Abstract
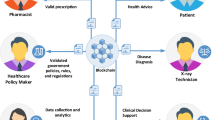
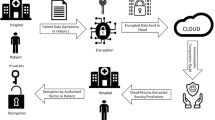
Currently, the move from traditional healthcare to smart healthcare systems is greatly aided by current technology. Healthcare proposes a new healthcare model that is patient-centered using advancements in wearable sensors, connectivity, and the Internet of Things (IoT). The administration of enormous amounts of data, including reports and pictures of every individual, increases human labour requirements and security hazards. This study shows how a blockchain-based Internet of Things might improve patient care while lowering costs by using medical resources more wisely. Initially, Resource Provider’s IoT data will be sensed and encrypts using Diffie Hellman Galois–Elliptic-curve cryptography (DHG-ECC). Next, from the extracted attributes, the optimal features will be selected by using Pearson Correlation Coefficient based Sand Cat Optimization Algorithm (PCC-SCOA). After that, the selected optimal features will be combined and converted into hashcode using the Digit Folding–Streebog Hashing algorithm. This hashcode will be constructed in the form of Smart Contract. Next, the Resource Requester (Doctor or Nurse) sends the Role Request with the Combined Linear Congruential Generator–Digital Signature Algorithm (CLCG-DSA). The next Resource Requester will be matching the hashed access policy with Blockchain. The proposed models are used to compare the performance of proposed design using feature selection time, Encryption time, Decryption time, security level, signature creation time and signature verification time. Our proposed method DHGECC approach achieves 96.123% higher security.















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The authors do not provide supplementary data and material
References
Aazam M, Zeadally S, Harras KA (2020) Health fog for smart healthcare. IEEE Consum Electron Maga 9(2):96–102
Akhter MH, Kazi T, Ixion C, Saadman S, Mohammad MK, Nawal A, Abdulmajeed A, Sami B (2022) Electronic health record monitoring system and data security using blockchain technology. Secur Commun Netw 2022:1–15
Ali F, El-Sappagh S, Islam SR, Kwak D, Ali A, Imran M, Kwak K-S (2020) A smart healthcare monitoring system for heart disease prediction based on ensemble deep learning and feature fusion. Inf Fusion 63:208–222
Ali F, El-Sappagh S, Islam SR, Ali A, Attique M, Imran M, Kwak KS (2021) An intelligent healthcare monitoring framework using wearable sensors and social networking data. Fut Gen Comput Syst 114:23–43
Awais M, Raza M, Ali K, Ali Z, Irfan M, Chughtai O, Khan I, Kim S, Ur Rehman M (2019) An internet of things based bedegress alerting paradigm using wearable sensors in elderly care environment. Sensors 19(11):2498
Chauhan N, Rajendra KD (2022) A secure design of the healthcare IoT system using blockchain technology. In: 2022 9th International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom), pp. 704–709. IEEE
Gholamhosseini L, Sadoughi F, Ahmadi H, Safaei A (2019) Health internet of things: strengths, weakness, opportunity, and threats. In: 2019 5th International Conference on Web Research (ICWR). 287–296
Griggs KN, Ossipova O, Kohlios CP et al (2018) Healthcare blockchain system using smart contracts for secure automated remote patient monitoring. J Med Syst 42(7):130
Haque AKMB, Bhushan B, Dhiman G (2022) Conceptualizing smart city applications: requirements, architecture, security issues, and emerging trends. Expert Syst 39(5):e12753
Hasnida A, Maarten OK, Elizabeth P (2021) Challenges in maintaining medicine quality while aiming for universal health coverage: a qualitative analysis from Indonesia. BMJ Global Health 6(Suppl 3):e003663
Honar Pajooh H, Rashid M, Alam F, Demidenko S (2021) Multi-layer blockchain-based security architecture for internet of things. Sensors. 21(3):772
Jaigirdar FT, Rudolph C, Bain C (2019) Can i trust the data i see? A physician’s concern on medical data in iot health architectures. In: Proceedings of the Australasian Computer Science Week Multiconference, pp 1–10
Jiang L, Chen L, Giannetsos T, Luo B, Liang K, Han J (2019) Toward practical privacy-preserving processing over encrypted data in iot: an assistive healthcare use case. IEEE Intern Things J 6(6):10177–10190
Kaur P, Kumar R, Kumar M (2019) A healthcare monitoring system using random forest and internet of things (IoT). Multimed Tools Applm 78(14):19905–19916
Khalaf OI, Muttashar Abdulsahib G (2021) Optimized dynamic storage of data (ODSD) in IoT based on blockchain for wireless sensor networks. Peer-to-Peer Netw Appl 14(5):2858–2873
Le NB, Lydia El, Elhoseny M, Pustokhina I, Pustokhin DA, Selim MM, Nguyen GN, Shankar K (2020) Privacy preserving blockchain technique to achieve secure and reliable sharing of IoT data. Comput Mater Contin 65(1):87–107
Leng J, Yan D, Liu Q, Xu K, Zhao JL, Shi R et al (2019) ManuChain: combining permissioned blockchain with a holistic optimization model as bi-level intelligence for smart manufacturing. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 50(1):182–192
Mahajan HB, Ameer SR, Aparna A, Nilesh U, Sarita DD, Pravin RF, Ahmed A, Bilal A (2023) Integration of Healthcare 40 and blockchain into secure cloud-based electronic health records systems. Appl Nanosci 13(3):2329–2342
Mohana M, Deotare VV, Ninu Preetha NS, Brammya G (2023) An adaptive elliptical curve cryptography-Rivest–Shamir–Adleman-based encryption for IoT healthcare security model with blockchain technology. J Mech Med Biol. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219519423500689
Nguyen DC, Pathirana PN, Ding M, Seneviratne A (2021) Secure computation offloading in blockchain-based IoT networks with deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans Netw Sci Eng 8(4):3192–3208
Ray PP, Dash D, Salah K, Kumar N (2020) Blockchain for IoT-based healthcare: background, consensus, platforms, and use cases. IEEE Syst J 15(1):85–94
Sadiku MNO, Eze KG, Musa SM (2018) Block chain technology in healthcare. Int J Adv Sci Res Eng 4(5):154–159
Saxena S, Bhushan B, Ahad MA (2021) Blockchain based solutions to secure IoT: background, integration trends and a way forward. J Netw Comput Appl 181:103050
Shynu PG, Menon VG, Kumar RL, Kadry S, Nam Y (2021) Blockchain-based secure healthcare application for diabetic-cardio disease prediction in fog computing. IEEE Access 9:45706–45720
Sicari S, Rizzardi A, Coen-Porisini A (2020) 5G in the internet of things era: an overview on security and privacy challenges. Comput Netw 179:107345
Tao H, Bhuiyan MZA, Abdalla AN et al (2018) Secured data collection with hardware-based ciphers for Iot-based healthcare. IEEE Intern Things J 6(1):410–420
Yaqoob I, Salah K, Jayaraman R, Al-Hammadi Y (2022) Blockchain for healthcare data management: opportunities, challenges, and future recommendations. Neural Comput Appl 34(14):11475–11490
Yun J, Goh Y, Chung JM (2020) DQN-based optimization framework for secure sharded blockchain systems. IEEE Internet Things J 8(2):708–722
Zhu H, Wu CK, Koo CH, Tsang YT, Liu Y, Chi HR, Tsang K-F (2019) Smart healthcare in the era of internet-of-things. IEEE Consum Electron Maga 8(5):26–30
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflict of interest.
Statement of Animal and Human Rights
All applicable institutional and/or national guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed Consent
For this type of analysis formal consent is not needed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rastogi, P., Singh, D. & Bedi, S.S. An improved blockchain framework for ORAP verification and data security in healthcare. J Ambient Intell Human Comput (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-024-04780-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-024-04780-4