Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the efficacy of autologous platelet-rich plasma in soft tissue healing & bone regeneration in mandibular third molar extraction socket.
Methods
The study was conducted in 10 patients visiting the outpatient Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, requiring extraction of bilateral mandibular third molars. Following extraction, autologous Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) was placed in one extraction socket, the other socket was studied as the control site with no PRP. The patients were assessed for postoperative pain, soft tissue healing, bone blending and trabecular formation. Radiological assessment of the extraction site was done for a period of 4 months to evaluate the change in bone density.
Results
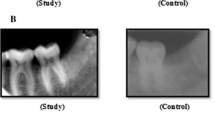
Pain was less in the study site compared to control site, soft tissue healing was better in study site. Evaluation for bone blending and trabecular bone formation started earlier in PRP site compared to control, non PRP site. The evaluation of bone density by radiological assessment showed the grey level values calculated after 4 months at the PRP site were comparatively higher than the average baseline value of bone density at extraction site in control site.
Conclusion
The study showed that autologous PRP is biocompatible and has significantly improved soft tissue healing, bone regeneration and increase in bone density in extraction sockets. However a more elaborate study with a larger number of clinical cases is essential to be more conclusive regarding its efficacy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dugrillon A, Eichler H, Kern S, Kluter H (2002) Autologous concentrated platelet-rich plasma (cPRP) for local application in bone regeneration. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 31(6): 615–619
Landry RG, Turnbull RS, Howley T (1988) Effectiveness of benzydamyne HCl in the treatment of periodontal postsurgical patients. Res Clin Forum 10: 105–118
Masse JF, Landry RG, Rochette C et al. (1993) Effectiveness of soft laser treatment in periodontal surgery. Int Dent J 43(2): 121–127
Choukroun J, Diss A, Simonpieri A et al. (2006) Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second — generation platelet concentrate. Part V: Histologic Evaluations of PRF effects on bone allograft maturation in sinus lift. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 101(3): 299–303
Kim SG, Kim WK, Park JC, Kim HJ (2002) A comparative study of osseointegration of Avana Implants in a Demineralized Freeze-Dried Bone Alone or With Platelet-Rich Plasma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60(9): 1018–1025
How to make autologous platelet gel? Available from URL:http://www.Londonperfusionscience.com/services_platelet_gel_make.html
Landesberg R, Moses M, Karpatkin M (1998) Risk of using Platelet rich plasma gel. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 56(9): 1116–1117
Soffer E, Ouhayoun JP, Anagnostou F (2003) Fibrin sealants and platelet preparations in bone and periodontal healing. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 95(5): 521–528
Tozum TF, Keceli HG, Serper A, Tuncel B (2006) Intentional replantation for a periodontally involved hopeless incisor by using autologous platelet-rich plasma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 101(6): e119–e124
Whitman DH, Berry RL, Green DM (1997) Platelet Gel: An autologous alternative to fibrin glue with applications in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 55(11): 1294–1299
Landesberg R, Roy M, Glickman RS (2000) Quantification of growth factor levels using simplified method of platelet-rich plasma gel preparation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 58(3): 297–300
Juan Oj, Arabj-Dutan J, Chamberlain Tm, Croston A (2000) Platelet-rich plasma-a adjuvant to wound healing. Int J Perio Res Dent 20: 487–495
Kassolis JD, Rosen PS, Reynolds MA (2000) Alveolar ridge & sinus augmentation utilizing platelet-rich plasma in combination with freeze-dried bone allograft: case series. J Periodontol 71(10): 1654–1661
Simon D, Manuel S, Geetha V, Naik BR (2004) Potential for osseous regeneration of platelet-rich plasma −a comparative study in mandibular third molar sockets. Indian J Dent Res 15(4): 133–136
Munhoz EA, Ferreira Junior O, Yaedu Ry, Granjeiro JM (2006) Radiographic assessment of impacted mandibular third molar socket filled with composite xenogenic bone graft. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 35(5): 371–375
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vivek, G.K., Sripathi Rao, B.H. Potential for osseous regeneration of platelet rich plasma: a comparitive study in mandibular third molar sockets. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 8, 308–311 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-009-0075-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-009-0075-y