Abstract
Aim
To evaluate the length of styloid process and to assess the clinical significance of it in Eagle’s syndrome.
Objectives
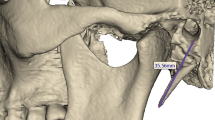
(1) To evaluate the length of styloid process using digital panoramic radiographs. (2) To evaluate the type of styloid process elongation using Langlais classification. (3) To assess the clinical symptoms of Eagle’s syndrome in patients with elongated styloid process.
Methods
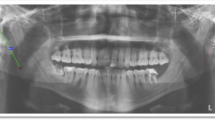
OPG of patients reporting to Dental OPD above 18 years from November 2021 to May 2022 with No history of trauma No known history of craniofacial anomalies and craniofacial surgery. No clinical significance of Eagle’s syndrome. All digital images used in the study have been taken using under standard settings with minimal radiation exposure using the ALARA principle. Measurements were obtained using the EzDent software.
Statistical Analysis
Descriptive: Mean and Standard Deviation Inferential: (1) Chi-square test—for comparison of length of styloid process. (2) Student’s t test—analyze the significance of the condition.
Results
About 31% of the total examined population has elongated styloid process with Type I Langlais classification and most of them are asymptomatic in nature. Second highest type is Type IV in 1.8% followed by Type II which was noted in about 1.2%, and the least noted is Type III in 0.6%.
Conclusion
Though most people with extended styloid process are asymptomatic, increasing styloid process length still does not show any manifestation of Eagle’s syndrome.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Standring S (2008) Gray’s anatomy: anatomical basis of clinical practice, 40th edn. Elsevier, London
Piagkou M, Anagnostopoulou S, Kouladouros K et al (2009) Eagle’s syndrome: a review of the literature. Clin Anat 22:545–558
Vadgaonkar R, Murlimanju B, Prabhu LV et al (2015) Morphological study of styloid process of the temporal bone and its clinical implications. Anat Cell Biol 48(3):195–200. https://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2015.48.3.195
Eagle WW (1937) Elongated styloid process. Arch Otolaryngol 25:584–587
Gokce C, Sisman Y, Tarim E et al (2008) Prevalence of styloid process elongation on panoramic radiography in the Turkey population from Cappodocia region. Eur J Dermatol 2:18–22
İlgüy M, İlgüy D, Güler N et al (2005) Incidence of the type and calcification patterns in patients with elongated styloid process. J Int Med Res 33(1):96–102
Murtagh RD, Caracciolo JT, Fernandez G (2001) CT findings associated with Eagle syndrome. Am J Neuroradiol 22:1401–1412
Balcioglu HA, Kilic C, Akyol M et al (2009) Length of the styloid process and anatomical implications for eagle’s syndrome. Folia Morphol (Wars) 68(4):265–270
AlZarea BK (2017) Prevalence and pattern of the elongated styloid process among geriatric patients in Saudi Arabia. Clin Interv Aging 12:611–617
Natsis K, Repousi E, Noussios G et al (2015) The styloid process in Greek population: an anatomical study with clinical implications. Anat Sci Int 90:67–74
Vieira EM, Guedes OA, De Morais S et al (2015) Prevalence of elongated styloid process in a central brazilian population. J Clin Diagn Res 9:90–92
Antonio G, Alberto DS, Giovanni B et al (2017) Elongated styloid process evaluation on digital panoramic radiograph in a North Italian population. J Clin Exp Dent 9(3):e400–e404
Guarna M, Aglianò M, Toriello G et al (2015) Variations in the length of the styloid process and the possible consequences on muscle ligamentous systems with the mandible and the hyoid bone. Ital J Anat Embryol 119(1):100. https://doi.org/10.13128/IJAE-15938
Langlais RP, Miles DA, Van Dis ML (1986) Elongated and mineralized stylohyoid ligament complex: a proposed classification and report of a case of Eagle’s syndrome. Oral Surg OralMed Oral Pathol 61(5):527–532
Haluk Ö, Burcu E, Ufuk T et al (2014) Cone-beam computed tomographic evaluation of styloid process: a retrospective study of 208 patients with orofacial pain. Head Face Med 10:5
Soylu E, Altan A, Sekerci AE et al (2017) An asymptomatic and overelongated styloid process. Case Rep Dent. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7971595
Kaufman SM, Elzay RP, Irish EF (1970) Styloid process variation: radiologic and clinical study. Arch Otolarngol 91:63–460
Jung T, Tschernitschek H, Hippen H et al (2004) Elongated styloid process: when is it really elongated? Dentomaxillofacial Radiol 33:119–124
Custodio ALN, Silva MRMA, Abreu MH et al (2016) Styloid process of the temporal bone: morphometric analysis and clinical implications. BioMed Res Int 2016:8792725
Bozkir MG, Boga H, Dere F (1999) The evaluation of elongated styloid process in panoramic radiographs in edentulous patients. Turk J Med Sci 29(4):481–486
Correll RW, Jensen JL, Taylor JB et al (1979) Mineralization of the stylohyoid-stylomandibular ligament complex. A radiographic incidence study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 48(4):286–291
Keur JJ, Campbell JP, Mccarthy JF et al (1986) The clinical significance of the elongated styloid process. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 61:399–404
Steinmann EP (1970) A new light on the pathogenesis of the styloid syndrome. Arch Otolaryngol 91:171–174
Funding
This study received no particular support from governmental, commercial, or not-for-profit funding entities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical Approval
The study was approved by Institutional Review Board (SVDC/IRB/2022/0606/PG SHORT STUDIES/59) and Institutional Ethical Committee (11/SVMCH/IEC-Cert/Aug 22).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Babu, N., Vaithilingam, Y., Arumugam, B. et al. To Determine the Association of Elongated Styloid Process and Eagle’s syndrome Using Digital Panoramic Radiograph: A Retrospective Study. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-023-02105-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-023-02105-0