Abstract
Introduction
Incision and drainage for dental infections performed blindly can result in more harm if it fails to locate and evacuate the abscess cavity completely. The use of ultrasonography (USG) in such situations may be beneficial. Therefore, the present study was designed to evaluate the efficacy of ultrasonography as a diagnostic tool for superficial space infections.
Materials and Methods
A prospective study was conducted on 40 patients of either gender, aged 18–60 years who presented with infection of facial spaces of odontogenic origin. Clinical and radiographic examinations of all patients were performed followed by an ultrasonography examination. USG echogenicity of tissues was used to stage the disease (pre-abscess, abscess, cellulitis). Smaller abscesses were drained by aspirating pus with an 18 gauge needle with the help of real-time ultrasound. Larger abscesses were drained by surgical incision and drainage under the static image guidance of ultrasound. Clinical and ultrasonography findings were recorded and data tabulated.
Results
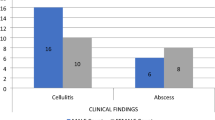
72.5% of patients were with single space involvement, whereas 27.5% had multiple spaces involvement. With clinical and radiographic examination alone, a correct diagnosis was made in only 16 out of 40 cases with a positive predictive value of 46.4% and a negative predictive value of 25%. USG and USG-guided intraoperative aspiration showed a sensitivity and specificity of 100% for diagnosing cases of facial space infection of odontogenic origin. Staphylococci (40.9%) were the predominant species, followed by Pseudomonas (31.8%), Klebsiella (13.6%) and Enterococcus (13.6%).
Conclusion
Ultrasonography (USG) is a valuable diagnostic tool for superficial space infections. It is much superior in defining the exact location of an abscess and guides the surgical approach by locating the abscess cavities. It avoids traditional open surgical incision and drainage in incorrectly diagnosed abscess cases and can be used to follow the course of the disease and its response to nonsurgical treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peleg M, Heyman Z, Ardekian L, Taicher S (1998) The use of ultrasonography as a diagnostic tool for superficial facial space infections. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 56:1129–1131
Wilson IR, Crocker EF, McKellar G, Rangaswamy V (1989) An evaluation of the clinical applications of diagnostic ultrasonography in oral surgery. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 67:242–248
Chodosh PL, Hillside NJ, Silbey R, Oen KT, Elizabeth NJ (1980) Diagnostic use of ultrasound in diseases of the head and neck. Laryngoscope 90:814–821
Cachovan G, Phark JH, Schon G, Pohlenz P, Platzer U (2013) Odontogenic infections: an 8 year epidemiologic analysis in a dental emergency outpatient care unit. Acta Odontol Scan 71:518–524
Rega AJ, Aziz SR, Ziccardi VB (2006) Microbiology and antibiotic sensitivity of head and neck space Infections of odontogenic origin. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 64:1377–1380
Siegert R (1987) Ultrasonography of inflammatory soft tissue swellings of head and neck. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 45:842–846
Ghali S, Katti G, Shahbaz S, Chitroda PK, Anukriti V, Divakar DD, Khan AA, Naik S, Al-Kheraif AA, Jhugroo C (2021) Fascial space odontogenic infections: ultrasonography as an alternative to magnetic resonance imaging. World J Clin C 9(3):573
Yusa H, Yoshida H, Ueno E, Onizawa K, Yanagawa T (2002) Ultrasound-guided surgical drainage of face and neck abscesses. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 31:328–330
Sharma M, Patil K, Guledgud MV (2014) Ultrasonographic evaluation of fascial space infections of odontogenic origin. J Oral Maxillofac Radiol 2:8–14
Bhosale GR, Muthe KV, Shah A (1992) Gray scale ultrasonography as a new diagnostic aid in oral and maxillofacial surgery. JIDA 63:165–167
Craig JG (1999) Ultrasound-guided procedures. Radiol Clin North Am 37:669–678
Hill CR (1993) History now and then. In: David C, Meire H, Dewbury K (eds) A comprehensive text: abdominal and general ultrasound. Churchill Livingstone, London
Baurmash HD (1999) Ultrasonography in the diagnosis and treatment of fascial abscesses. J oral maxillofac surg 57:635–636
Thiruchelvam JK, Songra AK (2002) Intraoperative ultrasound imaging to aid abscess drainage: a technical note. Int J Oral Maxillofac surg 31:442–443
Aarthi Nisha V, Parthiban J, Santana N, Giridhar AG, Yashoda Devi BK, Sujatha Reddy S, Rakesh N et al (2013) Role of color doppler ultrasonography in diagnosis of fascial space infections: a study. J Clin Diagn Res 7:962–967
Mukhi PU, Mahindra UR (2012) The use of ultrasonography in diagnosis and management of superficial fascial space infections. Indian J Dent Res 23:313–319
Bassiony M, Yang J, Abdel-Monem T, Elmogy S, Elnagdy M (2009) Exploration of ultrasonography in assessment of fascial space spread of odontogenic infections. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 107:861–869
Parker KL, Brunton LL, Lazo JS (2005) Goodman and Gilman’s The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 11th edn. McGraw-Hill Companies, New York, pp 1127–1154
Dahlén G (2000) Microbiology and treatment of dental abscesses and periodontal-endodontic lesions. Periodontol 2002(28):206–239
Topazian R, Moton H, Goldberg M, Hupp JR (2002) Oral and maxillofacial infections, 4th edn. W.B Saunders company, USA, pp 168–184
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Saifi, A.M., Anjum, O., Byra, P. et al. Ultrasonography as a Diagnostic Tool for Superficial Space Infections: A Prospective Study. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-024-02134-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-024-02134-3