Abstract
Background and Purpose
Dental implants are considered to be one of several treatment options that can be used to replace missing teeth. The objective of the study is to examine and compare the biomechanics of zygomatic and pterygoid implants planned on the atrophic maxilla with three different bone types.
Materials and Methods
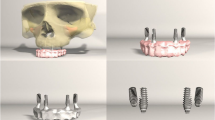
An in vitro finite element study was conducted on a three-dimensional model of zygomatic and pterygoid implants. In a total of 24 implants, two bilateral zygomatic and pterygoid implants with two anterior dental implants were inserted in models. 150 N vertical occlusal and 300 N load on masseter and medial pterygoid were simulated on the modeled prosthesis. The data were processed with ANSYS software. The stress on and deformations of the bones and implants were observed and compared.
Results
When comparing the D4, D3, and D2 bones in subgroup I with zygomatic implants, the D2 bone was subjected to less stress compared to D3 and D4. The smallest displacement (0.125784 mm) was seen in D4 followed by the largest displacement (0.74073 mm) in D2. Similarly, when comparing the D2, D3, and D4 bone in subgroup II with pterygoid implants, the D2 bone in the atrophic maxilla received the least amount of stress from the pterygoid implants compared to D3 and D4. Furthermore, the smallest displacement (0.030934 mm) was seen in D2, and the largest (0.046319 mm) in D4.
Conclusion
Results suggest firstly, that the overall stress was better distributed in D2 bone and secondly, the pterygoid implant showed higher stress concentration than the zygomatic implant.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Warreth A, Ibieyou N, O’Leary RB, Cremonese M, Abdulrahim M (2017) Dental implants: an overview. Dent Update 44(7):596–620
Balaji VR, Lambodharan R, Manikandan D, Deenadayalan S (2017) Pterygoid implant for the atrophic posterior maxilla. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 9(Suppl 1):S261
Albrektsson T, Wennerberg A (2005) The impact of oral implants-past and future, 1966–2042. J Can Dent Assoc 71(5):327
Peñarrocha-Diago M, Uribe-Origone R, Guarinos-Carbó J (2004) Implant-supported rehabilitation of the severely atrophic maxilla: a clinical report. J Prosthodont: Implant, Esthetic and reconstr. Dent. 13(3):187–191
Pi-Urgell J, Mir-Mari J, Figueiredo R, Gay-Escoda C (2010) Rehabilitation of atrophic maxillas using zygomatic implants. Int Mag Oral Implantol 11:2431
Ishak MI, Kadir MA, Sulaiman E, Kasim NA (2012) Finite element analysis of different surgical approaches in various occlusal loading locations for zygomatic implant placement for the treatment of atrophic maxillae. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 41(9):1077–1089
Grecchi F, Busato A, Grecchi E, Carinci F (2013) Surgically-guided zygomatic and pterygoid implants a no-grafting rehabilitation approach in severe atrophic maxilla a case report. Ann Oral Maxillofac Surg 1(2):1–5
Korkmaz FM, Korkmaz YT, Yaluğ S, Korkmaz T (2012) Impact of dental and zygomatic implants on stress distribution in maxillary defects: a 3-dimensional finite element analysis study. J Oral Implantol 38(5):557–567
Gümrükçü Z (2019) Biomechanical evaluation of zygomatic implant use in patients with different buccal maxillary defect levels. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1:1–33
Funding
Nil
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Daniel, D., Pande, D., Bakshi, J.H.I. et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of Zygomatic Implant Versus Pterygoid Implant in Atrophic Maxilla: An In vitro Finite Element Study. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-024-02128-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-024-02128-1