Abstract
Background
In Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, the majority of the condylar fractures are treated by closed reduction with generally satisfactory long term results. But in such cases of closed reduction, patient will be uncomfortable owing to long term application of inter maxillary fixation (IMF). Where as, Disadvantages of extra oral open reduction and fixation of condylar fracture includes facial nerve damage, facial scars etc. which are surely eliminated by the intraoral reduction and rigid fixation.
Aims and Objectives
The present study was conducted to determine the efficacy of reduction and fixation of low sub-condylar fractures through intra-oral approach.
Methodology
In this study, ten patients with low sub-condylar fracture, reported to department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. P.M.N.M. Dental College and Hospital Bagalkot were included. These patients were treated by open reduction and internal fixation through intra-oral approach. All the patients were evaluated postoperatively for mouth opening, occlusion and mandibular deviation with regular radiographic examination for 6 weeks.
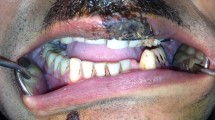
Results
All operated patients followed for 6 weeks, maximum mouth opening was more than 40 mm in seven patients (range from 40 to 50 mm) and less than 40 mm in three patients. Occlusion was satisfactory in all and none of the patients showed deviation of mandible on mouth opening. Statistical analysis showed that postoperative mouth opening was significant (‘t’ value = 7.88, ‘P’ = (0.000) < 0.05) and the test result was significant (S) at 5% level of significance. Statistical analysis of deviation of mouth opening was nonsignificant [‘t’ value = 1.96, ‘P’ value (0.081), 0.05]. For occlusion standard photographs were obtained at sixth week and found minor occlusal corrections in two patients are treated by elastic traction for few days.
Discussion and Conclusion
Open reduction with internal fixation through intraoral approach has proved to be safe for early function and also effective by avoiding the patient discomfort due to long term intermaxillary fixation, psychological effect, facial nerve damage, facial scar and weight loss.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Undt G, Karmer C, Rasse M, Sinko K, Ewers R (1999) Transoral miniplate osteosynthesis of condylar neck fractures. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 88:534–543
Veras RB, Kriwasly MS (2007) Long term outcomes after treatment of condylar fracture by intraoral access: a functional and radiological assessment. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65:1470–1476
Kallela I, Soderholm A-L (1995) Lag-screw osteosynthesis of mandibular condyle fractures: a clinical and radiological study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 53:1397–1404
Schon R, Gutwald R, Schramm A, Gellrich N-C, Schmelzeisen R (2002) Endoscopy assisted open treatment of condylar fractures of mandible: extraoral vs intraoral approach. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 31:237–243
Jeter TS, Van Sickels JE, Nishioka GJ (1988) Intra-oral open reduction with rigid fixation of mandibular subcondylar fractures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 46:1113–1116
Lachner J, Clanton JT, Waite PD (1991) Open reduction internal rigid fixation of subcondylar fractures via an intraoral approach. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 17:257–261
Kitayama S (1989) A new method of intra-oral open reduction using a screw applied through the mandibular crest of condylar fractures. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 17:16–23
Ellis E III, McFadden D, Siomon P, Throckmorton G (2000) Occlusal results after open or closed treatment of fractures of the mandibular condylar process. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 58:260–268
Behbehani F, Al-Aryan H, Al-Attar A, Al-Hamad N (2006) Perceived effectiveness and side effects of intermaxillary fixation for diet control. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 35:618–623
Jensen T, Jensen J et al (2006) Open reduction and rigid internal fixation of mandibular condylar fracture by an intraoral approach: a long-term follow-up study of 15 patients. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 64:1771–1779
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patil, R.S., Gudi, S.S. Management of Subcondylar Fracture through Intraoral Approach with Rigid Internal Fixation. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 10, 209–215 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-011-0209-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-011-0209-x