Abstract
Objectives
The aim of this study is to investigate the effect of the graft material combined with ozonized blood on bone healing in rabbit in maxillary sinus lifting applications histomorphometrically, immunohistochemically and microtomographically.
Materials and Methods
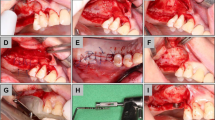
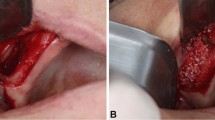
Twenty-eight New Zealand rabbits were randomly divided into 2 groups as experimental (n = 14) and control (n = 14). In experimental group, 5 ml (milliliter) blood obtained from the ear vein of each rabbit was ozonized by 80 µl (µl)/ml concentration ozone–oxygen mixture. Graft material was combined with this ozonized blood. In control group, the graft was combined with saline solution at 0.9% concentration. A 5 mm (millimeter) in diameter window was created on right maxillary sinus window in each rabbit under general anesthesia by local anesthesia support. Sinus membrane was elevated and the space was augmented by 1 cc (cubic centimeter) graft material. One rabbit from the control group which was planned to sacrifice at the end of 8 weeks could not participate in the evaluation because of the extensive inflammation at the operation site. Newly formed bone area and bone density were measured using by image analysis program. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and collagen-1 (COL-1) analyses were carried out immunohistochemically. The amount of the newly generated bone and the amount of the total augmented space were calculated volumetrically by microtomography.
Results
According to histomorphometrical analysis, although newly formed bone area has increased in both experimental and control group with time, statistically significant results were obtained when only O-8 (ozone-treated experimental group planned to be sacrificed after 8 weeks) and O-4 (ozone-treated experimental group planned to be sacrificed after 4 weeks) groups were compared (p = 0,037). The increase in new bone density was seen in both experimental and control groups with time and the results were statistically significant when O-8 group compared to O-4 and C-4 group (ozone-free control group planned to be sacrificed after 4 weeks) (p = 0,07 and p = 0,04, respectively) and C-8 (ozone-free control group planned to be sacrificed after 8 weeks) group compared to C-4 group (p = 0,023). According to immunohistochemical analysis, the intensity and the severity of field staining with anti-BMP-2 have increased in experimental group whereas it has decreased in control group but despite that there was no statistically significance among all groups compared to each other. The number of new vessels stained with anti-VEGF has increased in both experimental and control group with time and multiple comparison results were statistically significant when O-8 group compared with O-4 and C-4 (p = 0,000, p = 0,000, respectively), O-4 group compared with C-8 (p = 0,000) and C-8 group compared with C-4 (p = 0,000). Although the intensity and the severity of field staining with anti-COL-1 have increased in both experimental and control group with time, there was no statistically significance among all groups compared to each other. According to microtomographical analysis, the percentage of the volume of the newly generated bone in the total augmented space volume has decreased with time in both experimental and control groups.
Conclusions
Considering the results of this study, the graft material combined with the ozonized blood increased the density of the newly generated bone and the number of new vessels in maxillary sinus lifting applications in rabbits.
Clinical Relevance
We suggest further studies should be done combining the graft with ozone by different methods, dosages and exposure times.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cabbar F, Kürkçü M, İşeri U (2011) The effect of bovine bone graft with or without platelet-rich plasma on maxillary sinus floor augmentation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 69:2537–2547
García-Gareta E, Coathup MJ, Blunn GW (2015) Osteoinduction of bone grafting materials for bone repair and regeneration. Bone 81:112–121
Lambert F, Leonard A, Drion P, Sourice S, Pilet P, Rompen E (2013) The effect of collagenated space filling materials in sinus bone augmentation: a study in rabbits. Clin Oral Impl Res 24:505–511
Stübinger S, Sader R, Filippi A (2006) The use of ozone ın dentistry and maxillofacial surgery: a review, quintessence ınternational (Berlin, Germany: ). 37(5): 353–359
Erdemci F, Gunaydin Y, Sencimen M, Bassorgun I, Ozler M, Oter S, Gulses A, Gunal A, Sezgin S, Bayar GR, Doğan N, Gider IK (2014) Histomorphometric evaluation of the effect of systemic and topical ozone on alveolar bone healing following tooth extraction in rats. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 43(6):777–783
Bocci V (2005) Ozone, a new medical drug. Springer, Netherlands, pp 1–295
Vescovi P, Merigo E, Meleti M, Manfredi M, Fornaini C, Nammour S, Mergoni G, Sarraj A, Bagan JV (2014) Conservative surgical management of stage I bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Int J Dent
Vescovi P, Nammour S (2010) Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the Jaw (BRONJ) therapy: a critical review. Minerva Stomatol 59(4):181–203
Agrillo A, Ungari C, Filiaci F, Priore P, Iannetti G (2007) Ozone therapy in the treatment of avascular bisphosphonate-related jaw osteonecrosis. J Craniofac Surg 18(5):1071–1075
Bocci V (2006) Scientific and medical aspects of ozone therapy: state of the art. Arch Med Res 37:425–435
Xu H, Shimizu Y, Onodera K, Ooya K (2005) Long-term outcome of augmentation of the maxillary sinus using deproteinised bone particles experimental study in rabbits. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 43(1):40–45
Tevlin R, McArdle A, Atashroo D, Walmsley GG, Senarath-Yapa K, Zielins ER, Paik KJ, Longaker MT, Wan DC (2014) Biomaterials for craniofacial bone engineering. J Dent Res 93(12):1187–1195
Hing KA (2004) Bone repair in the twenty-first century: biology, chemistry or engineering? Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 362(1825):2821–2850
Torres J, Tamimi F, Martinez PP, Alkhraisat MH, Linares R, Hernández G, Torres-Macho J, López-Cabarcos E (2009) Effect of platelet-rich plasma on sinus lifting: a randomized-controlled clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol 36(8):677–687
Bolükbasi N, Ersanli S, Keklikoglu N, Basegmez C, Ozdemir T (2015) Sinus augmentation with platelet-rich fibrin in combination with bovine bone graft versus bovine bone graft in combination with collagen membrane. J Oral Implantol 41(5):586–595
Jensen T, Schou S, Stavropoulos A, Terheyden H, Holmstrup P (2012) Maxillary sinus floor augmentation with Bio-Oss or Bio-Oss mixed with autogenous bone as graft: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res 23(3):263–273
Rickert D, Sauerbier S, Nagursky H, Menne D, Vissink A, Raghoebar GM (2011) Maxillary sinus floor elevation with bovine bone mineral combined with either autogenous bone or autogenous stem cells: a prospective randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Impl Res 22:251–258
Sauerbier S, Stubbe K, Maglione M, Haberstroh J, Kuschnierz J, Oshima T, Xavier SP, Brunnberg L, Schmelzeisen R, Gutwald R (2010) Mesenchymal stem cells and bovine bone mineral in sinus lift procedures—an experimental study in sheep. Tissue Eng Part C Methods 16(5):1033–1039
Jensen SS, Broggini N, Hjørting-Hansen E, Schenk R, Buser D (2006) Bone healing and graft resorption of autograft, anorganic bovine bone and beta-tricalcium phosphate. A histologic and histomorphometric study in the mandibles of minipigs. Clin Oral Implants Res 17(3):237–243
Kim YS, Kim SH (2012) Rabbit maxillary sinus augmentation model with simultaneous implant placement: different responses to the graft materials. J Periodontal İmplant Sci 42:204–211
Watanabe K, Niimi A, Ueda M (1999) Autogenous bone grafts in the rabbit maxillary sinus. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 88(1):26–32
Allegrini S Jr, Yoshimoto M, Salles MB, König B Jr (2003) The effects of bovine BMP associated to HA in maxillary sinus lifting in rabbits. Ann Anat 185(4):343–349
Özdemir H, Toker H, Balcı H, Özer H (2013) Effect of ozone therapy on autogenous bone graft healing in calvarial defects: a histologic and histometric study in rats. J Periodont Res 48:722–726
Hu K, Olsen BR (2016) The roles of vascular endothelial growth factor in bone repair and regeneration. Bone 91:30–38
Hu K, Olsen BR (2016) Osteoblast-derived VEGF regulates osteoblast differentiation and bone formation during bone repair. J Clin Investig 126(2):509
Yang XB, Bhatnagar RS, Li S, Oreffo RO (2004) Biomimetic collagen scaffolds for human bone cell growth and differentiation. Tissue Eng 10(7–8):1148–1159
Young S, Athanasiou KA, Mikos AG, Wong MEK (2007) Oral and maxillofacial surgery. In: Lanza R, Langer R, Joseph V (eds) Principles of tissue engineering, 3rd edn. Elsevier, China, pp 1079–1094
Boyne PJ, Lilly LC, Marx RE, Moy PK, Nevins M, Spagnoli DB, Triplett RG (2005) De novo bone induction by recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2) in maxillary sinus floor augmentation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63:1693–1707
Funding
This project was financially sponsored by Scientific Research Council of Medical Sciences University Gülhane Education and Research Hospital (January 3rd 2014, AR-2014-24).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author Gamze ARICI declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author Metin ŞENÇİMEN declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Abdullah Tuğrul COKUN declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Hasan Ayberk ALTUĞ declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Servet GÜREŞCİ declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author Hakan Hamdi ÇELİK declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Muhammet Bora UZUNER declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Mert OCAK declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures were conducted incompliance with ethical principles for animal research, as approved by institutional guidelines of Medical Sciences University Gülhane Education and Research Hospital (February 14th 2014, No: 14/144).
Informed Consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supported by: Gülhane Education and Research Hospital, Center of Research and Development (AR-2014/24).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arıcı, G., Şençimen, M., Coşkun, A.T. et al. Evaluation of the Efficiency of the Graft Material Combined with Ozonized Blood in Maxillary Sinus Lifting Applications in Rabbits. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 21, 562–570 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-021-01653-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-021-01653-7