Abstract
Objectives
Comparison of the mechanical stability of 2.0 plates made of commercially pure titanium (cpTi) and a titanium–molybdenum (Ti–15Mo) alloy and two methods of internal fixation employed mandibular angle fractures, using 3D finite element analysis.
Materials and Methods
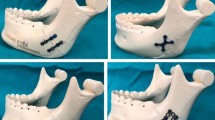
Four groups were evaluated. For the cpTi: group Eng 1P, one 4-hole plate and 4 screws 6 mm long, in the tension zone of the mandible; group Eng 2P, two 4-hole plates, one in the tension zone of the mandible and the other in the compression zone, both were fixed with 8 screws 6 mm long. The same groups were created for the Ti–15Mo alloy. A 100 N compressive load was applied to the occlusal surface of the mandibular first molar on the plated side.
Results
When considering the von Mises equivalent stress (σvM) values for the comparison between both groups with one plate, a decrease of 10.5% in the plate and a decrease of 29.0% in the screws for the Ti–15Mo group was observed. Comparing the same groups with two plates, a decrease of 28.5% in the screws was shown for the Ti–15Mo alloy group. No significant differences were observed when considering maximum and minimum principal stresses (σmax, σmin), and maximum principal strain (εmax) to the mandibular bone. The Ti–15Mo alloy plates substantially decreased the stress concentration in the screws for both internal fixation techniques and in the plate for the Ti–15Mo 1 plate group.
Conclusion
From a clinical standpoint, the use of Ti–Mo alloy with reduced stiffness will decrease the stress shielding between the hardware and bone, influencing the outcome of the treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chrcanovic BR (2013) Fixation of mandibular angle fractures: in vitro biomechanical assessments and computer-based studies. Oral Maxillofac Surg 17:251–268
Al-Moraissi EA, Ellis E 3rd (2014) What method for management of unilateral mandibular angle fractures has the lowest rate of postoperative complications? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 72:2197–2211
Zhan S, Jiang Y, Cheng Z, Ye J (2014) A meta-analysis comparing the 2.0-mm locking plate system with the 2.0-mm nonlocking plate system in treatment of mandible fractures. J Craniofac Surg 25:2094–2097
Kanubaddy SR, Devireddy SK, Rayadurgam KK, Gali R, Dasari MR, Pampana S (2016) Management of mandibular angle fractures: single stainless steel linear miniplate versus rectangular grid plate-a prospective randomised study. J Maxillofac Oral Surg 15:535–541
Lovald ST, Wagner JD, Baack B (2009) Biomechanical optimization of bone plates used in rigid fixation of mandibular fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:973–985
Kharazia AZ, Fathia MH, Bahmany F (2010) Design of a textile composite bone plate using 3D-finite element method. Mater Des 31:1468–1474
Niinomi M, Nakai M (2011) Titanium-based biomaterials for preventing stress shielding between implant devices and bone. Int J Biomater 2011:10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/836587
Jackson MJ, Ahmed W (2007) Titanium and titanium alloy applications in medicine. In: Mark JJ, Waqar A (eds) Surface engineered surgical tools and medical devices. Springer, Boston, pp 533–576
Kumar S, Narayanan TS (2008) Corrosion behaviour of Ti–15Mo alloy for dental implant applications. J Dent 36:500–507
Niinomi M (2008) Mechanical biocompatibilities of titanium alloys for biomedical applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 1:30–42
Oliveira NTC, Aleixo G, Caram R, Guastaldi AC (2007) Development of Ti–Mo alloys for biomedical applications: microstructure and electrochemical characterization. Mater Sci Eng, A 452–3:727–731
Oliveira NTC, Guastaldi AC (2008) Electrochemical behavior of Ti–Mo alloys applied as biomaterial. Corros Sci 50:938–945
Oliveira NTC, Guastaldi AC (2009) Electrochemical stability and corrosion resistance of Ti–Mo alloys for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater 5:399–405
Sumitomo N, Noritake K, Hattori T, Morikawa K, Niwa S, Sato K, Niinomi M (2008) Experiment study on fracture fixation with low rigidity titanium alloy: plate fixation of tibia fracture model in rabbit. J Mater Sci Mater Med 19:1581–1586
Lovald ST, Khraishi T, Wagner J, Baack B, Kelly J, Wood J (2006) Comparison of plate-screw systems used in mandibular fracture reduction: finite element analysis. J Biomech Eng 128:654–662
Wang H, Ji B, Jiang W, Liu L, Zhang P, Tang W, Tian W, Fan Y (2010) Three-dimensional finite element analysis of mechanical stress in symphyseal fractured human mandible reduced with miniplates during mastication. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:1585–1592
Huempfner-Hierl H, Schaller A, Hemprich A, Hierl T (2014) Biomechanical investigation of naso-orbitoethmoid trauma by finite element analysis. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 52:850–853
Darwich MA, Albogha MH, Abdelmajeed A, Darwich K (2016) Assessment of the biomechanical performance of 5 plating techniques in fixation of mandibular subcondylar fracture using finite element analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 74(794):e1–e8
Kharmanda G, Kharma MY (2017) Evaluating the effect of minimizing screws on stabilization of symphysis mandibular fracture by 3D finite element analysis. J Maxillofac Oral Surg 16:205–211
Wang R, Liu Y, Wang JH, Baur DA (2017) Effect of interfragmentary gap on the mechanical behavior of mandibular angle fracture with three fixation designs: a finite element analysis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 70:360–369
Yamaguchi S, Anchieta RB, Guastaldi FPS, Tovar N, Tawara D, Imazato S, Coelho PG (2017) In silico analysis of the biomechanical stability of commercially pure Ti and Ti–15Mo plates for the treatment of mandibular angle fracture. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 75:1004.e1–1004.e9
Bregagnolo LA, Bertelli PF, Ribeiro MC, Sverzut CE, Trivellato AE (2011) Evaluation of in vitro resistance of titanium and resorbable (poly-L-DL-lactic acid) fixation systems on the mandibular angle fracture. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 40:316–321
Almeida EO, Rocha EP, Assunção WG, Júnior AC, Anchieta RB (2011) Cortical bone stress distribution in mandibles with different configurations restored with prefabricated bar-prosthesis protocol: a three-dimensional finite-element analysis. J Prosthodont 20:29–34
Semeghini Guastaldi FP, Hochuli-Vieira E, Guastaldi AC (2014) Biomechanical study in polyurethane mandibles of different metal plates and internal fixation techniques, employed in mandibular angle fractures. J Craniofac Surg 25:2246–2250
Choi AH, Conway RC, Taraschi V, Ben-Nissan B (2015) Biomechanics and functional distortion of the human mandible. J Investig Clin Dent 6:241–251
Gilardino MS, Chen E, Bartlett SP (2009) Choice of internal rigid fixation materials in the treatment of facial fractures. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr 2:49–60
Ellis E 3rd, Esmail N (2009) Malocclusions resulting from loss of fixation after sagittal split ramus osteotomies. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:2528–2533
Geetha M, Singh AK, Asokamani R, Gogia AK (2009) Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—a review. Prog Mater Sci 54:397–425
Oliveira NT, Guastaldi FP, Perrotti V, Hochuli-Vieira E, Guastaldi AC, Piattelli A, Iezzi G (2013) Biomedical Ti–Mo alloys with surface machined and modified by laser beam: biomechanical, histological, and histometric analysis in rabbits. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 15:427–437
Niinomi M, Nakai M, Hieda J (2012) Development of new metallic alloys for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater 8:3888–3903
Ichim I, Swain M, Kieser JA (2006) Mandibular biomechanics and development of the human chin. J Dent Res 85:638–642
Sato FRL, Asprino L, Noritomi PY, Silva JVL, Moraes M (2012) Comparison of five different fixation techniques of sagittal split ramus osteotomy using three-dimensional finite elements analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 41:934–941
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Engimplan® (Rio Claro, SP, Brazil) for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guastaldi, F.P.S., Martini, A.P., Rocha, E.P. et al. Ti–15Mo Alloy Decreases the Stress Concentration in Mandibular Angle Fracture Internal Fixation Hardware. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 19, 314–320 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-019-01251-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-019-01251-8