Abstract
Introduction
Microvascular free flaps (MVFF) are the current standard of care for reconstruction of oral ablative defects; however, pedicled myocutaneous flaps (PMCF) are still used widely in India. The rationale behind the preference for selecting PMCF in the present era is not well understood. The associated complications and swallowing outcomes are variable.
Methods
We retrospectively analysed the records of patients who underwent reconstructive surgery for oral cancer ablative defects over a 3-year period.
Results
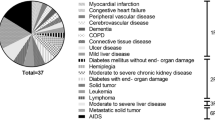
Ninety-seven pedicled myocutaneous flaps [89 pectoralis major myocutaneous (PMMC) flaps, eight lower trapezius island myocutaneous (TMC) flaps] and 113 MVFFs were performed. The reasons for selecting PMCF were financial constraints 38.7%, MVFF salvage 22.5%, medically compromised 10.7%, vessel-depleted neck 6.4%, old age with PS2 + 5.3%, early recurrence 5.3%, borderline resectable 4.3%, palliative resection 2.1%. Overall complication rate was 20.4%. Of patients, 50.7% and 34.7% were on regular and semisolid diet, respectively; 66.6% had acceptable swallowing-related social well-being.
Conclusion
PMCFs have an important role in developing countries with patients having financial constraints. The other potential reasons driven by patient factors were discussed. The swallowing outcomes are good, with majority of the people having socially acceptable swallowing function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ariyan S (1979) The pectoralis major myocutaneous flap. A versatile flap for reconstruction in the head and neck. Plast Reconstr Surg 63:73–81
Urken ML, Naidu RK, Lawson WBH (1991) The lower trapezius island musculocutaneous flap revisited. Report of 45 cases and a unifying concept of the vascular supply. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 117:502–511
Gabrysz-Forget F, Tabet P, Rahal A, Bissada E, Christopoulos AAT (2019) Free versus pedicled flaps for reconstruction of head and neck cancer defects: a systematic review. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 48:13
Schneider DS, Wu VWM (2012) Indications for pedicled pectoralis major flap in a free tissue transfer practice. Head Neck 34:1106–1110
Liu M, Liu W, Yang X, Guo HPH (2017) Pectoralis major myocutaneous flap for head and neck defects in the era of free flaps: harvesting technique and indications. Sci Rep 7:46256
Kekatpure VD, Trivedi NP, Manjula BV, Mathan Mohan A, Shetkar GKM (2012) Pectoralis major flap for head and neck reconstruction in era of free flaps. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 41:453–457
Mukesh, Gupta M, Singh S (2018) Sources of finance for hospitalized treatment in India: evidence for policy. Indian J Public Health 62:308–310
Kastor AMS (2018) Disease-specific out-of-pocket and catastrophic health expenditure on hospitalization in India: do Indian households face distress health financing? PLoS ONE 13:e0196106
Smeele LE, Goldstein D, Tsai V, Gullane PJ, Neligan P, Brown DHIJ (2006) Morbidity and cost differences between free flap reconstruction and pedicled flap reconstruction in oral and oropharyngeal cancer: matched control study. J Otolaryngol 35:102–107
Gao LL, Basta M, Kanchwala SK, Serletti JM, Low DWWL (2017) Cost-effectiveness of microsurgical reconstruction for head and neck defects after oncologic resection. Head Neck 39:541–547
Deganello A, Gitti G, Parrinello G, Muratori E, Larotonda GGO (2013) Cost analysis in oral cavity and oropharyngeal reconstructions with microvascular and pedicled flaps. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 33:380–387
Wei FC, Demirkan F, Chen HC, Chuang DC, Chen SH, Lin CH, Cheng SL, Cheng MHLY (2001) The outcome of failed free flaps in head and neck and extremity reconstruction: what is next in the reconstructive ladder? Plast Reconstr Surg 108:1154–1160
Schusterman MA, Miller MJ, Reece GP, Kroll SS, Marchi MGH (1994) A single center’s experience with 308 free flaps for repair of head and neck cancer defects. Plast Reconstr Surg 93:472–478
Jacobson AS, Eloy JA, Park E, Roman BGE (2008) Vessel-depleted neck: techniques for achieving microvascular reconstruction. Head Neck 30:201–207
Mahieu R, Colletti G, Bonomo P, Parrinello G, Iavarone A, Dolivet G, DA Livi L (2016) Head and neck reconstruction with pedicled flaps in the free flap era. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 36:459–468
Macnamara M, Pope S, Sadler A, Grant HBM (1994) Microvascular free flaps in head and neck surgery. J Laryngol Otol 108:962–968
Moran SL, Salgado CJSJ (2004) Free tissue transfer in patients with renal disease. Plast Reconstr Surg 113:2006–2011
Kuo YR, Jeng SF, Lin KM, Hou SJ, Su CY, Chien CY, Hsueh KLHE (2008) Microsurgical tissue transfers for head and neck reconstruction in patients with alcohol-induced mental disorder. Ann Surg Oncol 15:371–377
Lee AB, Dupin CL, Colen L, Jones NF, May JWCE (2008) Microvascular free tissue transfer in organ transplantation patients: is it safe? Plast Reconstr Surg 121:1986–1992
Chen HC, Demirkan F, Wei FC, Cheng SL, Cheng MHCI (1999) Free fibula osteoseptocutaneous-pedicled pectoralis major myocutaneous flap combination in reconstruction of extensive composite mandibular defects. Plast Reconstr Surg 103:839–845
Balasubramanian D, Thankappan K, Kuriakose MA, Duraisamy S, Sharan R, Mathew J, Sharma MIS (2012) Reconstructive indications of simultaneous double free flaps in the head and neck: a case series and literature review. Microsurgery 32:423–430
Kernohan MD, Clark JR, Gao K, Ebrahimi AMC (2010) Predicting the prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma after first recurrence. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 136:1235–1239
Tam S, Araslanova R, Low TH, Warner A, Yoo J, Fung K, MacNeil SD, Palma DANA (2017) Estimating survival after salvage surgery for recurrent oral cavity cancer. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 143:685–690
Miglani A, Patel VM, Stern CS, Weichman KE, Haigentz M Jr, Ow TJGE (2016) Palliative reconstruction for the management of incurable head and neck cancer. J Reconstr Microsurg 32:226–232
Teo KG, Rozen WMAR (2013) The pectoralis major myocutaneous flap. J Reconstr Microsurg 29:449–456
Pinto FR, Malena CR, Vanni CM, Capelli Fde A, Matos LLKJ (2010) Pectoralis major myocutaneous flaps for head and neck reconstruction: factors influencing occurrences of complications and the final outcome. Sao Paulo Med J 128:336–341
Su WF, Hsia YJ, Chang YC, Chen SGSH (2003) Functional comparison after reconstruction with a radial forearm free flap or a pectoralis major flap for cancer of the tongue. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 128:412–418
Farri A, Accornero ABC (2007) Social importance of dysphagia: its impact on diagnosis and therapy. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 27:83–86
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We have no conflicts of interest.
Ethics Statement/Confirmation of Patients’ Permission
As the study was retrospective, we neither required ethics approval nor patients’ permission.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lakshminarayana, G., Venkitachalam, S. & Mani, C.S. Choice of Regional Flaps for Oral Cancer Defects: Relevance in Current Era. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 20, 246–251 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-019-01305-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-019-01305-x