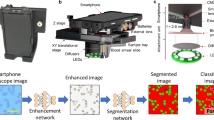
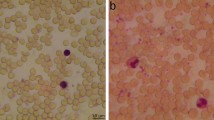
Abstract
Sickle cell diseases are marked by the occurrence of hemoglobin S, which results in the distortion of Red Blood Cells into crescent or sickle-shaped shapes. Thus the detection of sickle cells forms a crucial part in the prognosis or diagnosis of such diseases. The state-of-the-art approaches for mass detection of Sickle cells use deep learning-based methodologies. But these are often computationally expensive and also accompanied by a costly imaging setup. The existing image processing techniques fail to achieve considerable accuracy to be used for detection. The cheaper image processing-based methods do not show competitive reliability as compared to the existing deep learning counterparts. In this paper we propose mSickle, a novel image processing-based approach that can be easily incorporated into a smartphone along with a low-cost imaging device. The geometric properties of the sickle shape have been leveraged to identify the distortion caused by hemoglobin. The performance has been measured with the images in the erythrocyteIDB database and achieved an accuracy of 92.6% across all images. The setup is robust and has been tested across various devices. The presence of sickle-shaped cells acts as a strong indicator of diseases and can be sent for further medical inspection. Therefore, the high accuracy achieved makes it is an image processing alternative to the existing automated deep learning methods for mass detection of sickle cells.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data
The work uses referenced public datasets.
Code
github.com/ShaurjyaContributes/mSickle.
References
Adenmosun OO, Asghar W, Diaka JK (2017) Sickle cell sperm selection with hb-s mab: a future application for intracytoplasmic genotypically selected sperm injection (igsi). Arch Clin Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.4172/1989-8436.100064
Adeyemo T, Ojewunmi O, Oyetunji A (2014) Evaluation of high performance liquid chromatography (hplc) pattern and prevalence of beta-thalassaemia trait among sickle cell disease patients in Lagos, Nigeria. Pan Afric Med J. https://doi.org/10.11604/pamj.2014.18.71.4239
Alapan Y, Fraiwan A, Kucukal E, Hasan MN, Ung R, Kim M, Odame I, Little JA, Gurkan UA (2016) Emerging point-of-care technologies for sickle cell disease screening and monitoring. Expert Rev Med Dev 13(12):1073–1093. https://doi.org/10.1080/17434440.2016.1254038
Aliyu HA, Razak MAA, Sudirman R (2019) Segmentation and detection of sickle cell red blood image. AIP Conf Proc 2173(1):020004
Al-Khabori M, Al-Huneini M (2017) Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the sultanate of oman. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther 10(4):305–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hemonc.2017.05.024
Alzubaidi L, Fadhel MA, Al-Shamma O, Zhang J (2020) Robust and efficient approach to diagnose sickle cell anemia in blood. In: Ajith A, Aswani KC, Patricia M, Niketa G (eds) Intelligent systems design and applications. Springer, Cham, pp 560–570
Alzubaidi L, Fadhel MA, Al-Shamma O, Zhang J, Duan Y (2020) Deep learning models for classification of red blood cells in microscopy images to aid in sickle cell anemia diagnosis. Electronics 9(3):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9030427
de Martino CC, Alencar CS, Loureiro P, de Freitas CPAB, de Alvarenga MC, Afonso MR, Werneck RDO, Gaburo JN, Shannon K, Cerdeira SE (2019) Use of an automated pyrosequencing technique for confirmation of sickle cell disease. PLOS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0216020
Fadhel MA, Humaidi AJ, Oleiwi SR (2017) Image processing-based diagnosis of sickle cell anemia in erythrocytes. In: 2017 Annual conference on new trends in information & communications technology applications (NTICT). IEEE, pp 203–207
Fleming JK (2007) Evaluation of hba1c on the roche cobas integra 800 closed tube system. Clin Biochem 40(11):822–827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2007.03.017
Gardner RV (2018) Sickle cell disease: advances in treatment. Ochsner J 18(4):377–389. https://doi.org/10.31486/toj.18.0076
Ghosal S, Das D, Udutalapally V, Talukder AK, Misra S (2021) shemo: smartphone spectroscopy for blood hemoglobin level monitoring in smart anemia-care. IEEE Sens J 21(6):8520–8529. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2020.3044386
Gonzalez-Hidalgo M, Guerrero-Pena FA, Herold-García S, Jaume-i Capó A, Marrero-Fernández PD (2014) Red blood cell cluster separation from digital images for use in sickle cell disease. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 19(4):1514–1525
Haan KD, Koydemir HC, Rivenson Y, Tseng D, Elizabeth VD, Bakic L, Karinca D, Liang K, Ilango M, Esin G et al (2020) Automated screening of sickle cells using a smartphone-based microscope and deep learning. npj Digit Med. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-020-0282-y
Hahn E (1927) Sickle cell anemia. Arch Intern Med 39(2):233. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.1927.00130020072006
Herrick JB (2014) Peculiar elongated and sickle-shaped red blood corpuscles in a case of severe anemia. JAMA 312(10):1063. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.11011
Hu L, Pan X, Tan Z, Luo X (2021) A fast fuzzy clustering algorithm for complex networks via a generalized momentum method. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2021.3117442
Ilyas S, Sher M, Du E, Asghar W (2020) Smartphone-based sickle cell disease detection and monitoring for point-of-care settings. Biosens Bioelectron 165:112417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112417
Ingram MV (1989) A case of sickle-cell anaemia: a commentaryon abnormal human haeoglobins. i. the comparison of normal human and sickle-cell haemoglobins by fingerprinting by v.m. ingram biochim. biophys acta 28 (1958) 539545 with ii. the chymotryptic digestion of the trypsin-resistant core of haemoglobins a and s by j.a. hunt and v.m. ingram biochim. biophys. acta 28 (1958) 546549 (summary) and iii. the chemical difference between normal and sickle cell haemoglobins by v.m. ingram biochim. biophys acta 36 (1959) 402411 (summary). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Gen Subj 1000:147–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-3002(89)80014-9
Knowlton SM, Sencan I, Aytar Y, Khoory J, Heeney MM, Ghiran IC, Tasoglu S (2015) Sickle cell detection using a smartphone. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep15022
Liu W, Wang Z, Liu X, Zeng N, Liu Y, Alsaadi FE (2017) A survey of deep neural network architectures and their applications. Neurocomputing 234:11–26
Luo X, Liu Z, Jin L, Zhou Y, Zhou MC (2021) Symmetric nonnegative matrix factorization-based community detection models and their convergence analysis. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3041360
Makani J, Cox SE, Soka D, Komba AN, Oruo J, Mwamtemi H, Magesa P, Rwezaula S, Meda E, Mgaya J et al (2011) Mortality in sickle cell anemia in Africa: a prospective cohort study in Tanzania. PLoS One 6(2):e14699. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0014699
Mason VR (1985) Sickle cell anemia. JAMA J Am Med Assoc 254(14):1955. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1985.03360140113037
McDade WA, Carragher B, Miller CA, Josephs R (1989) On the assembly of sickle hemoglobin fascicles. J Mol Biol 206(4):637–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(89)90572-x
Singh PJ, Shrivastava AC, Shrikhande AV (2014) Prenatal diagnosis of sickle cell disease by the technique of pcr. Indian J Hematol Blood Transf 31(2):233–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-014-0427-8
Skandarajah A, Reber CD, Switz NA, Fletcher DA (2014) Quantitative imaging with a mobile phone microscope. PLoS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0096906
Wajcman H, Moradkhani K (2011) Abnormal haemoglobins: detection and characterization. Indian J Med Res 134(4):538–546
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2004) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(4):600–612. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2003.819861
Wu D, He Y, Luo X, Zhou MC (2021) A latent factor analysis-based approach to online sparse streaming feature selection. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2021.3096065
Wu D, Shang M, Luo X, Wang Z (2021) An l-and-l-norm-oriented latent factor model for recommender systems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3071392
Zakharov AV, Kol’tsov PP, Kotovich NV, Kravchenko AA, Kutsaev AS, Osipov AS (2013) A method for calculating the tangent on the basis of the hough transform. Pattern Recognit Image Anal 23(2):258–268. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1054661813020181
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandal, S., Das, D. & Udutalapally, V. mSickle: sickle cell identification through gradient evaluation and smartphone microscopy. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 14, 13319–13331 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-022-03786-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-022-03786-0