wu PC, et al. Wilson’s disease: 35 years’ experience. Q J Med. 1990;75:597–605.
Palkar VA, Shrivastava MS, Padwal NJ, et al. Renal tubular acidosis due to Wilson’s disease presenting as metabolic bone disease. BMJ Case Rep. 2011;2011:bcr0420114121.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization- AS, SK. Data curation- SK, MI, BRP, PKR Formal analysis- SK, MI, AG Funding acquisition- Not applicable. Investigation- SK, MI, BRP, PKR, AG, APK Methodology- SK, MI, BRP, PKR, AG, APK Project administration -AS, SK, MI, APK Resources - AS, SK, MI. Software- Not applicable Supervision - AS, SK. Validation- AS, SK. Visualization- SK, MI, BRP, PKR. Roles/Writing - original draft- SK, MI, AS. Writing - review & editing- SK, BRP, MI, AS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Waiver taken for retrospective study
Human Ethics
NA.
Consent for publication
NA.
Competing interests
SK, MI, BRP, PKR, AG, APK and AS declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Disclaimer
The authors are solely responsible for the data and the contents of the paper. In no way, the Honorary Editor-in-Chief, Editorial Board Members, the Indian Society of Gastroenterology or the printer/publishers are responsible for the results/findings and content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Irtaza, M., Patra, B.R. et al. Clinical profile of adult and pediatric patients with hepatic Wilson’s disease. Indian J Gastroenterol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12664-024-01586-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12664-024-01586-2