Abstract
Purpose
Glycoprotein is an important constituent of saliva, and the observed increase in salivary glycoproteins such as sialic acid in oral potentially malignant disorder (OPMDs) and OSCC has stimulated the interest of researchers to explore it as a possible biomarker.
Methods
The study used 60 subjects, who were divided into three groups: Group I—20 subjects who were clinically and histopathologically diagnosed with OSCC; Group II—20 subjects who were clinically and histopathologically diagnosed with OPMDs; and Group III—20 healthy subjects with good oral hygiene and with no systemic disorders detected. Two millilitres of unstimulated salivary samples was collected in a pre-sterilized container to analyse total salivary sialic acid (TSA) levels using a sialic acid kit and UV spectrophotometer.
Results
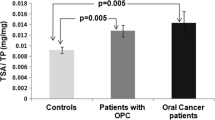
The TSA levels in OSCC (545.45 ± 100.04) were much higher when compared to the level in OPMDs (169.80 ± 66.43) and in healthy subjects (25.45 ± 16.07). Statically significant correlation was observed between different grades of OSCC. Moreover, sialic acid showed 100% sensitivity and specificity between all the three groups. Statistical analysis was done with Kruskal–Wallis, followed by Mann–Whitney post hoc test at P < 0.05. The results suggested the utility of sialic acid as an efficient biomarker.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jacob TV, Ramesh M, Murali S, Ramesh K, Sanjay PR, Abraham P (2016) A non-invasive study to estimate and compare salivary sialic acid level as tumor marker in patients with precancer and oral cancer. J Cancer Res Ther 12:634–639
Rajpura KB, Patel PS, Chawda JG, Shah RM (2005) Clinical significance of total and lipid bound sialic acid levels in oral pre-cancerous conditions and oral cancer. J Oral Pathol Med 34:263–267
Sanjay PR, Hallikeri K, Shivashankara AR (2008) Evaluation of salivary sialic acid, total protein and total sugar in oral cancer: a preliminary report. Indian J Dent Res 19:288–291
Chan DW, Schwartz MK (2002) Tumor markers. In: Diamandis EP, Fritsche HA, Lilja H, Chan DW, Schwartz MK (eds) Physiology, pathobiology, technology, and clinical applications. Tumor markers: introduction and general principles. AACC Press, Washington, pp 9–17
Segal A, Wong DT (2008) Salivary diagnostics: enhancing disease detection and making medicine better. Eur J Dent Educ 12:22–29
Cohen RE, Levine MJ (2000) Salivary glycoproteins. In: Tenovuo JO (ed) Human saliva: clinical, chemical and microbiology, vol 1. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 101–130
Shah MH, Telang SD, Shah PM, Patel PS (2008) Tissue and serum alpha 2-3- and alpha 2-6-linkage specific sialylation changes in oral carcinogenesis. Glycoconj J 25:279–290
Shah MH, Telang SD, Raval GN, Shah PM, Patel PS (2008) Serum fucosylation changes in oral cancer and oral precancerous conditions: alpha-l-fucosidase as a marker. Cancer 113:336–346
Chaudhary V, Pradeep GL, Prakash N, Mahajan AM (2016) Estimation of salivary sialic acid in oral premalignancy and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Contemp Clin Dent 7:451–456
Achalli S, Madi M, Babu SG, Shetty SR, Kumari S, Bhat S (2017) Sialic acid as a biomarker of oral potentially malignant disorders and oral cancer. Indian J Dent Res 28:395–399
Malati T (2007) Tumour markers: an overview. Indian J Clin Biochem 22:17–31
Mayerhofer TG, Popp J (2018) Beer’s law—why absorbance depends (almost) linearly on concentration. ChemPhysChem. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.201801073
Baxi BR, Patel PS, Adhvaryu SG, Dayal PK (1991) Usefulness of serum glycoconjugates in precancerous and cancerous diseases of the oral cavity. Cancer 67:135–140
Farhad ML, Honarmand M, Nakhaee A, Mollashahi G (2016) Salivary sialic acid levels in smokeless tobacco users. Int J High Risk Behav Addict. https://doi.org/10.5812/ijhrba.27969
Kurtul N, Gökpınar E (2012) Salivary lipid peroxidation and total sialic acid levels in smokers and smokeless tobacco users as Maraş powder. Mediat Inflamm. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/619293
Rathod SR, Khan F, Kolte AP, Gupta M (2014) Estimation of salivary and serum total sialic acid levels in periodontal health and disease. J Clin Diagn Res. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2014/9615.4800
Acknowledgements
All the authors have viewed and agreed to the submission.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Ethical clearance was obtained from the Institutional Ethical Committee on 14 November 2018 with Ref No: 240/2018-19.
Informed Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from each of the patients.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daniel, D., Jose, J. & Harish Kumar, A. Is Salivary Sialic Acid a Reliable Biomarker in the Detection of Oral Potentially Malignant Disorder and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 20, 83–89 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-019-01309-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-019-01309-7