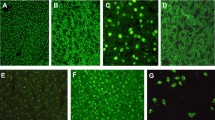
Abstract
Background
Autoantibody testing is used to diagnose autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), a cause of chronic liver disease (CLD). However, various autoantibodies are often detectable in patients with CLD due to other causes too. Since data on autoantibody prevalence in Indian patients with CLD are limited, we decided to undertake the current study.
Methods
Patients with CLD with a known cause other than AIH and a separate group of patients with CLD in whom no cause could be identified were studied. Indirect immunofluorescence assays were used to detect anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA), anti-smooth muscle antibodies (ASMA) and anti-liver-kidney microsomal antibodies (anti-LKM). Serum dilutions tested were 1:80 for ANA and 1:40 for other autoantibodies.
Results
Of the 175 patients with CLD of a known cause, 69 (39 %) had one or more autoantibodies, including ANA in 35 (20 %) patients and ASMA in 44 (25 %) patients. None had anti-LKM. The prevalence rates of any autoantibody, ANA and ASMA were similar in patients with CLD due to alcohol (34 %, 20 %, and 24 %, respectively), HCV infection (43 %, 20 %, and 26 %) and HBV infection (40 %, 18 %, and 25 %). The most common ANA pattern observed was speckled (29/35 patients), followed by nucleolar (5/35) and homogeneous (1/35). The ASMA titers did not exceed 1:80. The antibody prevalence rates were similar in patients with liver cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis, and in those with different disease severity. Serum IgG levels were similar in patients with and without detectable autoantibodies. Patients with no known cause of CLD (n = 50) had similar prevalence rates of autoantibodies, ANA or ASMA.
Conclusion
Autoantibodies were detected in a large proportion of patients with CLD, both cryptogenic and with known cause. Detection of autoantibodies in CLD does not necessarily indicate a diagnosis of AIH, and presence of homogenous pattern of ANA may be more relevant. Indiscriminate testing for autoantibodies in patients with CLD, especially those with a known cause, may not be warranted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lenzi M, Bellentani S, Saccoccio G. Prevalence of non-organ-specific autoantibodies and chronic liver disease in the general population: a nested case- control study of the Dionysos cohort and chronic liver disease in the general. Gut. 1999;45:435–41.
Abuaf N, Lunel F, Giral P, et al. Non-organ specific autoantibodies associated with chronic C virus hepatitis. J Hepatol. 1993;18:359–64.
Lenzi M, Johnson PJ, McFarlane IG, et al. Antibodies to hepatitis C virus in autoimmune liver disease: evidence for geographical heterogeneity. Lancet. 1991;338:277–80.
Cassani F, Muratori L, Manotti P, et al. Serum autoantibodies and the diagnosis of type-1 autoimmune hepatitis in Italy: a reappraisal at the light of hepatitis C virus infection. Gut. 1992;33:1260–3.
Cassani F, Cataleta M, Valentini P, et al. Serum autoantibodies in chronic hepatitis C: comparison with autoimmune hepatitis and impact on the disease profile. Hepatology. 1997;26:561–6.
Gluud C, Tage-Jensen U, Bahnsen M, Dietrichson O, Svejgaard A. Autoantibodies, histocompatibility antigens and testosterone in males with alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981;44:31–7.
Maradona Hidalgo JA, Arribas Castrillo JM. Immunoglobulins and non-organ-specific antibodies in alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Med Clin (Barc). 1981;76:154–7.
Unal F, Genel F, Ozgenc F, et al. Immune status and autoantibody formation in children with chronic hepatitis B infection. Panminerva Med. 2002;44:353–7.
Shim M, Han SB. Extrahepatic manifestations of chronic hepatitis B. Hepatitis B Annual. 2006;3:128–54.
Johnson JR, Gretch DR, Yamabe H, et al. Menbranoproliferative glomerulonephritis associated with hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:465–70.
Pawlotsky JM, Ben Hayia M, Andrè C, et al. Immunological disorders in C virus chronic active hepatitis: a prospective case–control study. Hepatology. 1994;19:841–8.
Alvarez F, Berg PA, Bianchi FB, et al. International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group report: review of criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol. 1999;31:929–38.
Ghosh P, Dwivedi S, Naik S, et al. Antinuclear antibodies by indirect immunofluorescence: optimum screening dilution for diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Indian J Med Res. 2007;126:34–8.
Ghonaim M, Al-Ghamdi A, El-Bana H, et al. Autoantibodies in chronic liver disease. Egypt J Immunol. 2005;12:101–11.
Czaja AJ, Carpenter HA, Santrach PJ, et al. Immunologic features and HLA association in chronic viral hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1995;108:157–64.
Laskin CA, Vidins E, Blendis LM, Soloninka CA. Autoantibodies in alcoholic liver disease. Am J Med. 1990;89:129–33.
Shantha S, Thyagarajan SP, Premavathy RK, et al. Correlation of autoimmune reactivity with hepatitis B and C virus (HBV and HCV) infection in histologically proven chronic liver diseases. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2002;20:12–5.
Reddy KR, Krawitt EL, Homberg JC, Jeffers LJ, de Medina M, Chastenay B. Absence of anti-LKM-1 antibody in hepatitis C viral infection in the United States of America. J Viral Hepat. 1995;2:175–9.
Yachha SK, Srivastava A, Chetri K, Saraswat VA, Krishnani N. Autoimmune liver disease in children. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001;16:674–7.
Cassani F, Bianchi FB, Lenzi M, Volta U, Pisi E. Immunomorphological characterisation of antinuclear antibodies in chronic liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1985;38:801–5.
Prytz H, Holst-Christensen J, Korner B, Liehr H. Portal venous and systemic endotoxaemia in patients without liver disease and systemic endotoxaemia in patients with cirrhosis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1976;11:857–63.
Triger DR, Wright R. Hyperglobulinaemia in liver disease. Lancet. 1973;1:1494–6.
Gregorio GV, Choudhuri K, Ma Y, et al. Mimicry between the hepatitis C virus polyprotein and antigenic targets of nuclear and smooth muscle antibodies in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 2003;133:404–13.
Gregorio GV, Choudhuri K, Ma Y, Vegnente A, Vergani GM, Vergani D. Mimicry between the hepatitis B virus DNA polymerase and the antigenic targets of nuclear and smooth muscle antibodies in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Immunol. 1999;162:1802–10.
Wasmuth HE, Stolte C, Geier A, et al. The presence of nonorgan-specific autoantibodies is associated with a negative response to combination therapy with interferon and ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C. BMC Infect Dis. 2004;4:4.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ms Pallavi Shukla, Department of Gastroenterology, and Mr Rajeshwar Dayal, Department of Immunology, for technical assistance with laboratory work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daschakraborty, S., Aggarwal, A. & Aggarwal, R. Non-organ-specific autoantibodies in Indian patients with chronic liver disease. Indian J Gastroenterol 31, 237–242 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12664-012-0247-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12664-012-0247-4