Abstract
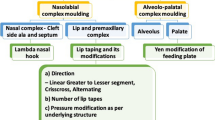
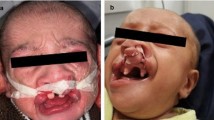
Presurgical orthopedics in one or the other form has been an important part of the multidisciplinary approach towards the better cleft care. Presurgical nasoalveolar molding (PNAM) was described as a modified approach to the conventional form of orthopedics. PNAM not only reduces the severity of the alveolar defect before surgery, it also reduces the nasal deformity bringing it near to the normal. Nonsurgical nasal correction forms an important adjunct to the primary nasal repair at the time of primary lip repair. However, acceptance of nasoalveolar molding in Indian set-up has not been wide spread due to various reasons such as lack of the resources and inability of the parents to comply with the frequent adjustment schedule. At the Nitte Meenakshi Institute of Craniofacial surgery at the Nitte University, Mangalore, authors have developed a modification of the PNAM appliance previously described in the literature. The key modification is done at the time of fabrication of the occlusal prosthesis. This modification has made the overall procedure simpler and at the same time helped to reduce the recall visits by half of the originally required. This article describes the fabrication procedure of the modified nasal alveolar molding appliance and the modified treatment protocol in a stepwise manner.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Converse JM, Hogan VM, Borton FE (1977) Secondary deformities of cleft lip, cleft lip and nose, and cleft palate. In: Converse JM (ed) Reconstructive Plastic Surgery, vol 4, 2nd edn. Saunders, Philadelphia
Bennum RD, Perandones C, Sepliarsky VA, Chantiri SN, Aguirre MI, Dogliotti PL (1999) Nonsurgical correction of nasal deformity in unilateral complete cleft lip: a six-year follow-up. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:616
Levine JP, Bradely JP, Shahinian HK et al (1999) Nasal expansion in the fetal lamb: a first step toward management of cleft nasal deformity in utero. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:607
Matsuo K, Hirose T, Tonomo T (1984) Nonsurgical correction of congenital auricular deformities in the early neonates: a preliminary report. Plast Reconstr Surg 73:38–50
Matsuo K, Hirose T, Otagiri T, Norose N (1989) Repair of cleft lip with nonsurgical correction of nasal deformity in the early neonatal period. Plast Reconstr Surg 83:25
Matsuo K, Hirose T (1991) Preoperative non-surgical over-correction of cleft lip nasal deformity. Br J Plast Surg 44:5
Grayson BH, Santiago PE, Brecht LL, Cutting CB (1999) Presurgical nasoalveolar molding in infants with cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 36:486
Hotz M (1969) Pre- and Early postoperative growth-guidance in cleft lip and palate cases by maxillary orthopedics (an alternative procedure to primary bone grafting). Cleft Palate J 6:368–372
Liou EJ, Subramanian M, Chen PK (2004) Huang CS: The progressive changes of nasal symmetry and growth after nasoalveolar molding: a three-year follow-up study. Plast Reconstr Surg 114:858–864
Prahl C, Kuijpers-Jagatman AM, van’t Hof MA, Prahl-Andersen B (2001) A randomized prospective clinical trial into the effect of infant orthopedics on the maxillary arch dimensions in unilateral cleft lip and palate (Dutchcleft). Eur J Oral Sci 109:297–305
Prahl C, Kuijpers-Jagatman AM, van’t Hof MA, Prahl-Andersen B (2003) A randomized prospective clinical trial of the effect of infant orthopedics in unilateral cleft lip and palate: Prevention of collapse of alveolar segments (Dutchcleft). Cleft Palate Craniofac J 40:337–342
Salyer KE (2004) Unilateral cleft lip-nose repair–long-term outcome. Clin Plast Surg 31:191–208
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bajaj, A., Rao, K.S., Sharma, S.M. et al. Modified Presurgical Nasoalveolar Molding in the Infants with Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate: A Stepwise Approach. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 10, 275–280 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-011-0232-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-011-0232-y