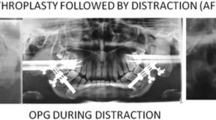
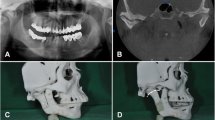
Abstract
Patient with TMJ ankylosis are affected with mandibular hypoplasia which in turn causes functional and esthetic problems. Restoration of normal function and esthetics is the prime goal in treatment of such patients with distraction becoming an important treatment option. The present study also was conducted on patients with mandibular hypoplasia secondarily to TMJ ankylosis treated with distraction. Since function and esthetics improvement was the prime aim behind the treatment with distraction, evaluation of functional and esthetics outcome becomes an important aspect. Thus the study was indigenously designed and aimed at qualitative evaluation of the functional and esthetic outcome after correction of mandibular hypoplasia secondary to temporomandibular ankylosis with Distraction osteogenesis. Patients treated with distraction were evaluated on the basis of parameters for function and esthetics. Parameters for function were occlusion, airway, mouth opening and chewing-biting perception of patient pre and post distraction. Parameters for esthetics used were patient and panel perception. All parameters for function and occlusion improved with distraction in all the patients except one in whom occlusion and chewing- biting pattern worsened. It is concluded that distraction is a good option for improving patients functional and esthetic outcome in cases of mandibular hypoplasia secondary to temporomandibular ankylosis as the results achieved are stable with negligible chances of relapse.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behcet E, Rezzan T, Belgin G (2006) A clinical study on ankylosis of the temporo-mandibular joint. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 34:100–106
Rajkumar GC, Manjunath, Shashikala R, Veerendra KD (2011) Distraction osteogenesis in the management of temporomandibular joint ankylosis. Int J Clin Dent Sci 2:22–26
McCarthy JG, Schrieber J, Karp N (1992) Lengthening of the human mandible by gradual distraction. Plast Reconstr Surg 89:1–9
Menon S et al (2005) Distraction osteogenesis in management of mandibular deformities. MJAFI 61:345–347
Gonzalez M, Egbert M, Guerrero CA, Van Sickels JE (2008) Vertical and horizontal mandibular lengthening of the ramus and body. Atlas Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 16:215–236
Gavrill A, Ilizarov AM (1989) Part-1 the tension-stress effect on the genesis and growth of tissues. Clin Relat Res 238:249–281
Van Strigen PJ et al (2003) Complications in bilateral mandibular distraction osteogenesis using internal devices. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 96:392–397
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, G.M., Gupta, P., Sharma, A. et al. Evaluation of Functional and Esthetic Outcome After Correction of Mandibular Hypoplasia Secondary to Temporomandibular Ankylosis Treated by Distraction Osteogenesis. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 13, 152–158 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-013-0480-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-013-0480-0