Abstract
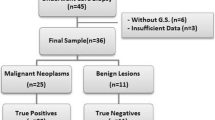
Tru-cut (core needle) biopsy has many advantages over open biopsy. It is quick and easy to perform, may be carried out in the outpatient department, avoids incision through previously irradiated skin and has few complications. The purpose of this study is to compare the two available biopsy techniques that are Tru-cut biopsy and incisional biopsy in achieving prompt diagnosis of maxillofacial pathology. A prospective study was conducted in 25 patients reported to our department. The Tru-cut biopsy was performed by using 14 gauge disposable Tru-cut biopsy needles (Baxter, made in the USA) by means of two successive insertions with different angulations of the needle into the core of the lesion followed by incisional biopsy. The diagnostic criteria which were evaluated include: sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV) and accuracy. Tru-cut biopsy had sensitivity of 68.42%; specificity of 83.33%; PPV of 92.86%; NPV of 45.45% with accuracy rate of 72%. The Tru-cut biopsy method was evaluated as a very helpful method for prompt diagnosis of maxillofacial pathology since it is practical to perform, causes minimum trauma to the tissue, decreases the metastatic risk of malignant lesions during the procedure and relatively free from complications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayhan NK, Keskin C, Olgac V, Dedeoglu K, Yaltirik M, Erseven G et al (2003) Tru-cut and fine needle aspiration biopsy diagnosis of lesions of the jaws. Turk J Med Sci 33:249–253
Kissin MW, Fisher C, Carter RL, Horton LW, Westbury G (1986) Value of Tru-cut biopsy in the diagnosis of soft tissue tumors. Br J Surg 73(9):742–744
Mokamel MI. Evaluation of Trucut Needle versus Excisional Testicular Biopsy in Azoospermic Patients. Faculty of Commerce – Males (Cairo), 2007.
Dupuy DE, Rosenberg AE, Punyaratabandhu T, Tan MH, Mankin HJ (1998) Accuracy of CT-guided needle biopsy of musculoskeletal neoplasms. AJR Am J Roentgenol 171(3):759–762
Joshi A, Magar SR, Chand P, Panth R, Khatri Chhetri BR (2013) Tru-cut biopsy as the initial method of tissue diagnosis in bone tumors with soft tissue extension. Indian J Orthop 47(2):195–199
Yamashita Y, Kurokawa H, Takeda S, Fukuyama H, Takahashi T (2002) Preoperative histologic assessment of head and neck lesions using cutting needle biopsy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 93(5):528–533
Zikan M, Fischerova D, Pinkavova I, Dundr P, Cibula D (2010) Ultrasound-guided tru-cut biopsy of abdominal and pelvic tumors in gynecology. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 36(6):767–772
Issakov J, Flusser G, Kollender Y, Merimsky O, Lifschitz-Mercer B, Meller I (2003) Computed tomography-guided core needle biopsy for bone and soft tissue tumors. Isr Med Assoc J 5(1):28–30
Kesse KW, Manjaly G, Violaris N, Howlett DC (2002) Ultrasound guided biopsy in the evaluation of focal lesions and diffuse swelling of the parotid gland. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 40(5):384–388
Wan YL, Chan SC, Chen YL, Cheung YC, Lui KW, Wong HF, Hsueh C, See LC (2004) Ultrasonography-guided core-needle biopsy of parotid gland masses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25(9):1608–1612
Breeze J, Andi A, Williams MD, Howlett DC (2009) The use of fine needle core biopsy under ultrasound guidance in the diagnosis of a parotid mass. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 47(1):78–79
Hodges S, Williams MD, Moody AB, Ramesar K, Howlett DC (2010) Ultrasound-guided core biopsy for investigation of cervical lymph node: chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and metastatic squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 48(1):46–47
Sharma G, Jung AS, Maceri DR, Rice DH, Martin SE, Grant EG (2011) US-guided fine-needle aspiration of major salivary gland masses and adjacent lymph nodes: accuracy and impact on clinical decision making. Radiology 259(2):471–478
Schmidt RL, Hall BJ, Layfield LJ (2011) A systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy for salivary gland lesions. Am J Clin Pathol 136(4):516–526
Maharaj B, Pillay S (1991) “Tru-Cut” needle biopsy of the liver: importance of the correct technique. Postgrad Med J 67(784):170–173
Serpell JW, Fish SH, Fisher C, Thomas JM (1992) The diagnosis of soft tissue tumours. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 74(4):277–280
Nath ME, Robinson TM, Tobon H, Chough DM, Sumkin JH (1995) Automated large-core needle biopsy of surgically removed breast lesions: comparison of samples obtained with 14-, 16-, and 18-gauge needles. Radiology 197(3):739–742
Koscick RL, Petersilge CA, Makley JT, Abdul-Karim FW (1998) CT-guided fine needle aspiration and needle core biopsy of skeletal lesions. Complementary diagnostic techniques. Acta Cytol 42(3):697–702
Yang YJ, Damron TA (2004) Comparison of needle core biopsy and fine-needle aspiration for diagnostic accuracy in musculoskeletal lesions. Arch Pathol Lab Med 128(7):759–764
Jacobson BC, Dubinchik IV, Swan N (2006) A method of assessing the adequacy of trucut biopsy specimens obtained with a 19-gauge trucut core biopsy needle. Acta Cytol 50(2):141–146
Ansarin M, De Fiori E, Preda L, Maffini F, Bruschini R, Calabrese L et al (2007) Ultrasound-guided transcutaneous Tru-Cut biopsy to diagnose laryngopharyngeal masses: a pilot study. Cancer 109(11):2258–2272
Bdour M, Hourani S, Mefleh W, Shabatat A, Karadsheh S, Nawaiseh O et al (2008) Comparison between Fine needle aspiration cytology and Tru-cut biopsy in the diagnosis of breast cancer. J Surg Pak (Int) 13(1):19–21
Rathod K, Deshmukh H, Nihal L, Basappa S, Rathi P, Bhatia S (2008) Transjugular liver biopsy using Tru-cut biopsy needle: KEM experience. J Assoc Physicians India 56:425–428
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all co-authors, the corresponding author declares that they have no conflict of interest. The copy of the signed form is attached separately.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Institutional Review Board of Bapuji Dental College and Hospital, Davangere, Karnataka and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments. Ethical Approval Letter by the Institutional Review Board is attached separately.
Informed Consent
Written consent is obtained from all patients involved in this study after explaining surgical procedures and its complications in detail. Except for age and sex which are necessary for this study, no other personal information of the patients was revealed in the script. Example of informed consent which is involved in this study is attached separately.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kansagara, P.R., Shrinivas, Kumar, H.R.S. et al. Comparison of Tru-Cut Biopsy and Incisional Biopsy in Achieving Prompt Diagnosis of Maxillofacial Pathology. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 20, 479–485 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-021-01557-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-021-01557-6