Abstract
Introduction
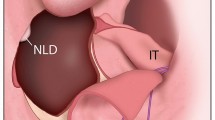
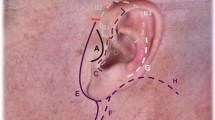
A generous exposure of the midface region is essential for a comprehensive and thorough execution of midface surgical procedures, especially bilateral procedures. Traditional approaches to the midface the midface like the lateral rhinotomy and Weber–Fergusson/Dieffenbach incision with their modifications leave a visible scar, and they are limited in their unilateral exposure. The midface degloving approach with its exclusive intranasal and intraoral incisions leaves no external scars and lends excellent bilateral exposure of the maxilla, zygoma, paranasal areas and infraorbital margins from one side to the other. The midface degloving approach is mainly used to expose pathologies of the maxilla, nasal cavities, paranasal sinuses, nasopharynx, and the central compartment of the anterior and middle cranial base. This approach can also be used to treat midface trauma and perform high-level osteotomies.
Materials and Methods
We describe the midface degloving procedure for nine cases operated in the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery over a period of 7 years (2012–2018): seven maxillary tumors and two maxillary cysts.
Results
We obtained excellent exposure for all the cases using this approach. Complications included mild distortion of the lower lateral nasal cartilages and oro-nasal communication.
Conclusion
The midface degloving approach lends excellent surgical access to the midfacial skeleton including the maxilla, the paranasal areas, the maxillary sinus, the zygoma, and infraorbital rims. The advantages of this approach besides its generous exposure, is the excellent cosmesis it provides leaving no external scars.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Har-El G (1999) Medial Maxillectomy via midfacial degloving approach. Oper Tech Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 10(2):82–86
Baumann A, Ewers R (2001) Midfacial degloving: an alternative approach for traumatic corrections in the midface. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 30(4):272–277
Parameswaran A, Jayakumar NK, Ramanathan M et al (2017) Mid-face degloving: an alternate approach to extended osteotomies of the midface. J Craniofac Surg 28(1):245–247
Jaber JJ, Ruggiero F, Zender CA (2010) Facial degloving approach to the midface. Oper Tech in Otolaryngol 21(3):171–174
Price JC, Holliday MJ, Johns ME et al (1988) The versatile midface degloving approach. Larynoscope 98(3):291–295
Casson PR, Bonnano PC, Converse JM (1974) The midface degloving procedure. Plast Reconstr Surg 53(1):102–103
Kitagawa Y, Baur D, King S, Helman JI (2003) The role of midfacial degloving approach for maxillary cysts and tumors. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61(12):1418–1422
Maniglia AJ (1986) Indications and techniques of midfacial degloving: a 15-year experience. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 112(7):750–752
Maniglia AJ, Phillips DA (1995) Midfacial degloving for the management of nasal, sinus, and skull-base neoplasms. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 28(6):1127–1143
Howard DJ, Lund VJ (1992) The midfacial degloving approach to sinonasal disease. J Laryngol Otol 106(12):1059–1062
Howard DJ, Lund VJ (1999) The role of midfacial degloving in modern rhinological practice. J Laryngol Otol 113(10):885–887
Browne JD (2001) The midfacial degloving procedure for nasal, sinus, and nasopharyngeal tumors. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 34(6):1095–1104
Helman JI (1997) Maxillectomy. Atlas Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 5(2):75–89
Adelstein DJ, Kalish LA, Adams GL et al (1993) An eastern cooperative oncology group pilot study: concurrent radiation therapy and chemotherapy for locally unresectable squamous cell head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol 11(11):2136–2142
Dragovic J, Doyle TJ, Tilchen EJ et al (1995) Accelerated fractionation radiotherapy and concomitant chemotherapy in patients with stage IV inoperable head and neck cancer. Cancer 76(9):1655–1661
Benasso M, Corvo R, Numico G et al (1995) Concomitant administration of two standard regimens of chemotherapy and radiotherapy in advanced squamous carcinoma of the head and neck: a feasibility study. Anticancer Res 15(6B):2651–2654
Kitagawa Y, Sadato N, Azuma H et al (1999) FDG PET to evaluate combined intra-arterial chemotherapy and radiotherapy for head and neck neoplasms. J Nucl Med 40(7):1132–1137
Kyoshima K, Matsuo K, Kushima H et al (2002) Degloving transfacial approach with Le Fort I and nasomaxillary osteotomies: alternative transfacial approach. Neurosurgery 50(4):813–820
Krause GE, Jafek BW (1999) A modification of the midface degloving technique. Laryngoscope 109(11):1781–1784
Yang SJ, Choi JW, Chung YS et al (2012) Midfacial degloving approach for resectioning and reconstruction of extensive maxillary fibrous dysplasia. J Craniofac Surg 23(6):1658–1661
Acknowledgements
Line diagrams: courtesy of Dr Vidya Devi, MDS (OMFS). E-mail: vidya.devi.vuyyuru@gmail.com.
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from the individual participant included in the study. Additional informed consent was obtained from the individual participant for whom identifying information is included in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zachariah, T., Neelakandan, R.S. Utility of the Midface Degloving Approach for Extended Exposure in Maxillary Pathologies. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 19, 217–224 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-019-01287-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-019-01287-w