Abstract
Background
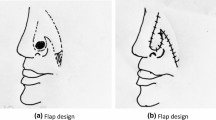
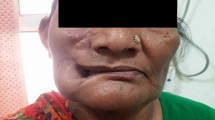
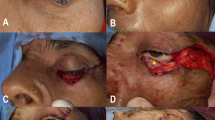
Both nasolabial and forehead flaps are utilized for the reparation of nasal soft tissue defects that result from basal cell carcinoma. Utilizing the forehead flap needs twice operation for scar correction and flap base amputation while the nasolabial flap is a more effective one-stage technique.
Material and methods
This prospective study was performed on patients with BCC involving nasal tip and ala regions based on the results of the initial biopsy and was admitted to the surgery department of the Loghman-Hakim Hospital to resect the lesion.
Results
The paramedian forehead flap, in contrast with the nasolabial flap, covers more tissue defects (nasolabial flap 14.38 mm and paramedian forehead flap 19 mm). Patients’ satisfaction with the nasolabial flap was much higher than the paramedian forehead flap (nasolabial flap 94.9% and paramedian forehead flap 91.1%). The need to modify the flap donor site scar of the paramedian forehead flap was much higher than the nasolabial flap (paramedian forehead flap 100%). Infiltrative BCC tumor was the most prevalent one in both the nasolabial and paramedian forehead flaps as compared with other types of BCC (nasolabial flap 38.5% and paramedian forehead flap 54.5%).
Conclusion
This study aimed at comparing the nasolabial flap and paramedian forehead flap for nasal tissue defect repair caused by basal cell carcinoma, attempting to highlight the advantages and disadvantages of each technique. The nasolabial flap is found to be more time-efficient, provides better patient satisfaction, and results in less noticeable scarring, while the paramedian forehead flap offers greater coverage for larger defects. Further studies are needed to assess long-term outcomes and provide more comprehensive evidence on efficacy and complications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brunicardi F, Andersen D, Billiar T, Dunn D, Hunter J, Matthews J et al (2015) Schwartz’s principles of surgery, 10th edn. McGraw-Hill Education, New York, pp 1831–1835
Mccarthy JG, MD Lawrence, Bell D. Professor of plastic surgery and director of reconstructive New York University Medical Center vol 3. pp 1933–1987
Bullocks JM, Hsu PW, Izaddoost SA (2017) Plastic surgery principle and techniques, vol 1, 2nd edn. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart
Zollinger RM, Ellison EC (2016) Zollinger’s atlas of surgical operations, 10th edn. McGraw Hill LLC
Tan NC, Huahsieh C, Riva FMG, Jenny SF (2013) The nasolabial flap as a one-stage procedure for reconstruction of intermediate-to-large lip defects with functional and aesthetic assessments. J Plast Reconstruct Aesthet Surg 66:352–357
Russell D, Brigg MD, Karen H, Calhoun MD (2001) Department of otolaryngology, Garmel Rounds presentation October 3, 2001
Robert S, Andrew S, Luigi S (2015) American Academy of Dermatology and MOHS surgery. pp 23–34
Courtney M. Townsend, MD, Mark Evers B, MD, Daniel Beauchamp, MD Sabiston textbook of surgery 20th Edition vol1 747.2017
Shetty SK, Sarkar S (2019) The versatility of nasolabial flaps in maxillofacial surgery. J Maxillofac Oral Surg 18(4):589–595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-018-1162-8. (Epub 2018 Oct 8)
Correa BJ, Weathers WM, Wolfswinkel EM, Thornton JF (2013) The forehead flap: the gold standard of nasal soft tissue reconstruction. Semin Plast Surg 27(2):96–103. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1351231
Hakim E, Behravesh S, Zadeh MH (2020) Comparison of the nasolabial flap and paramedian forehead flap in the reconstruction of nasal defects. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 78(3):358–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2019.09.019
Piazza C, Taglietti V, Paderno A et al (2020) Nasolabial versus forehead flap in nasal reconstruction: patient-reported outcomes, objective outcomes, and aesthetic evaluations. Head Neck 42(2):219–229. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.25973
Kallappa S, Shah N (2019) Outcome of nasolabial flap in the reconstruction of head and neck defects. Indian J Surg Oncol 10(4):577–581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13193-019-00948-z. (Epub 2019 Jul 17)
Tang C, Yan X, Jiao J et al (2021) Nasolabial flap versus paramedian forehead flap for nasal reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 79(5):1002–1015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2020.11.014
Chakraborty SS, Goel AD, Sahu RK, Midya M, Acharya S, Shakrawal N (2023) Effectiveness of nasolabial flap versus paramedian forehead flap for nasal reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aesthet Plast Surg 47(1):313–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-022-03060-w. (Epub 2022 Sep 14)
Hu W, Fan C, Li Q et al (2020) Comparative study of nasolabial and forehead flaps for nasal reconstruction after malignant tumor excision. J Craniofac Surg 31(4):e389–e394. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000006164
Acknowledgements
Thanks to the Loghman-Hakim Hospital’s clinical personnel who sincerely helped the researchers to conduct the present study.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval has been granted by the medical school of Shahid-Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (IR.SBMU.MSP.REC.1395.24).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rashnoo, F., Yegane, R.A. & Hassanpour, A. The Comparison Competence Nasolabial and Forehead Flap for Reparation Nasal Tissue Defect of Basal Cell Carcinoma. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-023-02093-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-023-02093-1