Abstract
Introduction
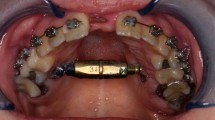
The diversity of the proposed techniques in the treatment of maxillary transverse deficiency in adults reflects the conflicting opinions about the primary area of resistance to maxillary expansion in the craniofacial skeleton. In order to evaluate the efficiency of the surgical expansion in which no osteotomies of the pterygomaxillary junction were made, we have carried out a retrospective study with 14 patients with maxillary transverse deficiency, who were treated from 2003 to 2006.
Material and methods
In the study, models were made prior to and after surgery, and the intercanine and intermolar distances and the improvement of the interocclusal relationships were analyzed. Breathing function and the complications that occurred during and after the surgeries were also analyzed.
Results
All expansions were carried out according to pre-surgical planning so that expansion completely corrected the crossbite, resulting in the desired final occlusion for all patients. Intraoperative complications were limited to one Hyrax appliance deformation. Two patients had minor postoperative complications that included wound dehiscence and pain. Improvements in nasal breathing were observed in all patients that complained of breathing problems prior to the surgery.
Conclusion
The satisfactory results obtained turns the surgical protocol described in this study recommended for the treatment of maxillary transverse deficiency in adults. Importantly, we found that pterygomaxillary osteotomy is not essential for maxillary expansion. The morbidity of the procedure was low with fairly minor complications, and surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion was shown to improve nasal breathing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berretin-Felix G, Yamashita RP, Filho HN, et al. (2006) Short- and long-term effect of surgically assisted maxillary expansion on nasal airway size. J Craniofac Surg 17(6): 1045–1049
Betts NJ, Vanarsdall RL, Barber HD et al. (1995) Diagnosis and treatment of transverse maxillary deficiency. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg 10(2): 75–96
Vandersea BA, Ruvo AT, Frost DE (2007) Maxillary transverse deficiency — surgical alternatives to management. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 19(3): 351–368
Kennedy JW 3rd, Bell WH, Kimbrough OL, James WB (1976) Osteotomy as an adjunct to rapid maxillary expansion. Am J Orthod 70(2): 123–137
Pinto PX, Mommaerts MY, Wreakes G, Jacobs WV (2001) Immediate postexpansion changes following the use of the transpalatal distractor. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 59(9): 994–1000
Bays RA, Greco JM (1992) Surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion: an outpatient technique with long-term stability. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 50(2): 110–113
Will LA (1995) Transverse maxillary deformities: diagnosis and treatment. Selected Readings in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 5: 1–28
Anttila A, Finne K, Nisula KK et al. (2004) Feasibility and long-term stability of surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion with lateral osteotomy. Eur J Orthod 26(4): 391–395
Goldenberg DC, Alonso N, Goldenberg FC et al. (2007) Using computed tomography to evaluate maxillary changes after surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion. J Craniofac Surg 18(2): 302–311
Ilizarov GA (1990) Clinical application of the tension-stress effect for limb lengthening. Clin Orthop Relat Res 250: 8–26
Handelman CS, Wang L, BeGole EA et al. (2000) Nonsurgical rapid maxillary expansion in adults: report on 47 cases using the Haas expander. Angle Orthod 70(2): 129–144
Glassman AS, Nahigian SJ, Medway JM et al. (1984) Conservative surgical orthodontic adult palatal expansion: sixteen cases. Am J Orthod 86(3): 207–213
Lehman JA Jr, Haas AJ, Haas DG (1984) Surgical orthodontic correction of transverse maxillary deficiency: a simplified approach. Plast Reconstr Surg 73(1): 62–68
Shetty V, Caridad JM, Caputo AA et al. (1994) Biomechanical rationale for surgical-orthodontic expansion of the adult maxilla. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 52(7): 742–749
Byloff FK, Mossaz CF (2004) Skeletal and dental changes following surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion. Eur J Orthod 26(4): 403–409
Marin C, Gil JN, Lima SM Jr (2009) Surgically assisted palatine expansion in adult patients: evaluation of a conservative technique. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67(6): 1274–1279
Han UA, Kim Y, Park JU (2009) Three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution and displacement of the maxilla following surgically assisted rapid maxillary expansion. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 37(3): 145–154
Wertz RA (1968) Changes in nasal airflow incident to rapid maxillary expansion. Angle Orthod 38(1): 1–11
Wriedt S, Kunkel M, Zentner A et al. (2001) Surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion: an acoustic rhinometric, morphometric and sonographic investigation. J Orofac Orthop 62(2): 107–115
Ramires T, Maia RA, Barone JR (2008) Nasal cavity changes and the respiratory standard after maxillary expansion. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 74(5): 763–769
Ribeiro Júnior PD, Gonçalves ES, Souza PCU, Nary Filho H, Luz JGC (2006) Clinical evaluation of surgically assisted maxillary expansion (SAME). Rev Dent Press Ortod Ortop Facial 11: 44–59
Mehra P, Cottrell DA, Caiazzo A, Lincoln R (1999) Life-threatening, delayed epistaxis after surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion: a case report. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 57(2): 201–204
Lanigan DT, Mintz SM (2002) Complications of surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion: review of the literature and report of a case. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60(1): 104–110
Chuah C, Mehra P (2005) Bilateral lingual anesthesia following surgically assisted rapid palatal expansion: report of a case. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63(3): 416–418
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Contar, C.M.M., Muller, P.R., Brunetto, A.R. et al. Surgical treatment of maxillary transverse deficiency: retrospective study of 14 patients. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 8, 249–253 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-009-0061-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-009-0061-4