Abstract
Aim
To compare the displacement gap of mandible fracture segments treated with different designs of mini-plates under various loading conditions.
Materials and Methods
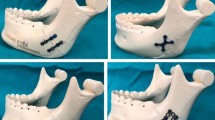
Fracture in the body of mandible was bridged with 15 different designs and configuration of titanium mini-plates. Bite forces were applied at 3 locations, ipsilateral fractured side, contra lateral side and incisor site. 3D finite element methods (FEM) model of mandible was generated using 10 nodal tetrahedral elements. A commercial FE solver was used to solve bone inter fragmentary displacement during loading.
Results
Superior position of mini-plates produced better stability than inferior position. Positive bending moments can be reduced by larger plate in lower border in 2 plate system. Results of X mini-plate are comparable to 2 plate configuration. If length of middle portion of plate increased, stability decreased. Number of screws did not affect fracture stability.
Conclusion
Finite element methods analysis is used to determine the gap between mandible fragments which is otherwise impossible to measure clinically. The results obtained from this study offered us a choice of mini-plate design and configuration for clinical application.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gruss JS, Phillips JH (1989) Complex facial trauma: the evolving role of rigid fixation and immediate bone graft reconstruction. Clin Plast Surg 1989:93
Hobar PC (1992) Methods of rigid fixation. Clin Plast Surg 19:31–39
Cox T, Kohn MW, Impelluso T (2003) Computerized analysis of Resorbable Polymer plates and screws for the rigid fixation of mandibular angle fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61:481–487
Korkmaz HH (2007) Evaluation of different mini-plates in fixation of fractured human mandible with the finite element method. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 103:1–13
Hart RT, Hennebel VV, Thongpreda N, Buskirk WCV, Anderson RC (1992) Modelling the biomechanics of the mandible. A three dimensional finite element study. J Biomech 25:261–286
Iseri H, Tekkaya E, Oztan O, Bilgic S (1998) Biomechanical effects of rapid maxillary expansion on the craniofacial skeleton studied by the finite element method. Eur J Orthod 20:347–356
van Eijden TMGJ, Korfage JAM, Brugma P (1997) Architecture of the human jaw: closing and jaw-opening muscles. Anat Rec 248:464–474
Chuong CJ, Borotikar B, Schwartz-Dabney C, Sinn DP (2005) Mechanical characteristics of the mandible after bilateral sagittal split ramus osteotomy: comparing 2 different fixation techniques. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63:68–76
Meijer HJA, Starmans FJM, Bosman F, Sten WHA (1993) A comparison of three finite element models of an edentulous mandible provided with implants. J Oral Rehab 20:147–157
Simsek B, Erkmen E, Yilmaz D, Eser A (2006) Effects of different inter-implant distances on the stress distribution around endosseous implants in posterior mandible: a 3D finite element analysis. Med Eng Phys 28:199–213
Cox Tyler, Kohn MW, Impelluso T (2003) Computerized analysis of resorbable polymer plates and screws for the rigid fixation of mandibular angle fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61:481–487
Kroon FH, Mathisson M, Cordey JR et al (1991) The use of mini-plates in mandibular fractures. An invitro study(1991). J Craniomaxillofac Surg 19:199–204
Tams J, Van Loon JP, Rozema FR et al (1996) A three-dimensional study of loads across the fracture for different fracture sites of the mandible. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 34:400–404
Tams J, van Loon J-P, Otten E et al (1997) A three-dimensional study of bending and torsion moments for different fracture sites of the mandible: an in vitro study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 26:383
Tate G, Ellis E III, Throckmorton GS (1994) Bite forces in patients treated for mandibular angle fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 52:734–736
ANSYS—Engineering Analysis System (1989) Theoretical manual-theory reference. Swanson Analysis Systems, Canonsburg
Dichard A, Klotch DW (1994) Testing biomechanical strength of repairs for the mandibular angle fracture. Laryngoscope 104:201–208
Champy M, Lodde JP, Jaegar JM, Wilk A, Jerber JC (1976) Mandibular osteosynthesis according to the Michelet Technique. I. Biomechanical basis. II. Presentation of new material. Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac 1976:569–582
Champy M, Lodde JP (1976) Mandibular synthesis. Placement of the synthesis as a function of mandibular stress. Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac 77:971–976
Michelet FX, Deymes J, Dessus B (1973) Osteosynthesis with miniaturised screwed plates in maxillofacial surgery. J Maxillofac Surg 1:79–84
Iizuka T, Lindqvist C, Hallikainen D, Paukku P (1991) Infection after rigid internal fixation of mandibular fractures: a clinical and radiologic study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 49:585–593
Alpert B, Gutwald R, Schmelzeisen R (2003) New innovations in craniomaxillofacial fixation: the 2.0 locks system. Keio J Med 52:120–127
Gutwald R, Alpert B, Schmelzeisen R (2003) Principle and stability of locking plates. Keio J Med 52:21–24
Champy M, Pape HD, Gerlach KL (1986) Lodde JR Mandibular fractures. In: Kroger E, Schilli W, Worthington P (eds) Oral and Maxillofacial Traumatology, vol 2. Quintessence, Chicago
Schili W, Luhr HG (1982) Rigid internal fixation by means of compression plates. In: Kroger E, Schilli W (eds) Oral and maxillofacial traumatology. Quintessence, Chicago, pp 308–370
Tams J, Van Loon JP, Otten B, Bos RM (2001) A computer study of biodegradable plates for internal fixation of mandibular angle fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2001:404–407
Perren SM (1979) Physical and biological aspects of fracture healing with special reference to internal fixation. Clin Orthop 1979:175–196
Harada K, Watanabe M, Ohkura K, Enomoto S (2000) Measure of bite force and occlusal contact area before and after bilateral sagittal split rams osteotomy of the mandible using a new pressure-sensitive device. A preliminary report. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 58:370–373
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joshi, U., Kurakar, M. Comparison of Stability of Fracture Segments in Mandible Fracture Treated with Different Designs of Mini-Plates Using FEM Analysis. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 13, 310–319 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-013-0510-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-013-0510-y