Abstract
Introduction
Transport distraction osteogenesis (TDO) is a novel reconstructive modality for mandibular ablative defects, precluding donor site morbidity. Assessing of TDO regenerate that could assist in modifying the distraction strategy for patient specific needs.
Materials and Methods
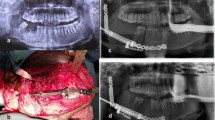
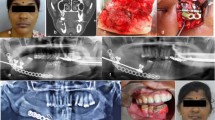
Present study enrolled 17 patients with mandibular defects of size < 12 cm, divided in two groups ≤35 years (A) and > 35 years (B); and assessed the TDO regenerate by clinically examining intra as well as post operatively, using orthopantomogram (OPG), ultrasonography (USG), color Doppler (CD) and cone beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Results
Group B had a longer latency period (p = 0.001) and consolidation period (p = 0.002) than group A. Paired sample correlation study of clinical defect and TDO regenerate (p 0.004) indicate that a better length of regenerate is possible with TDO in mandibular defects. OPG, USG and CBCT shown a significant difference in bone mineralization observed within different age groups except for CD. USG representing earlier detection of mineralization than OPG over the consolidation period.
Conclusion
Use of TDO for reconstruction of mandibular defects is advantageous as the regenerated bone and soft tissues matches the existing anatomical tissues. Evaluation by USG, OPG and CBCT could aid in providing patient specific protocols for TDO in Maxillofacial region.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neelakandan RS, Bhargava D (2012) Transport distraction osteogenesis for maxillomandibular reconstruction: current concepts and applications. J Maxillofac Oral Surg 11(3):291–299
Elsalanty ME, Taher TN, Zakhary IE, Al-Shahaat OA, Refai M, El-Mekkawi HA (2007) Reconstruction of large mandibular bone and soft-tissue defect using bone transport distraction osteogenesis. J Craniofac Surg 18(6):1397–1402
Kumar BP, Venkatesh V, Kumar KA, Yadav BY, Mohan SR (2016) Mandibular reconstruction: overview. J Maxillofac Oral Surg 15(4):425–441
Nanjappa M, Natashekara M, Sendil Kumar C, Kumaraswamy SV, Keerthi R, Ashwin DP, Gopinath AL (2011) “Transport distraction osteogenesis for reconstruction of mandibular defects”: our experience. J Maxillofac Oral Surg 10(2):93–100
Raghoebar GM, Jansma J, Vissink A, Roodenburg JL (2005) Distraction osteogenesis in the irradiated mandible. A case report. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 33(4):246–250
Pereira MA, Luiz de Freitas PH, da Rosa TF, Xavier CB (2007) Understanding distraction osteogenesis on the maxillofacial complex: a literature review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65(12):2518–2523
Costantino PD, Shybut G, Friedman CD, Pelzer HJ, Masini M, Shindo ML, Sisson GA Sr (1990) Segmental mandibular regeneration by distraction osteogenesis. An experimental study. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 116(5):535–545
Hatefi S, Hatefi K, Le Roux F, Alizargar J, Behdadipour Z, Yihun Y, Abou-El-Hossein K (2020) Review of automatic continuous distraction osteogenesis devices for mandibular reconstruction applications. Biomed Eng Online 19(1):17
Zapata U, Elsalanty ME, Dechow PC, Opperman LA (2010) Biomechanical configurations of mandibular transport distraction osteogenesis devices. Tissue Eng Part B Rev 16(3):273–283
Zimmermann CE, Harris G, Thurmüller P, Troulis MJ, Perrott DH, Rahn B, Kaban LB (2004) Assessment of bone formation in a porcine mandibular distraction wound by computed tomography. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 33(6):569–574
Troulis MJ, Coppe C, O’Neill MJ, Kaban LB (2003) Ultrasound: assessment of the distraction osteogenesis wound in patients undergoing mandibular lengthening. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61(10):1144–1149
Kaban LB, Thurmüller P, Troulis MJ, Glowacki J, Wahl D, Linke B, Rahn B, Perrott DH (2003) Correlation of biomechanical stiffness with plain radiographic and ultrasound data in an experimental mandibular distraction wound. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 32(3):296–304
Risselada M, Kramer M, Saunders JH, Verleyen P, Van Bree H (2006) Power Doppler assessment of the neovascularization during uncomplicated fracture healing of long bones in dogs and cats. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 47(3):301–306
Dabas J, Mohanty S, Chaudhary Z, Rani A (2016) Assessment of mandibular distraction regenerate using ultrasonography and cone beam computed tomography: a clinical study. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr 9(1):69–75
Hariri F, Chin SY, Rengarajoo J, Foo QC, Abidin SNNZ, Badruddin AFA (2018) Distraction osteogenesis in oral and craniomaxillofacial reconstructive surgery. In: Yang H (ed) Osteogenesis and bone regeneration. IntechOpen, London
Green AA (2011) The Ilizarov method of distraction osteogenesis. In: Hamdy RC, McCarthy JJ (eds) Management of limb length discrepancies. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, Rosemont, pp 39–44
Ilizarov GA, Ledyasev VI, Shitin VP (1969) Experimental studies of bone lengthening. Eksp Khir Anesteziol 14:3
Balaji SM (2016) Total reconstruction of mandible by transport distraction after complete resection for benign and malignant tumors. Indian J Dent Res 27(2):205–212
Young JW, Kostrubiak IS, Resnik CS, Paley D (1990) Sonographic evaluation of bone production at the distraction site in Ilizarov limb-lengthening procedures. AJR Am J Roentgenol 154(1):125–128
Bell WH, Gonzalez M, Samchukov ML, Guerrero CA (1999) Intraoral widening and lengthening of the mandible in baboons by distraction osteogenesis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 57(5):548–562
Hughes CW et al (2003) Ultrasound monitoring of distraction osteogenesis. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 41(4):256–258
Campos HG, Martins BOL, Ferreira D, Bronzatto EJM (2016) Sonographic Monitoring during distraction osteogenesis. In: Zorzi AR, de Miranda JA (eds) Advanced techniques in bone regeneration. IntechOpen, London
Bruno C, Minniti S, Buttura-da-Prato E, Albanese M, Nocini PF, Pozzi-Mucelli R (2008) Gray-scale ultrasonography in the evaluation of bone callus in distraction osteogenesis of the mandible: initial findings. Eur Radiol 18(5):1012–1017
Rowe NM, Mehrara BJ, Luchs JS, Dudziak ME, Steinbrech DS, Illei PB, Fernandez GJ, Gittes GK, Longaker MT (1999) Angiogenesis during mandibular distraction osteogenesis. Ann Plast Surg 42(5):470–475
Scarfe WC, Farman AG (2007) Cone beam computed tomography: a paradigm shift for clinical dentistry. Aust Dent Pract 18:102–110
Kontogiorgos E, Elsalanty ME, Zapata U, Zakhary I, Nagy WW, Dechow PC, Opperman LA (2011) Three-dimensional evaluation of mandibular bone regenerated by bone transport distraction osteogenesis. Calcif Tissue Int 89(1):43–52
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vishwakarma, A.K., Dhiman, N.K., Sharma, N.K. et al. Evaluation of Transport Distraction Osteogenesis in Maxillofacial Region. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-024-02137-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-024-02137-0