Abstract
Aim
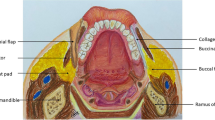
Aim of this study was to evaluate the split skin graft held in place with a polyethylene stent for the treatment of oral submucous fibrosis.
Methods
Fifteen prospective patients diagnosed clinically with oral submucous fibrosis, from June 2011 to 12 December 2012, were recruited for this study. All patients were treated surgically using the same surgical technique of fibrotomy followed by split skin graft along with a polyethylene stent. Preoperative and postoperative mouth opening measurements at 1 week and after a minimum of 6 months were evaluated by measuring the inter incisal distance.
Results
Mean follow up was 9.8 months with a minimum of 6 months. Mean preoperative mouth opening was 12.9 mm (6–20 mm). Intraoperatively mean mouth opening was 37.9 mm (36–41 mm). After 1 week mean mouth opening was 35.8 mm (31–40 mm). At 6 months follow up, mean mouth opening was 33 mm (20–40 mm).
Conclusion
Fibrotomy followed by split skin graft along with a polyethylene sheet stent and sufficient postoperative physiotherapy is a simple, cost effective and viable treatment modality for oral submucous fibrosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pindborg JJ, Sirsat SM (1966) Oral submucous fibrosis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 22:764–779
Pindborg JJ (1989) Oral submucous fibrosis: a review. Ann Acad Med Singapore 18:603–607
Sinor PN, Gupta PC, Murti PR et al (1990) A case control study of oral sub-mucous fibrosis with special reference to the etiologic role of areca nut. J Oral Pathol Med 19:94–98
Tilakaratne WM, Klinikowski MF, Saku T, Peters TJ, Warnakulasuriya S (2006) Oral submucous fibrosis: review on aetiology and pathogenesis. Oral Oncol 42:561–568
Rajalalitha P, Vali S (2005) Molecular pathogenesis of oral submucous fibrosis—a collagen metabolic disorder. J Oral Pathol Med 34:321–328
Freihofer HPM (1991) Restricted opening of the mouth with an extra-articular cause in children. J Carniomaxillofac Surg 19:289–298
Rajendran R (2003) Oral submucous fibrosis. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 7:1–4
Utsunomiya H, Tilakaratne WM, Oshiro K et al (2005) Extracellular matrix remodeling in oral submucous fibrosis: its stage-specific modes revealed by immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization. J Oral Pathol Med 34:498–507
Lai DR, Chen HR, Lin LM, Huang YL, Tsai CC (1995) Clinical evaluation of different treatment methods for oral submucous fibrosis. A 10-year experience with 150 cases. J Oral Pathol Med 24:402–406
Kerr AR, Warnakulasuriya S, Mighell AJ et al (2011) A systematic review of medical interventions for oral submucous fibrosis and future research opportunities. Oral Dis 17(Suppl. 1):42–57
Yen DJC (1982) Surgical treatment of submucous fibrosis. Oral Surg 54:269–271
Yeh CJ (1996) Application of the buccal fat pad to the surgical treatment of oral submucous fibrosis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 25:130–133
Bande CR, Datarkar A, Khare N (2013) Extended nasolabial flap compared with the platysma myocutaneous muscle flap for reconstruction of intraoral defects after release of oral submucous fibrosis: a comparative study. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 51:37–40
Khanna JN, Andrade NN (1995) Oral submucous fibrosis: a new concept in surgical management. Report of 100 cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 16:609–614
Huang IY, Wu CF, Shen YS et al (2008) Importance of patient’s cooperation in surgical treatment for oral submucous fibrosis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 66:699–703
Tideman H, Bosanquet A, Scott J (1986) Use of the buccal fat pad as pedicled graft. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 44:435–440
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soh, C.L., Muthusekhar, M.R. Treatment of Oral Submucous Fibrosis Using Split Skin Graft and a Polyethylene Stent: A Prospective Study. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 14, 370–373 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-014-0661-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-014-0661-5